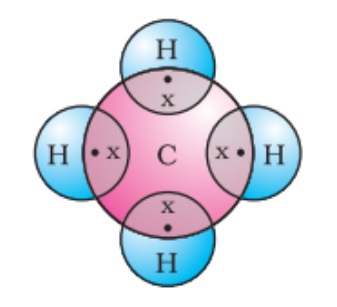
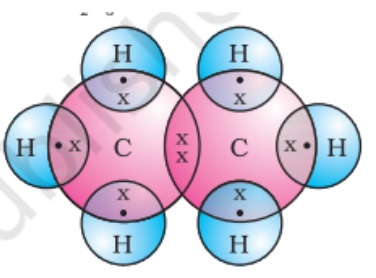
The tetravalency of carbon is its ability to form bonds with other atoms by sharing its valence electrons. A carbon atom forms four covalent bonds hence carbon is said to be tetravalent, where tetra means ‘four.’
Carbon is an element that is found in abundance in nature. It is useful to human beings in both elemental and combined form. All living beings are made up of some form of carbon. Despite its rarity, which is about 0.03% in the atmosphere and 0.02% in the earth’s crust, carbon is of immense importance to human beings.
Carbon can share its valence electrons with not only another carbon but also with atoms of other elements. For example, hydrogen is one of the simplest molecules formed by sharing valence electrons.
- FAQs on Carbon Tetravalency
FAQs on Carbon Tetravalency
Q. Who discovered tetravalency of carbon?
Q. Where is carbon naturally found?
Q. Why is the valency of carbon 4?
Q. What are allotropes of carbon?
Q. What is carbon catenation?
Chemistry Carbon and its Compounds Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test