
Saumya JainAssistant Manager- Content
CFA syllabus consists of the concepts of the academic disciplines of Finance and Investment. The CFA syllabus for all three levels, i.e. Level I, II and III is the same (more or less), however, the weightage of the questions differs at each level. It assesses the candidates on a varied range of concepts, such as Financial, Accounting-related or Mathematical. Shiksha brings you a is a comprehensive blog that details the CFA syllabus and weightage of the questions, important topics and subtopics, etc. Read below to know the detailed CFA syllabus 2025.
Also Read: When is the CFA exam?
Q: How tough is the CFA exam? What are important preparation tips for the CFA exam?
Q: How will I get the study material for CFA course?
To obtain the study material for the CFA course, there are the following options:
- The CFA institute proivdes an official curriculum for each exam level. This curriculum covers all the required topics and is considered the rimary source of the study material for the CFA exam. Students are given the option to purchase the curriculum directly from the institute's website.
- Many third-party vendors also offer study materials for the CFA exam which is specifically designed to help the aspirants prepare for the exam. These materials often include study guides, practice questions, mock tests, online course and/or video lectures.
- There are various online sources available for obtaining the CFA study material. Websites, forums and online communities dedicated to CFA exam preparation provide free or low-cost study materials, practice papers, and other helpful preparation tips.
- Joining or forming a study group can be beneficial for sharing study materials and insights with fellow aspirants. It will help you discuss challenging topics, solve practice questions, and gain different prespectives on the exam content.
It is important to find authentic study material which aligns with our learning style and preferences. Consider your buget, time constraints, and the level of support and guidance you need to prepare for the CFA exam. Additionally, always refer to the CFA curriculum provided by the CFA institute for accurate and up to date information.
Q: What is the mode of CFA exam?
The CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) exams are conducted in a computer-based testing (CBT) format. The transition from paper-based exams to computer-based exams was implemented by CFA Institute to provide a more efficient and secure testing experience for candidates.
Under the CBT format, candidates take the exams on a computer at designated testing centers. The exams are administered over multiple sessions, with each session focusing on specific topics. The CFA Level I exam consists of multiple-choice questions, while the Level II and Level III exams include item-set questions (also known as vignettes) and constructed response (essay) questions.
The CBT format offers several advantages, such as immediate exam results, standardized navigation tools, the ability to mark and review questions, and an enhanced exam security system. Additionally, candidates have the flexibility to choose their preferred exam date within the available testing window.
It's important to note that while the CFA exams are computer-based, they still maintain the same level of rigor and depth in assessing candidates' knowledge and skills in finance and investment management.
CFA Syllabus 2025: Level I
Refer to the table below to know the CFA syllabus for the Level I exam:
| Topic | Weightage (in Percentage) | Sub-Topics |
|---|---|---|
| Ethical and Professional Standards |
15-20 | Global investment performance standards, Standard of Professional Conduct |
| Quantitative Methods |
6-9 | Discounted Cash Flow Applications, Time, Value and Money, Statistical Concepts and Market Returns |
| Economics |
6-9 | Firm and Market Scheme, Demand and Supply Analysis, Aggregate Output, Prices, Economic Growth |
| Financial Reporting and Analysis |
11-14 | Income statement, Drafting Balance Sheet, Financial Reporting Mechanics and Standards |
| Corporate Issuers |
6-9 | Cost of Capital, Capital Budgeting, Corporate Ownership Structures, Business Models |
| Portfolio Management |
8-12 | Basics of Portfolio Planning and Construction |
| Equity Investments |
11-14 | Market Efficiency, Security Market Indices, Market Organization and Structure |
| Fixed Income |
11-14 | Fixed Income Markets, Fixed Income Securities, Introduction to Fixed Income Valuation |
| Derivatives |
5-8 | Derivative Markets and Instruments |
| Alternative Investments |
7-10 | Mutual Funds and Real Estate |
Changes in Level I Syllabus
- According to the research, many Level I candidates have mastered various introductory financial concepts during their graduation or early career roles. Hence, to avoid duplication and streamline the Level I CFA curriculum, exam conducting authorities have moved some of the content and are now providing it separately as reference material for registered candidates.
