Introduction
Three primary components make up carbohydrates, starch, fibre, and sugar. Although starch and fibre are complex carbohydrates, sugar is a basic carb. The nutrient content is determined based on the quantity of these components present in food.
Sugar molecules are made up of complex carbohydrates, strung together in long, complex chains. In foods like beans, peas, vegetables, and whole grains, complex carbohydrates can be contained.
A significant energy source for your body is complex carbohydrates. They supply the sustained fuel that your body requires for exercise, daily life tasks, and even rest.
Single units (monosaccharides), which are connected, are also complex carbohydrates.
Type of Complex Carbohydrate
Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides contain long units of monosaccharides united by glycosidic bonding together.
- Most of them serve as storage for food, e.g. from starch. The primary storage polysaccharide for plants is starch.
- It is an alpha glucose polymer that is made up of two components: amylose and amylopectin.
- Also, cellulose is one of the polysaccharides found mainly in plants.
- It consists of β-D-glucose units connected by a glycosidic bond between one glucose unit's C1 and the next glucose unit's C4.
Foods Containing Complex Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are the primary sources of nutrition to the body.
- Foods that produce complex carbohydrates include important minerals, vitamins, and fibre for good health.
- Instead of refined sugars that do not have vitamins and minerals found in normal and complex carbohydrates, much of the carbohydrates come from complex carbohydrates and natural sugars.
- Refined carbohydrates, though they have much less health content, are often known as hollow calories.
Complex Carbohydrates in Class 12
You will learn about complex carbohydrates in biomolecules. In this chapter, you will be taught about the types and structures of different carbohydrates. This chapter holds a weightage of 5 marks in your final exam.
Illustrated Examples
1. What foods are rich in carbohydrates?
Answer: In a diverse variety of nutritious and unsafe foods, carbohydrates are present in bread, rice, whey, popcorn, potatoes, biscuits, noodles, and soft drinks. Others even appear in a diversity of compositions. Sugars, starches, and fibres are the most natural furthermore ample modes.
2. What are the main carbohydrate functions?
Answer: The four main carbohydrate roles in the body are to supply nutrition, preserve energy, produce macromolecules, and spare protein and fat for other purposes. The energy of glucose is stored in the form of glycogen, with the remainder found in the muscle and liver.
3. Which carbohydrates are the important ones?
Answer: Bread, vegetables and fruits, as well as dairy, include foods high in carbohydrates. The sugars, starches and fibres found in the products of fruit, wheat, vegetables, and milk are carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are important to a balanced diet as one of the core food classes, although sometimes maligned in trendy diets.
FAQs on Complex carbohydrates
Q Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
A: Carbohydrates are an essential compound for the organic life It is used as primary source of energy by plants and animals. It also fulfill other needs like synthesizing of other chemicals and provide the structure for cells within the body. Energy is stored in it in the form of starch which, provide either complex or simple type of sugars. Complex sugars i.e., polysaccharides, give a constant supply of energy while simpler sugars, like monosaccharides, supplies a quicker jolt before dissolving. Animals receive these starches through foods, especially those made from plant life such as grains and bread. Plants manufacture their own carbohydrates through photosynthesis, which uses energy absorbed from light to break up carbon dioxide and water into energy.
The two main functions of carbohydrates in plants are:-
- Cellulose , a polysaccharide , is used to build the cell wall
- Polysaccharides such as starch serve as storage
Q: Glucose or sucrose is soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) is insoluble in water. Explain.
A: Glucose and sucrose are carbohydrates (optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones).
Structure of glucose:
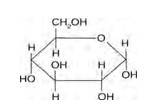
Structure of sucrose:
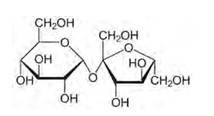
As you can see both the compounds have five –OH and eight –OH groups respectively. These –OH groups are responsible for the extensive hydrogen bonding with water. This –H bonding is responsible for the solubility of glucose and sucrose in water.
In case of cyclohexane or benzene (simple six-membered ring compounds) , they do not contain any – OH groups. Hence, they cannot undergo –H bonding with water and are insoluble.
Q: What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
A: Glycogen is a polysaccharide-type of carbohydrate. In animals, carbohydrates are stored as glycogen. But starch is a carbohydrate which consists of two components –amylase (15 -20 %) and amylopectin (80 – 85%). However, glycogen is also like amylopectin but branching will take place after every 5 to 6 glucose unit. Also, glycogen is highly branched.
Q: What is the differentiation between carbohydrates that are complex and simple?
A: In such foods as bread and pasta, complex carbohydrates are contained. Basic carbohydrates are present in foods, such as table sugar and syrup. There are longer sugar molecular chains with complex carbohydrates than mere carbohydrates. The body transforms these sugar molecules to glucose, which it uses for energy.
Q: What are the four carbohydrate types?
A: Four chemical groups are known as saccharides: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, etc. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars.
Q: Why do complex carbohydrates matter?
A: Complex carbohydrates also provide the energy and other nutrients and fibre required by the body. This choice is easier. STARCH- In the body, basic sugars break down. The body needs to break down all the sugar/starch into glucose in order to consume it.
Q: What are complex carbohydrates?
A: In long, complicated chains, complex carbohydrates consist of sugar molecules.
Q: What are good carbohydrates to consume?
A: Vitamins, minerals and fibre, whole grains are the best source of carbohydrates. Instead of heavily processed foods, including white flour and white rice, consuming whole grains as much as possible will help minimise the risk of heart disease and diabetes and keep the digestive system safe.
News & Updates
Chemistry Biomolecules Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test
