Diazonium salts, also known as Diazonium compounds, are organic compounds with a general formula R−N2+X−. Here, X is an organic or inorganic anion, and R is an alkyl or aryl group. Diazonium salts are often used in the preparation of aromatic compounds such as dyes.
Preparation method of diazonium salts
Diazonium salts are prepared by the diazotization process. It is the process of converting an organic compound into diazonium salts. The process generally uses aromatic compounds for the conversion. Sodium nitrite is added to the primary amines (aryl or alkyl) in the presence of hydrochloric acid.
One of the most common methods is the reaction of aromatic amines with nitrous acid. Since the diazonium group is highly unstable at room temperature, diazonium salts are used immediately after preparation as they cannot be stored. Another factor that needs attention is the temperature while preparing diazonium salts. It is crucial to keep the temperature at five degree Celsius.
Properties of diazonium salts
- These are colourless crystalline solids but change colour when exposed to air
- They are ionic in nature and thus soluble in water and react with warm water. However, Benzene diazonium fluoride is insoluble in water.
- Diazonium salts are explosive whenever dried up. Therefore, they are used in the hydrated form
- These are good conductors of electricity
- Aromatic diazonium salts are more stable than aliphatic diazonium salts
Importance of diazonium salts
Despite being unstable at normal conditions, diazonium salts have importance as follows:
- Diazonium salts are extensively used in pigment industries in the production of fabric dye
- These are used for cyanobenzene production because direct halogenations is not possible while preparing aryl iodides and fluorides
- Diazonium salts are used in document reproduction as they can break down near ultraviolet light
- Synthesis of organic compounds such as aryl derivative often uses diazonium salts
- These salts are also used as the intermediates for introducing –F, –Br, –Cl, –I, –NO2, –OH, and –CN in the aromatic rings
The topic of diazonium salts is covered in the chapter ‘Amines’ of class 12 CBSE curriculum. It is a part of the third unit of the curriculum. The unit holds a value of 28 marks in the examination. The chapter is, therefore, important for both practical and theoretical questions. If you are preparing for the class 12 CBSE examination, understanding the concepts of amines and diazonium salts are essential.
Illustrated Examples
Example 1. Explain why diazonium salts of aromatic amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines.
Solution. Resonance is the delocalization of electrons and polyatomic ions in certain molecules. The resonance in diazonium salts of aromatic amines causes the dispersal of positive charge on the benzene ring. Whereas there is no resonance happen in aliphatic amines making them less stable than diazonium salts of aromatic amines.
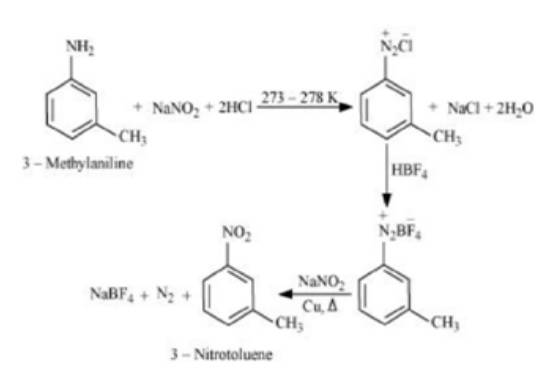
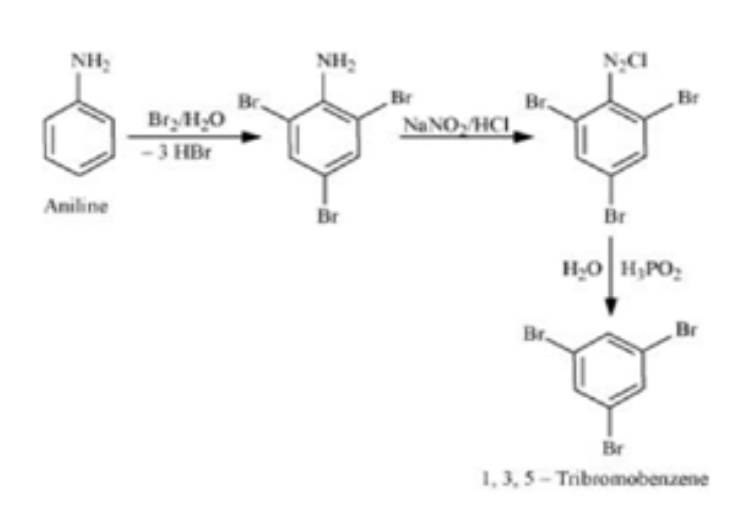
Example 2. Convert 3-Methylaniline into 3-nitrotoluence, and Aniline into 1,3,5-tribromobenzene
Solution. 3-Methylaniline to 3-nitrotoluence
Aniline to 1,3,5-tribromobenzene
FAQs on Diazonium Salts
Q. What are organic compounds?
Q. What are inorganic compounds?
Q. What is an Azo dye?
Q. What is nitrous acid?
Q. What are Amines?
News & Updates
Chemistry Amines Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test