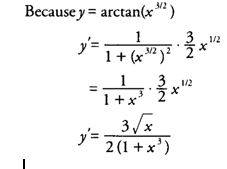- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions with their Domains and Ranges
- Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions in Class 12
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs
Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Inverse trigonometric functions are often referred to as arcus functions, anti-trigonometric functions, or cyclometric functions. These functions are often used to produce an angle for a trigonometric value. Inverse trigonometric functions have diverse uses in engineering, geometry, navigation, etc.
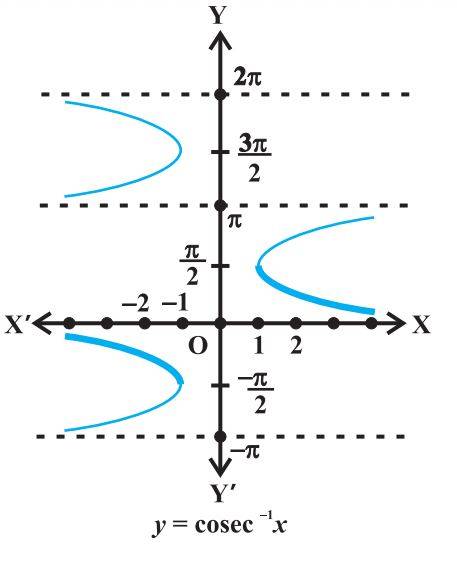
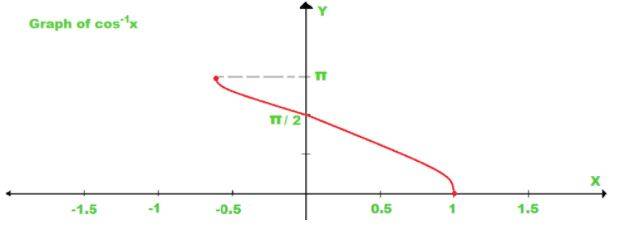
Inverse Trigonometric Functions with their Domains and Ranges
sin–1 : [–1, 1] → [-π/2, π/2]
cos –1 : [–1, 1] → [0, π]
cosec–1 : R – (–1,1) → [-π/2, π/2] – {0}
sec –1 : R – (–1, 1) → [0, π] – { π/2 }
tan–1 : R → [-π/2, π/2]
cot–1 : R → (0, π)
Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
(i) sin–1 1/x = cosec–1 x, x ≥ 1 or x ≤ – 1
(ii) cos–1 1/x = sec –1 x, x ≥ 1 or x ≤ – 1
(iii) tan–1 1/x = cot–1 x, x > 0
(iv) sin–1 (–x) = – sin–1 x, x ∈ [– 1, 1]
(v) tan–1 (–x) = – tan–1 x, x ∈ R
(vi) cosec–1 (–x) = – cosec–1 x, | x | ≥ 1
(vii) cos–1 (–x) = π – cos–1 x, x ∈ [– 1, 1]
(viii) sec–1 (–x) = π – sec–1 x, | x | ≥ 1
(ix) cot–1 (–x) = π – cot–1 x, x ∈ R
(x) sin–1 x + cos–1 x = π/2 , x ∈ [– 1, 1]
(xi) tan–1 x + cot–1 x = π/2 , x ∈ R
(xii) cosec–1 x + sec–1 x = π/2 , | x | ≥ 1
(xiii) tan–1 x + tan–1 y = tan–1 x + y / 1– xy , xy
(xiv) tan–1 x – tan–1 y = tan–1 x – y/1 + xy , xy > – 1
(xv) 2tan–1 x = sin–1 2x/1+x2, | x | ≤ 1
(xvi) 2tan–1 x = cos–1 1-x2/1+x2, x ≥ 0
(xvii) 2 tan–1 x = tan–1 2x/1-x2, – 1
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
| arcsin x |
1/1-x2 |
| arccos x |
-1/1-x2 |
| arctan x |
1/1+x2 |
| arccot x |
-1/1+x2 |
| arcsec x |
1/|x| x2 - 1 |
| arccsc x |
-1/|x| x2 - 1 |
Example:
Differentiate the function f(x) = cos-1x using the first principle.
limh->0 {f(x + h) – f(x)} / h
cos-1x + sin-1x = pi/2
cos-1x = pi/2 – sin-1x
f(x) = cos-1x
f(x + h) = cos-1(x + h)
limh->0 {cos-1(x + h ) – cos-1(x)} / h
limh->0 {pi/2 – sin-1(x + h) – (pi/2 – sin-1x) } / h
limh->0 {pi/2 – sin-1(x + h) – pi/2 + sin-1x } / h
– limh->0 {sin-1(x + h) – sin-1x} / h
limh->0 { sin-1(x + h) – sin-1x } / h = 1 / √(1 – x2)
– 1 / √(1 – x2)
Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions in Class 12
This concept is taught under the chapter Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
in class 12. In this chapter, you will learn about the nature of inverse trigonometric functions and their derivatives and use this knowledge to solve questions. The weightage of this chapter is four marks.
Illustrated Examples
1. Find y’ if y=arctanx3
2. Find f′( x) if f( x) = cos −1(5 x).
f’(x) = -1/1-(5x)2 . 5
= -5/1-25x2
3. Differentiate y=5x6−sec−1(x)
dy/dx=30x5−1/x√x2−1
FAQs
Q: What are the six inverse trig functions?
Q: What is the derivative of an inverse function?
Q: What is the derivative of tan inverse?
Q: Is arctan inverse tan?
Q: What is the formula for derivatives?
Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test