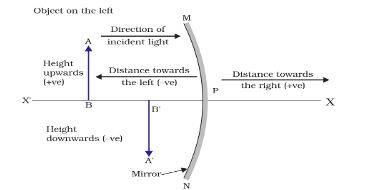
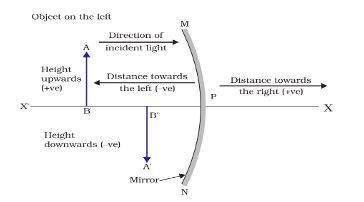
What is Mirror Formula?
The mirror formula shows the relation between the object distance and the image distance with the help of focal length. It is also called the “mirror equation.”
The equation is written as:
1 / v + 1 / u = 1 / f
Here, u is the object distance,
V is the image distance,
And the f is the focal length.
The illustration of the mirror formula can be seen below:
Image source: ncert
In a spherical mirror, the object distance is the distance between the pole and the object of the mirror.
The image distance is the distance between the pole and the image of the mirror.
The focal length is the distance between pole and principal focus.
This formula can be used for both concave and convex lenses for all object positions.
- Assumptions for the Derivation of Mirror Formula
- Derivation of Mirror Formula
- Derivation of Mirror Formula for Class 12
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs on Derivation of Mirror Formula
Assumptions for the Derivation of Mirror Formula
Few assumptions are taken into account while deriving the mirror formula which is listed below:
- It is assumed that the negative sign is the indication of the distance in the opposite direction and the positive sign indicates the distance in the same direction.
- The distance above the axis is positive, and the distance below the axis is negative.
Derivation of Mirror Formula
I explained the derivation of the mirror formula below:
Let us assume that the object AB is at the distance of U from P, the pole of the mirror. And we can assume that the A1B1 points are formed at V from the mirror.
So, now we can say that:
∠ACB = ∠A1CB1
Now let us consider that the D and P points are close, we can write:
BC / B1C = PF / FB1
From this, we can say:
(PC – PB) / PB1 – PC = PF / (PB1 – PF)
Let us now substitute the values:
PC = -R
PB = u
PF = -f
PB1 = -v
Now, the equation is as follows:
(-R – (-u)) / (-v – (-R)) = -f / (-v – (-f))
(u – R) / (R – v) = -f (f – v)
(u – R) / (R – v) = f / (v – f)
After solving, we get
Uv – uf – Rv + Rf = Rf – vf,
Uv – uf – Rv + vf = 0,
We know that R = 2f,
So, Uv – uf – 2fv + vf = 0,
Uv – uf – vf = 0
After solving it we get,
1 / v + 1 / u = 1 / f
Derivation of Mirror Formula for Class 12
As per the new pattern 2021, the chapter ‘Optics’ holds a weightage of 7 marks. It includes 2 questions in total, consisting of one short question of 2 marks and one long question of 5 marks.
Illustrated Examples
Example 1) Illustrate the mirror formula.
Answer – The illustration is as follows:
Example 2) Write the equation of mirror formula
Answer – The formula of mirror formula is
1 / v + 1 / u = 1 / f
Here, u is the object distance,
V is the image distance,
And the f is the focal length.
Example 3) Write the meaning of R in the mirror formula.
Answer – The radius of the curvature in the mirror formula is denoted as R.
FAQs on Derivation of Mirror Formula
1) What do you mean by the Mirror formula?
2) What is the formula of a spherical mirror?
3) What is the Lens formula?
4) What is the SI unit of focal length?
5) What is the magnification formula for the mirror?
Physics Optics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test