- The content has been moved to pre-read topics such as time and value of money, basic statistics, microeconomics, and introduction to company accounts, etc. which are building blocks for later learning. By not directly assessing these topic areas, there is more room for advanced practice concepts and more time for the new practical skills modules.
- Students who do not have exposure to such concepts, or who simply wish to review materials during their preparation for the Level I CFA exam, can access the content as pre-read materials at no additional charges. Registered candidates can also use these materials to get a sense of gaps in their knowledge and assess their readiness for the exam.
Also Read: What to Expect of CFA Level 1 Exam
Q: What changes have been made to the Level I CFA syllabus?
The following changes have been made to the Level I CFA curriculum:
- A new chapter titled – “Introduction to Geopolitics” has been introduced under the Economics section
- Corporate Ownership and Structures and Business Models are the two new readings that have been added under Corporate Issuers section.
- Majour changes to the Capital Structure readings have been made.
- Minor changes to the Introduction to Corporate Governance & Other ESG Considerations reading has also been made.
Q: What subjects are there in CFA Level 1?
The CFA Level I exam covers a broad range of topics. Here are the major subject areas included in the Level I syllabus:
Ethical and Professional Standards: This section emphasizes the ethical and professional responsibilities of investment professionals, including the CFA Institute's Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.
Quantitative Methods: This area focuses on quantitative techniques and methods used in investment analysis, including statistical concepts, probability theory, time value of money, and basic regression analysis.
Economics: The economics section covers microeconomics and macroeconomics, including supply and demand analysis, market structures, monetary and fiscal policy, and international trade.
Financial Reporting and Analysis: This section explores the principles and analysis of financial reporting, including the interpretation of financial statements, financial ratio analysis, and understanding key accounting concepts.
Corporate Finance: This area covers topics related to corporate finance, including capital budgeting, cost of capital, capital structure, dividend policy, and corporate governance.
Equity Investments: The equity investments section focuses on equity markets, equity valuation models, industry and company analysis, and equity portfolio management.
Fixed Income: This section delves into fixed income securities, bond valuation, yield measures, fixed income markets, and fixed income portfolio management.
Derivatives: This area covers derivatives instruments, including options, futures, forwards, and swaps, along with their valuation and strategies for their use.
Alternative Investments: This section introduces alternative investment types, such as real estate, private equity, hedge funds, and commodities, along with their characteristics and valuation.
Portfolio Management and Wealth Planning: This final section addresses portfolio management concepts, including portfolio theory, risk management, performance evaluation, and wealth planning strategies.
These topics provide a general overview of the major subject areas covered in the CFA Level I syllabus. Each subject area encompasses various subtopics, and the CFA Institute provides a detailed curriculum that outlines the specific learning outcomes for each level. It's essential to refer to the official CFA Institute curriculum and study materials for a comprehensive understanding of the exam content.
Q: What is the exam structure of CFA exam Level I?
The CFA Level I exam comprises a total of 180 multiple-choice questions to be answered in two sessions of 135 minutes each. There are 90 MCQ questions for each session. The first session includes topics such as professional standards, financial reporting, and quantitative methods, while the second session includes questions about corporate finance, fixed income, derivatives, alternative investments, and portfolio management. This exam is given twice a year, once in June and once in December.
CFA Syllabus 2025: Level II
Refer to the table below to know the CFA syllabus for the Level II exam:
| Topic | Weightage |
|---|---|
| Ethical and Professional Standards |
15 |
| Quantitative Methods |
15 |
| Economics |
10 |
| Financial Reporting and Analysis |
15 |
| Corporate Finance |
10 |
| Portfolio Management |
10 |
| Equity Investments |
15 |
| Fixed Income |
15 |
| Derivatives |
5 |
| Alternative Investments |
5 |
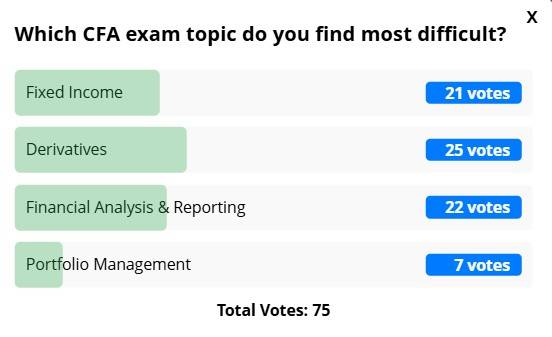
Shiksha conducted a poll on which CFA topic students find the most difficult. Here are the poll results:
Q: How much time should I devote to complete Level II CFA syllabus?
