What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids consist of large polymers molecules, monomers which are called nucleotides. The other name of nucleic acids is polynucleotides. RNA and DNA are the two types of nucleic acids grouped under it and are responsible for the inheritance of the generations and more. The properties of both nucleic acids are different from each other.
Structure of Nucleic Acid
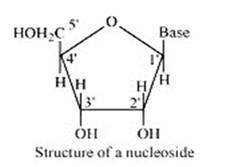
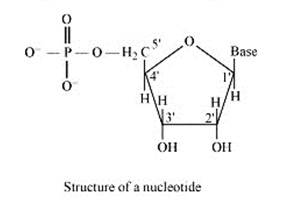
The formation of nucleoside occurs by the combination of sugar and base. The sugar is numbered as 1,2,3 and so on, inside the nucleoside to differ them from each other. When phosphorus acids link with nucleoside, by the sugar numbered as 5, the nucleotide is formed. The structure of this chemical formation of nucleoside and nucleotide is presented below:
Types of Nucleic acid
There are two types of Nucleic acids which are:
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA consists of phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and other bases that have nitrogen concentration. These other nitrogen concentrated elements are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The structure of DNA plays an important role, and the placement of every element in the DNA orbits is very crucial. The structure of every element is illustrated below:
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic is made up of phosphorus acid, pentose sugar, and bases of nitrogen, but in RNA, the concentrations of nitrogen are slightly different compared to DNA. The four bases of nitrogen are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and Uracil (U). RNA is further classified into three types which are:
- Messenger RNA
- Ribosomal RNA
- Transfer RNA
Functions of nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are present in every human mankind and hold a different level of importance. Some of the major functions of nucleic acids are as follows:
- The synthesis of protein in our body is regulated due to the presence of nucleic acids in our body.
- The transfer of intrinsic personality from parent to a child takes place due to the presence of nucleic acids. Physical personalities of children depend upon the parents, which is possible through nucleic acids
- The digital fingerprinting of DNA can identify the parent of the child.
Nucleic acid for class 11
The chapter of biomolecules of class 12 holds a light weightage of 5 marks which consists of 3 questions (2 objective types questions of one mark each and 1 short question of 3 marks). The nucleic acid topic is very important because of one objective type of question expected from this topic.
Illustrated Examples
1. Explain one advantage of Nucleic Acid.
Answer: The synthesis of protein in our body is regulated due to the presence of nucleic acids in our body.
2. Present an illustration of the structure of DNA.
Answer:
3. Explain digital fingerprinting of DNA.
Answer: The digital fingerprinting of DNA can identify the parent of the child. It is used by criminal investigation departments to identify the disguised criminals through their DNA test reports.
[Image courtesy: NCERT]
FAQs on Nucleic Acids
Q: What are nucleic acids? Mention their two important functions.
A: Nucleic acids are Biomolecules which are found in the nuclei of all living cells, inform of nucleoproteins or chromosomes (proteins containing nucleic acids as the prosthetic group). Nucleic acids are of two types: – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are also known as Polynucleotide as they are long- chain polymers of nucleotides.
The two important functions of nucleic acids are listed below:-
- DNA which is responsible for the transference of hereditary effects from one generation to another, which is due to their property of replication during cell division as a result of which two identical DNA strands are transferred to the daughter
- Nucleic acids (both DNA and RNA) are responsible for synthesis of all proteins needed for the growth and maintenance of our body. Actually, the proteins are synthesised by various RNA molecules in the cell but the message for the synthesis of a particular protein is given by DNA molecules
Q: What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
A: A nucleoside is formed when l-position of a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine or uracil) or 9- position of a purine (guanine or adenine) base is attached to C-l of sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) by a linkage. Thus in general, nucleosides may be represented as: Sugar-Base.
Nucleoside = sugar + base
On the other hand , all the three basic components of nucleic acids (i.e., pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and base) are present in a nucleotide.These are obtained by esterification of C5’ –OH group of the pentose sugar by phosphoric acid. Thus, in general, a nucleotide is represented as:-
Nucleotide= sugar + base + phosphoric acid
Q: The two strands in DNA are not identical but are complementary. Explain.
A: In the helical structure of DNA, the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between specific pairs of bases. Cytosine from hydrogen bond with guanine, while adenine forms hydrogen bond with thymine. As a result , the two strands are complementary to each other.
DNA consists of two strands of nucleic acid chains coiled around each other in the form of a double helix. The base of one strand of DNA is paired with bases on other strand by means of hydrogen
bonding. This hydrogen bonding is very specific as the bases can only base pair in a complementary manner. Adenine pairs with only thymine via 2 hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine through 3 hydrogen bonds. Thus, the two strands of DNA are complementary to each other in the sense that the sequence of bases in one strand automatically determines that of the other. So the DNA stands cannot be identical, but they are complementary to each other.
Q: What are two different types of Nucleic Acids?
A: RNA and DNA are the two types of nucleic acids grouped under it and are responsible for the inheritance of the generations and more.
Q: What does DNA stand for?
A: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Q: What does RNA stand for?
A: Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Q: Name different classifications of RNA,
A: Messenger RNA, Ribosomal RNA, Transfer RNA
Q: Explain the structural integrity of Nucleic Acid.
A: The formation of nucleoside occurs by the combination of sugar and base. The sugar is numbered as 1,2,3 and so on, inside the nucleoside to differ them from each other. When phosphorus acids link with nucleoside, by the sugar numbered as 5, a nucleotide is formed.
News & Updates
Chemistry Biomolecules Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test