Amines are considered one of the most important compounds in organic chemistry. These nitrogen-containing molecules are like the building blocks of life itself, as they form the amino acids, proteins, and hormones, and are responsible for many biological processes. From the caffeine in your morning coffee to the DNA in your cells, amines are everywhere around us.
In Chemistry, the Amines class 12th, you learn various topics around amine, such as the structure of amines, their classifications, preparation, physical properties, chemical properties, and many more. But you may agree that Amines NCERT content is provided in a more complex manner, which is difficult to understand and more time-consuming.So, we at Shiksha created Amines Class 12 notes for the students going to appear in the CBSE board exam and preparing for the NEET and JEE exams. The notes below cover all the topics in the chapter in depth, but in a simpler manner with easy explanations and examples.
- What are Amines?
- Structure of Amines
- Classification of Amines
- Nomenclature of Amines
- Preparation of Amines
- Physical Properties of Amines
- Chemical Reactions of Amines
- What are Diazonium Salts?
- Method of Preparation of Diazonium Salts
- Physical Properties of Diazonium Salts
- Chemical Reactions of Diazonium Salts
- Importance of Diazonium Salts
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- About the Content Reviewer
- Amines FAQs
What are Amines?
According to the NCERT textbook, “Amines can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, obtained by replacement of one, two, or all three hydrogen atoms by alkyl and/or aryl groups.”
Simply, it can be explained as:
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH₃) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups.
They keep the basic nitrogen personality but gain new characteristics from their organic attachments. From the proteins in your muscles to the neurotransmitters in your brain, amines play crucial roles in most biological processes.
Amines have a unique combination of properties. The nitrogen atom carries a lone pair of electrons, which gives amines their basic nature of attracting to protons and electron-deficient species, which explains why amines are so reactive and versatile. The general formula of Amines is- R₃N, where R can be hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl groups.
Structure of Amines
Amines are originally ammonia (NH₃) molecules where one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by organic groups.
The nitrogen atom in amines is at the center with its lone pair of electrons. This lone pair is what gives amines their basic nature, that is, to attract electrons-deficient molecules.
The nitrogen atom in amines is sp³ hybridized, creating a pyramidal shape. This is a three-dimensional shape.
Basic Structure of Amines
The structure of an amine can be written as:
- Primary amine: R-NH₂
- Secondary amine: R-NH-R’
- Tertiary amine: R-N(R’)-R’’
Where R, R’, and R’’ represent alkyl or aryl groups.
Classification of Amines
Classification of amines depends on how many organic groups are attached to the nitrogen atom. This classification directly affects their properties and reactivity.
Based on the Number of Alkyl/Aryl Groups, Amines are classified as Primary Amines, Secondary Amines, and Tertiary Amines.
Primary Amines (1°)
The structure of primary amines is R-NH₂, with examples such as Methylamine (CH₃NH₂) and ethylamine (C₂H₅NH₂). In a primary amine, two hydrogen atoms are still attached to nitrogen.
Secondary Amines (2°)
The structure is R-NH-R’ or R₂NH, examples such as Dimethylamine ((CH₃)₂NH), Diethylamine ((C₂H₅)₂NH). In a secondary amine, a hydrogen atom is still attached to nitrogen
Tertiary Amines (3°)
The structure is R-N-R’-R’’ or R₃N. For example-Trimethylamine ((CH₃)₃N), Triethylamine ((C₂H₅)₃N). No hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen
Based on the Type of Carbon Attachment:
Aliphatic Amines are organic compounds in which a hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl groups and attached to nitrogen
Examples: Methylamine, Ethylamine, Propylamine
Aromatic Amines are organic compounds in which NH₂ is attached directly to an aromatic ring.
Examples: Aniline (C₆H₅NH₂), N-methylaniline
Nomenclature of Amines
Naming amines is like learning a new language; once you understand the patterns, naming becomes much more straightforward and follows specific rules that help communicate clearly about these compounds..
