- What is alcohol?
- What is a phenol?
- Difference between alcohol and phenol
- FAQs regarding Alcohols and Phenols
What is alcohol?
Alcohol is one of the most commonly found compounds in nature. They contain at least one hydroxyl functional group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon or an alkyl group. Further, the type of carbon attached to the hydroxyl group determines whether the alcohol is a primary, secondary, or tertiary compound.
Structure of alcohol:
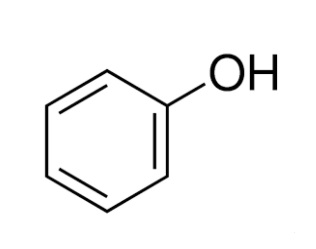
What is a phenol?
Phenols or phenolics are chemical compounds that consist of a hydroxyl group attached to an aromatic hydrocarbon. They are known as a subset of alcohol but exhibit different physical and chemical properties in comparison. They are also called carbolic acids and are used to prepare nylons, herbs, detergents, and other pharmaceutical products.
Structure of Phenol
Difference between alcohol and phenol
We know that phenol is sometimes considered a type of alcohol. However, various factors can help us differentiate between the two compounds. Some of the differentiating factors between alcohols and phenols are as follows:
| ALCOHOL |
PHENOL |
|---|---|
| Alcohol is an organic compound that contains one or more hydroxyl functional groups attached to a saturated carbon atom |
Phenols are organic compounds that consist of a hydroxyl group attached to a group of hydrocarbons or arene |
| Alcohol consists of aliphatic hydrocarbons |
Phenol consists of aromatic hydrocarbons |
| Alcohols are less acidic |
Phenols are more acidic in comparison with alcohol and need to be diluted before use |
| Alcohol is used as an ingredient in alcoholic beverages, ink, pharmaceuticals, and various other chemical products |
Phenols are commonly used as antiseptic agents |
| Alcohols are colourless and are found in the liquid state |
Phenols are also colourless but are crystalline at standard temperature and pressure |
| Alcohols are neutral and hence, show no reaction on litmus paper or other tests |
Phenols are acidic and change the colour of litmus paper to red |
| Alcohols do not react with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) |
Phenols react with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form phenoxides |
Alcohols and Phenols in class 11: In class 11, the basic structure and reaction of different compounds with alcohols and phenols are mentioned in various chapters.
Alcohols and phenols in class 12: The chapter on Alcohols, Phenols, and Ether in class 12 includes a complete and detailed explanation of alcohols and phenols. It consists of a thorough explanation of the physical and chemical properties of alcohols and phenols.
The chapter also discusses the reactions involved in the preparation of these compounds and correlates the physical properties with their structure.
FAQs regarding Alcohols and Phenols
Q. What are the different methods for the preparation of alcohol?
Q. What are the different compounds used for the preparation of phenol?
A. Phenols are prepared using haloarenes, benzene sulphonic acids, cumene, and diazonium salts.
Q. Are alcohols and phenols polar?
A. Yes, both alcohols and phenols are polar.
Q. Can alcohols and phenols be oxidized?
A. Yes, both phenols and alcohols can undergo oxidization.
Q. Who discovered phenol?
A. Phenol was discovered in 1834 by a German chemist Dr. Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge.
Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test