What Is Starch?
Starch is a complex chemical that is produced by plants during photosynthesis. It is a polysaccharide in nature that comprises amylose and amylopectin. Both of the polymers are insoluble in water. It is mainly present in potatoes, rice, cereals, bread and many other food items. Human beings need to consume starch in their diet as it provides energy to our body tissues. It also offers other health benefits like it lowers our increased insulin level or glucose level. It is also used as a thickening agent in baking cakes and pastries, a bulking agent in dairy items, a binding agent in soups and sauces, and a sweetening agent in beverages.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is made up of hundreds or thousands of glucose units. It helps the plants to stay firm. It is present in plant walls. Unlike starch, humans are incapable of digesting cellulose. Cellulose is insoluble in water as compared to starch which is soluble in water.
Difference between Starch and Cellulose
Starch and cellulose are polymers with very similar properties. They both are made of the same monomer. The monomer is glucose, and both consist of the same glucose-based repeat units. But, there is a structural difference between starch and cellulose.
In starch, the glucose repeat units are linked together in such a manner that they are all in the same orientation. Whereas, in cellulose, the glucose repeat units are linked together so that alternating molecules are rotated 180 degrees from each other.
This orientation of glucose-based repeat units increases the strength and makes cellulose stronger than starch. The cellulose fibres form rigidity by stacking up just like corrugated sheets piled on top of each other. The starch fibres are tied to each other weakly because of their structure and can break easily compared to cellulose.
To see the structural difference between starch and cellulose in detail, study this formation.
- Cellulose is a straight-chain polysaccharide of β-D-glucose units joined by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage (β-link)
Starch and Cellulose in Class 11
The cellulose is well explained in Class 11 textbooks. There is a diagrammatic representation of a portion of glycogen, to explain the cellulose. The cellulose is described as a polymeric polysaccharide. Similarly, starch is also described with its molecular structures.
Starch and Cellulose in Class 12
The starch and cellulose are further explained in class 12 books with their basic and structural difference. In class 12 textbooks, the structural difference between cellulose and starch is described in more details with the structure of glucose repeat units.
In class 12 boards, the Biomolecules chapter holds 4 marks.
[Image courtesy: NCERT]
FAQs on Starch and Cellulose
Q: What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
A: Starch consists of two components – amylase and amylopectin. Amylose is a long linear chain of α–D-(+)-glucose units joined by C1-C4glycosidic linkage (α -link).
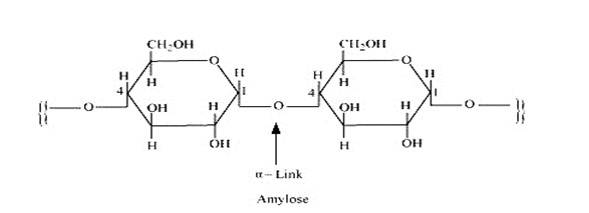
Amylopectin is a branched-chain polymer of –D-glucose units, in which the chain is formed by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage and the branching occurs by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.

On the other hand, cellulose is the main structural material of tree and other plants. Wood is 50% cellulose, while cotton wool is almost pure cellulose. It is linear chain natural polymers of β-D-glucose units joined by 1, 4-glycosidic linkage (natural linear polymers).

Q: What makes cellulose stronger than starch?
A: The molecular structure of cellulose makes it stronger as compared to scratch. The cellulose consists of glucose repeat units linked together in such a manner that alternating molecules are rotated 180 degrees from each other. The orientation makes the cellulose stronger.
Q: What are the fundamental differences between starch and cellulose?
A: The starch is soluble in water and cellulose is insoluble in water. Humans can digest starch easily, whereas cellulose is difficult to digest by humans. Starch helps the plants to store energy and cellulose helps plants to provide stiffness.
Q: What are the components of starch?
A: There are two components of starch; amylose and amylopectin.
Q: How are starch and cellulose similar?
A: Starch and cellulose are made up of the same monomer; glucose.
Q: What is the structure of cellulose?
A: Cellulose is a straight-chain polysaccharide of β-D-glucose units joined by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage (β-link).
News & Updates
Chemistry Biomolecules Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test