IUPAC Nomenclature
For Primary Amines
Replace the ‘e’ in the alkane name with ‘amine’
-Examples:
- CH₃NH₂ → Methanamine
- C₂H₅NH₂ → Ethanamine
- C₃H₇NH₂ → Propanamine
For Secondary and Tertiary Amines
The largest alkyl group is considered the parent chain, and other groups are treated as N-substituents
Examples:
- (CH₃)₂NH → N-methylmethanamine
- (C₂H₅)₂NH → N-ethylethanamine
- (CH₃)₃N → N, N-dimethylmethanamine
Common Names
Many amines have traditional names that are still used in practice. These names often reflect the compound’s origin or properties:
- Aniline: C₆H₅NH₂ (from indigo plant)
- Toluidine: CH₃C₆H₄NH₂ (methylaniline)
- Benzylamine: C₆H₅CH₂NH₂
- Putrescine: H₂N(CH₂)₄NH₂ (found in decaying matter)
Preparation of Amines
In the process of preparing amines, many compounds are used as intermediates in the making of many other important molecules. We can prepare amines through the following methods.
Reduction of Nitriles
This method involves reducing nitriles, which are compounds with the -CN group, to primary amines.
R-CN + 4[H] → R-CH₂-NH₂
Reducing agents used are lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH₄), hydrogen with nickel catalyst (H₂/Ni), Sodium in ethanol (Na/C₂H₅OH).
Example: CH₃CN + 4[H] → CH₃CH₂NH₂ (ethylamine from acetonitrile)
Reduction of Nitro Compounds
Nitro compounds can be reduced to give primary amines, useful for aromatic amines.
R-NO₂ + 6[H] → R-NH₂ + 2H₂O
Example: C₆H₅NO₂ + 6[H] → C₆H₅NH₂ + 2H₂O (nitrobenzene to aniline)
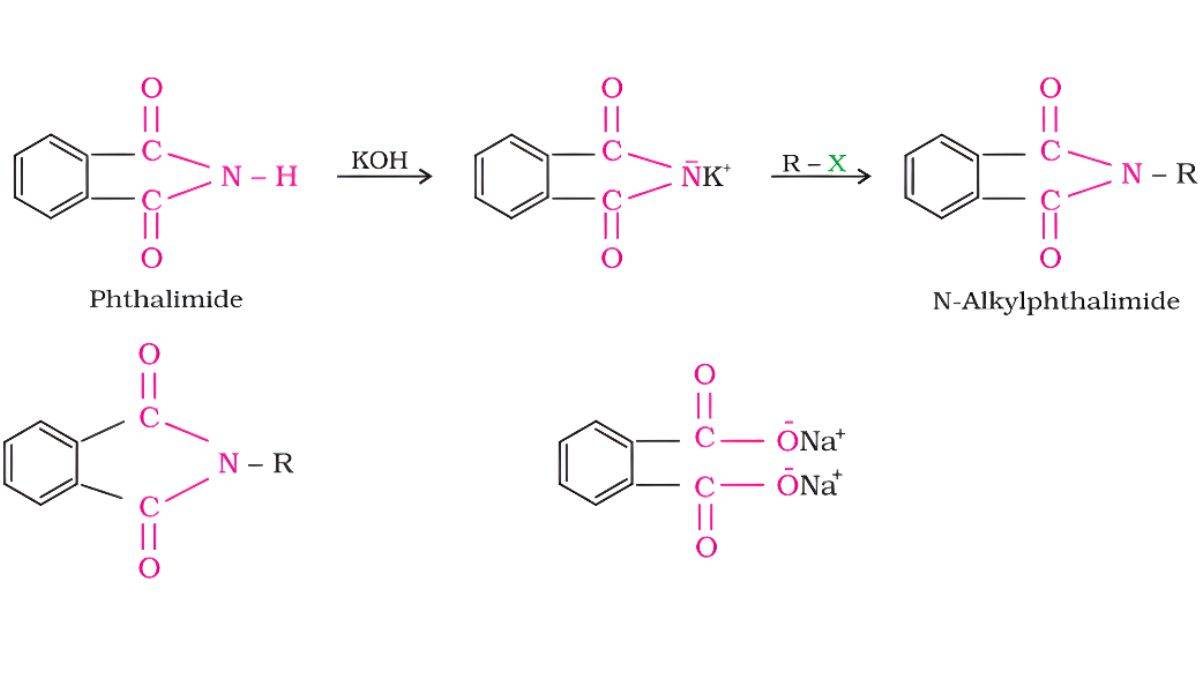
Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis
This method is used specifically for producing primary amines without any secondary or tertiary amine contamination.
Phthalimide reacts with KOH to form potassium phthalimide. Alkyl halide displaces potassium to form N-alkylphthalimide. Hydrolysis releases the primary amine.