The amount of time needed to complete the Level II CFA syllabus can vary depending on factors such as your prior knowledge, study efficiency, and personal commitments. However, it is generally recommended to allocate a significant amount of time for Level II preparation due to the complexity of the material. Here are some considerations:
The CFA Institute suggests that candidates should aim to spend approximately 300 hours preparing for each level of the exam. This is a rough guideline, and some candidates may require more or less time depending on their individual circumstances.
Level II builds upon the foundational knowledge covered in Level I and delves deeper into complex topics such as financial statement analysis, equity and fixed income valuation, derivatives, and portfolio management. It requires a more comprehensive understanding and application of concepts compared to Level I.
Level II involves a significant amount of practice questions and item set exercises. It is essential to devote time to solve practice questions and thoroughly review the answers, as this helps reinforce your understanding and improve exam performance.
Creating a study plan is crucial to effectively manage your time. Break down the syllabus into smaller study sessions, allotting time for each topic and regularly assessing your progress. A well-structured study plan can help you stay organized, focused, and on track.
Identify your weaker areas and allocate more time to studying those topics. Level II requires a deeper understanding of certain subjects, so dedicating extra time to challenging areas can help improve your overall comprehension and exam readiness.
Taking mock exams and practicing under timed conditions is essential for Level II preparation. Allocate time for multiple mock exams to familiarize yourself with the exam format, manage time effectively, and identify areas that need further improvement.
Remember, everyone's study pace and learning style are different, so customize your study plan based on your strengths, weaknesses, and personal commitments. It's important to start early and maintain a consistent study routine to cover the entire syllabus thoroughly.
Q: Can I use third-party study materials to supplement the CFA syllabus?
Yes, you can use third-party study materials to supplement the official CFA curriculum and enhance your CFA exam preparation. Many candidates find that using additional study resources from reputable providers can be highly beneficial. Third-party study materials often provide comprehensive coverage of the CFA exam curriculum. They condense and explain complex topics, making them easier to understand. Some third-party providers offer concise study notes that summarize key concepts and formulas. When using third-party study materials, it's essential to choose reputable providers with a track record of success. The CFA Institute provides a list of approved prep providers on its website, which can be a good starting point.
Q: What are the main topic areas covered in the CFA syllabus?
The CFA syllabus covers a wide range of topic areas related to investment management, financial analysis, ethics, and professional standards. These topic areas are divided into specific readings and Learning Outcome Statements (LOS) within each level of the CFA exam. The main topic areas covered in the CFA syllabus are:
1. Ethics and Professional Standards
2. Quantitative Methods:
3. Economics:
4. Financial Reporting and Analysis
5. Corporate Finance
6. Equity Investment
7. Fixed Income
8. Derivatives
9. Alternative Investments
10. Portfolio Management and Wealth Planning
These main topic areas are consistent across all three levels of the CFA exam, but the depth and complexity of coverage increase as candidates progress from Level I to Level III.
CFA Syllabus 2025: Level III
Refer to the table below to know the CFA syllabus for the Level III exam:
| CFA Syllabus 2025 Level III | |
|---|---|
| Behavioral Finance |
Capital Market Expectations |
| Asset Allocation & Related Decisions in Portfolio Management |
Derivatives & Currency Management |
| Fixed-Income Portfolio Management |
Equity Portfolio Management |
| Alternative Investments for PM |
Private Wealth Management |
| PM- Institutional Trading, Performance Evaluation, and Manager Selection |
Cases in Portfolio Management and Risk Management |
| Ethics and Related Topics |
|
Q: Is the CFA Level III syllabus tough?