Phthalimide + KOH → K⁺ phthalimide⁻
K⁺ phthalimide⁻ + R-X → N-alkylphthalimide + KX
N-alkylphthalimide + H₂O/H⁺ → R-NH₂ + phthalic acid
Hofmann Bromamide Degradation
This reaction converts amides to primary amines with one less carbon atom.
R-CONH₂ + Br₂ + 4NaOH → R-NH₂ + Na₂CO₃ + 2NaBr + 2H₂O
Mechanism:
- An amide reacts with bromine in an alkaline medium, forming N-bromoamide intermediate
- Rearrangement occurs to give isocyanate
- Hydrolysis produces an amine
Example: CH₃CONH₂ + Br₂ + 4NaOH → CH₃NH₂ + Na₂CO₃ + 2NaBr + 2H₂O
Physical Properties of Amines
The physical properties of amines are determined by their ability to form hydrogen bonds and by their molecular structure. Physical properties make amines unique among organic compounds and are used to explain their practical applications.
-
State and Odor
Lower amines (C₁-C₄):
Gaseous at room temperature, smells strongly fishy- ammonia-like odor. Highly soluble in water.
Medium amines (C₅-C₁₂):
Liquids at room temperature have less intense odor. Moderate water solubility.
Higher amines (>C₁₂):
Solids at room temperature with little to no odor are Insoluble in water.
-
Boiling Points
Amines generally have higher boiling points than corresponding hydrocarbons but lower than alcohols with similar molecular weight.
Order of boiling points:
Primary > Secondary > Tertiary amines
Primary amines can form more hydrogen bonds than secondary, and secondary more than tertiary.
Examples:
- Methylamine (CH₃NH₂): -6°C
- Dimethylamine ((CH₃)₂NH): 7°C
- Trimethylamine ((CH₃)₃N): 3°C
-
Solubility
Considering water solubility, lower aliphatic amines are highly soluble due to hydrogen bonding.
- Solubility decreases as carbon chain length increases
- Aromatic amines are less soluble due to the hydrophobic benzene ring
Solubility in organic solvents:
All amines are soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and ether. Organic solvents are useful for extraction and purification.
Hydrogen Bonding
Amines can act as both hydrogen bond donors (through N-H bonds) and acceptors (through lone pair on nitrogen).
Hydrogen bonding effects result in an increase in boiling point, an increase in water solubility, and affect density and viscosity.
Chemical Reactions of Amines
Amines participate in many chemical reactions due to their basic nature and the presence of lone pair electrons on nitrogen.
The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen makes amines nucleophilic (they’re attracted to electron-deficient centers). This nature drives most of the chemical reactions of amines you read below:
Basic Nature of Amines
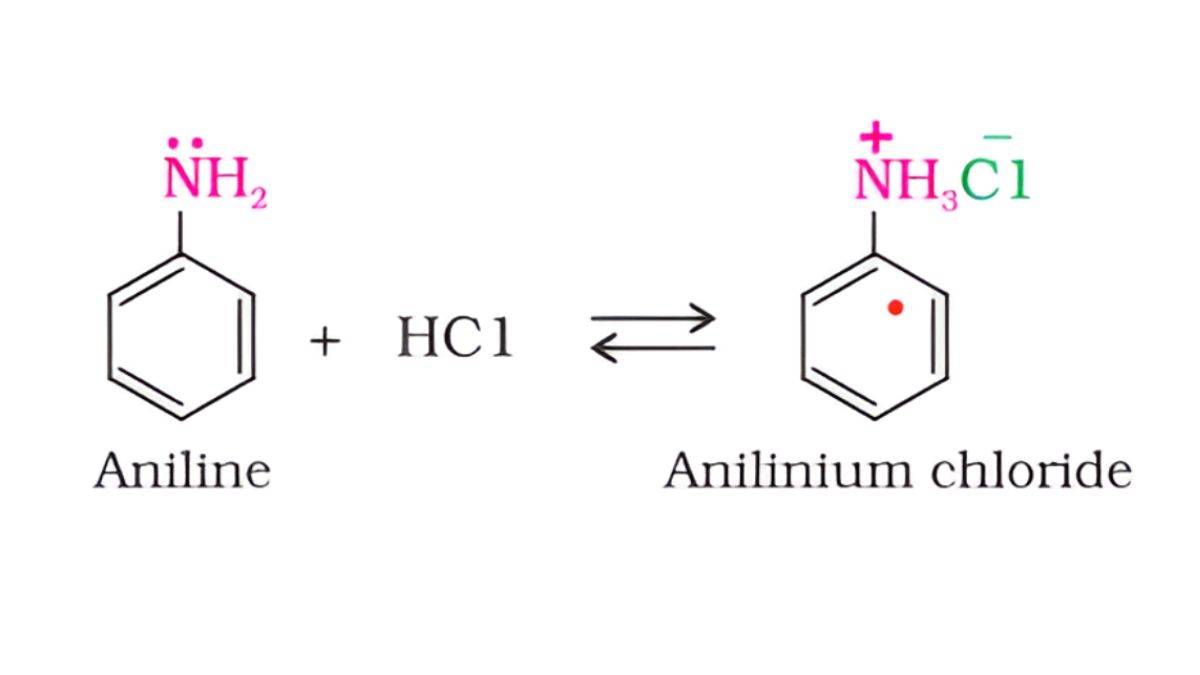
Amines are bases because they can accept protons (H⁺) from acids, forming salts.