The CFA Level III syllabus can be considered tough, as it covers a wide range of advanced topics in finance and investment, and the exam format is challenging. The syllabus consists of 11 essay sets and 11 item sets, and candidates have to complete the exam in 4 hours and 24 minutes, which can be time-consuming and pressure-filled.
However, it's important to note that the difficulty level of the exam can vary based on the candidate's prior knowledge and experience. Candidates who have studied and prepared well for the exam may find it less challenging, while those who are new to the subject matter may find it more difficult. It's also worth mentioning that the pass rate for the CFA Level III exam is relatively low, which indicates that the exam is challenging and requires a high level of proficiency in finance and investment.
Q: Is the CFA syllabus updated regularly?
Yes, the CFA syllabus is updated regularly to reflect changes in the investment industry and to ensure that candidates are prepared for the latest industry practices and trends. The CFA Institute, the governing body for the CFA exam, reviews and updates the syllabus on a regular basis, typically every three to five years.
For example, the CFA Institute updated the Level I syllabus in 2020 to include new topics such as digital assets and sustainability, and to reflect changes in the investment industry. The Level II and Level III syllabi were also updated in 2020 to include new topics and to reflect changes in the industry.
This year, a new chapter titled – “Introduction to Geopolitics” has been introduced under the Economics section for the Level I CFA syllabus. Corporate Ownership and Structures and Business Models are the two new readings that have been added under Corporate Issuers section. Major changes to the Capital Structure readings have been made. Minor changes to the Introduction to Corporate Governance & Other ESG Considerations reading has also been made for the Level I CFA curriculum.
CFA Level 3 Specialised Pathways
CFA 2025 exam onwards for Level 3, CFA institute has introduced two new versions of Level 3 in Private Wealth and Private Markets while also keeping the traditional pathway, Portfolio Management. Candidates can choose the path according to their interests and aspirations. The three pathways of Level 3 will have one common core of the curriculum and additional specialised content for each pathway.
Candidates can choose one of the three pathway options during the CFA registration. Candidates must carefully choose the pathway as they cannot be changed after registration. The common core of the curriculum will have 65% to 75% weightage and 25% to 25% weightage will be given to the specialised pathway.
Common Core Curriculum
The common core will include the following:
- Asset Allocation- Capital market expectations, macro forecasting, handling constraints
- Portfolio Construction- Equity, Fixed Income and Alternatives Portfolio Construction, Institutional versus Private Wealth Portfolio Construction, Trading Costs
- Performance Measurement- Performance Attribution, Manager Selection, Global Investment Performance Standards
- Derivatives and Risk Management- Options strategies, swaps/ forwards/ futures strategies, Currency Hedging Strategies
- Ethics- Code of Ethics, Standards of Professional Conduct, Asset Manager Code
Private Wealth Pathway
The private wealth pathway offers a global perspective and universal guidelines for working with High Net Worth clients who have a net worth of 5 million dollars. It follows a journey from a young adult starting to build wealth, through working with a private wealth manager, to eventually transferring wealth to the next generation. This pathway expands on previous CFA Program content, going beyond just investment management and financial planning. It now includes new topics such as family management, philanthropy, and serving star athletes. This specialised pathway is further divided into seven chapters:
- Private Wealth Management Industry: Different kinds of business models in the wealth management industry which have different fee and compensations structures, coordinating with various advisors and understanding regulatory and compliance issues for wealth managers
- Working With Wealthy: Includes family dynamics and human psychology. Understanding social and psychological aspects of wealth whilst dealing with complex family structures and developing the skills to serve and educate high net-worth clients.
- Wealth Planning: Creating goal-based financial plans, managing financial risks, protecting assets, understanding tax impacts and developing liquidity strategies.
- Investment Planning: Recommending investment portfolios to private clients, maximizing tax efficiency, helping clients plan retirement through retirement and saving plans, evaluating investment performance through reporting, etc.
- Preserving Wealth: Identifying the various types of risks to human capital using insurance and other products, and strategies to protect against inflation and currency volatility.
- Advising the Wealthy: Navigating citizenship, nationality and residency issues whilst handling complex family financial situations. Maximizing the net worth of wealthy professionals along with managing their business assets.
- Transferring Wealth: Using gifts and bequests to transfer wealth and strategies for charitable giving and philanthropy.
Private Markets Pathway
This pathway addresses the investments made by the private markets from the perspective of the General Partner (GP). It expands on important valuation skills and other key concepts from all four asset classes of the CFA program. The curriculum includes recent engaging examples from the private markets such as Elon Musk’s acquisition of Twitter, Facebook’s acquisition of WhatsApp, Blackstone REIT, events at Silicon Valley Bank, Gabon’s debt-for-nature swap and several high-profile LBOs such as Thyssen elevators in 2020. It is further divided into seven chapters:
- Private Investments and Structures: As the name suggests, it focuses on understanding the private investments and structures. It includes the methods and structures of debt, equity, infrastructure, etc. It also explores the difference between the various types of performance metrics and compares the risk and return profiles of private versus public markets within strategic asset allocation.
- GP and LP Perspectives: This explores the roles and responsibilities of GPs or General Partners and Limited Partners (LPs) in managing the private investment fund. Learning about fee structures, fund performance and alignment of interests between investors and investment firms. One will also get to explore favourable characteristics of investment targets, due diligence, business planning, and alternative exit routes and their impact on value.
- Private Equity: Delves into the private equity strategies which include venture capital, growth equity, and buyout investments. It also includes private equity investments and the risk and return as compared to other investments.
- Private Debt: Examines the use of debt financing in private market strategies including leveraged loans, high-yield bonds, mezzanine debt, and uni-tranche debt. Candidates can learn about the private debt profile and ratio analysis while comparing the risk and return on other debt investments.
- Private Social Situations: Explores event-driven opportunities which involve financial dislocation or distress, financing alternatives for issuers in distress and investment strategies such as capital structure arbitrage.
- Private Real Estate: Focuses on the features and economic drivers of private real estate investments including farmland and timberland. Understanding the due diligence and valuation process for real estate and comparing their risk and return profiles within strategic asset allocation.
- Infrastructure: Talks about private infrastructure investment features, vehicles and methods. It studies the overall investment process including the roles of equity financing and debt and compares their risk and return profiles within strategic asset allocation.
Read More:
Q: Which is the easiest pathway in CFA exam Level 3?
No pathway will be easier than the other. Each pathway is designed in a way that they are at par with each other. This does not mean that the CFA pass rate will be also be the same between each as many factors influence pass rate such as quality of the cohort, mix of the cohort, difficulty of the given set of questions in a given window, demographic factors, etc.
Q: Why has the CFA institute introduced specialised pathways for Level 3?
The CFA institute has introduced the specialised pathways because:
- Career discovery
- Mastering a specific field
- Choosing which field aligns best with interests and aspirations of the students
- Credentialing. Passing a challenging exam for the role will benefit the candidates by benefiting their clients and their employers.
Q: Can I change my pathway after registering for the level 3 CFA exam?
No, candidates cannot change their pathway in the middle of the CFA registration process. If the candidate is taking the CFA Level 3 exam for the second time, then they have the option of changing their specialised pathway. The content for all the three pathways are available online for CFA preparation.
FAQs Related to CFA Syllabus
Check some of the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on CFA syllabus:
Q: Can I self-study for the CFA exam?
Yes, of course you can self-study for the CFA exam. Many students prefer to choose this option for preparation because of the flexibility it offers. The CFA insitute provides an official curriculum for each level of the exam. It serves as a comprehensive guide and primary source of study material. You can follow the curriculum independently and study at your own pace.
Besides the CFA Institute curriculum, there are number of other resources available for the CFA study material. These may include guides, sample papers, video lectures, tutorials, etc. You can utilize these resources to supplement your self study efforts and reinforce your understanding of the important topics of the CFA syllabus.
Create an effective study plan that outlines your study schedule, goals and progress. This will help you stay organised and improve time management. You can also engage with online forums and communities and various social media groups dedicated to CFA preparation. These platforms provide the opportunity to connect with fellow candidates, seek clarification, share insights and access additional study resources.
While self-studying is a viable option, keep in mind that the CFA exams are rigorous and the material can be complex. Ensure that you allocate sufficient time, maintain discipline and monitor your progress regularly.