R₃N + HCl → R₃NH⁺Cl⁻
- Basicity order in gas phase: Tertiary > Secondary > Primary > NH₃
- Basicity order in aqueous solution: Secondary > Primary > Tertiary > NH₃
Electron-releasing groups (alkyl groups) will increase the basicity, and Electron-withdrawing groups (aryl groups) will decrease the basicity.
Alkylation Reactions
Amines can react with alkyl halides to form higher amines through nucleophilic substitution.
Primary amine reaction: R-NH₂ + R’-X → R-NH-R’ + HX
Problem with alkylation: Over-alkylation occurs, producing mixtures of products:
R-NH₂ + R’-X → R-NH-R’ (secondary amine)
R-NH-R’ + R’-X → R-N(R’)₂ (tertiary amine)
R-N(R’)₂ + R’-X → R-N⁺(R’)₃X⁻ (quaternary ammonium salt)
Acylation Reactions
Amines react with acid chlorides or anhydrides to form amides.
With acid chlorides: R-NH₂ + R’-COCl → R-NH-CO-R’ + HCl
With acid anhydrides: R-NH₂ + (R’-CO)₂O → R-NH-CO-R’ + R’-COOH
Advantages of acylation are- no over-acylation occurs, clean reaction with a single product, and is used to protect amino groups during synthesis.
Carbylamine Reaction
This is a specific test for primary amines using chloroform and alcoholic KOH.
R-NH₂ + CHCl₃ + 3KOH → R-NC + 3KCl + 3H₂O
Carbylamine formed: R-NC
It has a foul odor as one of its characteristics.
Only primary amines give a positive carbylamine test
Reaction with Nitrous Acid
Different amines react differently with nitrous acid (HNO₂), So, this test is useful to distinguish between them.
- Primary aliphatic amines:
R-NH₂ + HNO₂ → R-OH + N₂ + H₂O (nitrogen gas evolved)
- Primary aromatic amines:
Ar-NH₂ + HNO₂ + HCl → Ar-N₂⁺Cl⁻ + 2H₂O (diazonium salt formation)
- Secondary amines:
R₂NH + HNO₂ → R₂N-NO + H₂O (N-nitrosoamine formation, yellow oil)
- Tertiary amines:
R₃N + HNO₂ → R₃NH⁺NO₂⁻ (salt formation, no other reaction)
Hofmann Elimination
Quaternary ammonium hydroxides undergo elimination when heated to form alkenes.
R-CH₂-CH₂-N⁺(CH₃)₃OH⁻ → R-CH=CH₂ + (CH₃)₃N + H₂O
Hofmann’s rule: The least substituted alkene is the major product.
What are Diazonium Salts?
Method of Preparation of Diazonium Salts
Physical Properties of Diazonium Salts
Chemical Reactions of Diazonium Salts
Importance of Diazonium Salts
Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
About the Content Reviewer
Amines FAQs
Commonly asked questions
What is the difference between Amines and Amides?
In Amines, the nitrogen atom bonds with alkyl or aryl groups replacing hydrogen, whereas in amides, the nitrogen atom bonds directly with the carbonyl group (-CO-).
Why are Amines called bases?
Amines are bases because they have a lone pair of electrons on nitrogen and their nucleophilic nature (they are electron-rich, so they are attracted to electron-deficient species to donate electrons and accept protons.
Is NH? can be called Amine?
Yes, NH? is a primary amine; it is also known as the amino group. Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups.
Chemistry Amines Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test