Q: How can I prepare for CFA?
Preparing for the CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) exam requires a systematic and disciplined approach. Here are some steps to help you with your preparation:
Familiarize yourself with the exam structure, including the number of levels, topic areas, and the weightage assigned to each topic.
Develop a comprehensive study plan that covers all the topics and allows for sufficient time for review and practice. Set realistic goals and create a schedule that works for you, taking into account your other commitments.
The CFA Institute provides official curriculum materials that cover all the exam topics in detail. Make sure to study from these materials as they are comprehensive and aligned with the exam content.
Practice is crucial for success in the CFA exam. Solve mock exams and practice questions to get familiar with the exam format and to assess your understanding of the topics. Review your performance and identify areas that require further study.
Engage with other CFA candidates through study groups or online communities. Discussing and exchanging ideas can enhance your understanding of complex topics and provide additional support during your preparation journey.
The CFA exam is concept-driven, so it's essential to develop a strong understanding of the underlying principles and theories. Avoid rote memorization and strive for a deeper comprehension of the material.
Regularly review the topics you have studied to reinforce your knowledge. Create concise notes or flashcards to summarize key concepts, formulas, and important details.
- The CFA curriculum undergoes periodic updates. Stay informed about any changes or updates to the syllabus and adjust your study plan accordingly.
Remember, the CFA exam requires dedicated effort and perseverance. It is essential to stay disciplined, motivated, and consistent in your study routine. Good luck with your CFA preparation!
Q: What is the syllabus and exam pattern of CFA exam?
Chartered financial analyst designation is a professional credential that is offered by the CFA institute to the financial and investment professionals. The designation of the Chartered Financial Analyst or CFA Charter is the most recognized and respected credential in the field of investment banking. It is a globally recognized credential. There are three levels in CFA Program that students will have to go through. Based on the historical data, pass rate for the CFA examination is about 40 percent.
There is a wide range of topics related to investment management, stocks, derivatives, financial analysis which give you great understanding of everything you need in order to become a better Financial Analyst/Investment banker.
CFA Level I Exam: This is the first examination that students will have to go through. In level one, students will have to focus on the concepts and tools that are applied to investment management and valuation. The CFA Level 1 exam is conducted in two sessions, each 3 hours long. It consists of 240 multiple-choice questions in two sessions of 120 questions each. The questions are designed based on the topic weightages given in the CFA Level 1 Exam Syllabus, with very slight deviation.
CFA Level II Exam: This is the second examination that students will have to go through after passing the CFA level I Exam. In Level II, students will have to deal with the assets valuation. Students must have the ability to apply the concepts and tools that they have learned in level I. There are total 20 item set questions, split in two sessions. The morning and evening sessions have 10 item set questions each. The total number of questions in the CFA Level II exam is 120. The duration of the exam is 360 minutes. Some of the CFA level II topics are covered only in the morning session and other topics are covered only in the evening session.
CFA Level III Exam: This is the last CFA exam that students will have to pass to become a CFA charterholder. In the level 3 examination, students will have to go through portfolio management in depth. CFA Level I and CFA Level II revolved around basic financial knowledge, investment valuation comprehension and the application of both. CFA Level III exam focuses on portfolio management and wealth planning. All the best.
Q: How can I get guidance for CFA course?
News & Updates
Get all exam details, important updates and more.
CFA Exam Exam
Student Forum
Answered 2 months ago
Here are some practical tips to help you perform your best on the CFA exam.
- Financial Statement Analysis: Questions on this topic are based on International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) unless otherwise noted. If a question references U.S. GAAP, this will be explicitly stated.
- No penalty for g
A
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 2 months ago
Follow the steps mentioned below to learn how to fill out the CFA application form
- Visit the official website of the CFA institute
- Click on the application link or copy https://login.cfainstitute.org/LoginApplication.
- Create a login account with the candidate’s email ID.
- The candidate will be asked to e
A
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 2 months ago
CFA Charter Holders have the distinct advantage of applying their skills in several professional roles. They can work in areas like wealth management, hedge funds, fixed income, insurance and equity research.
A
Contributor-Level 10


Can you share some tips to prepare for CFA exam?