- Continuity and Differentiability
- Weightage of Continuity and differentiability
- Illustrative Examples on Continuity and differentiability
- FAQs on Continuity and differentiability
Continuity and Differentiability
The terms continuity and differentiability are crucial linking concepts that explain the linkage derivatives and limits. Continuity explains whether the function is continuous in a given interval. In contrast, differentiability is achievable when the slope of a function is possible to plot on a graph.
Concept of Continuity
Continuity of a function can be explained as the characteristics of a functional value and function. Moreover, it is a continuous function if the curve does not have any breaking or missing point on a given domain or interval. In short, the curve is continuous at each point of its domain.
It can be explained as:
limq→bf(q) exists, and
limq→bf(q) = f(b)
However, if the function does not exist or is undefined, it is a discontinuous function.
Continuity for the Closed Interval [x,y]
A function f(x) will be continuous for the closed interval [x,y] subjected to the satisfaction of the following conditions:
- f(q) will be continuous for the open interval (x,y)
- f(q) will be continuous at the point of right side, i.e., limq→x f(q)=f(x)
- f(q) will be continuous at the point from left side, i.e., limq→y f(q)=f(y)
Concept of Differentiability
F(x) will be explained as differentiable at the point q = x if the derivative f ‘(q) exists at every single point of its domain. It can be demonstrated as:
F’(q) = Limh→0 f(x+h)-f(x)/h
Although a function differentiable at any point q = x within the domain must be continuous at that specific point, the vice-versa of that is not always true.
Following are the derivatives of some basic trigonometric functions:
- d/dA(sinA) = cosA
- d/da (cosA) = sinA
- d/dA (cotA) = -cosec2A
- d/dA(cosecA) = -cosecA cotA
- d/dA (tanA) = sec2A
- d/dA (secA) = secA tanA
Weightage of Continuity and differentiability
Continuity and differentiability are considered to be two strong pillars of Class 12th Calculus. Here students will learn the concepts of derivatives of a function, continuity at a point, continuity on an interval, and application of limiting properties on various complex and real numbers. The questions related to this topic are asked for 8-10 marks in boards.
Explore exams which ask questions on Maths Differentiation
Select your preferred stream
Illustrative Examples on Continuity and differentiability
1.
Solution:
Since f(x) is continuous at x=0
∴ lim x→0−f(x)=f(0)=x→0+limf(x)
⇒lim x→0− (1+∣sinx∣) a/∣sinx∣=b= lim x→0+ e tan2x/ tan3x
⇒ea=b=e2/3
∴a=2/3
And, a = logeb
2. Interpret the continuity of the function f(A). If, f(A) = SinA . CosA
Solution:
Both Sin A and Cos A are continuous functions. However, the product of two continuous functions will also result in a continuous function.
Therefore, we can interpret that function f(A) = Sin A . Cos A is a continuous function.
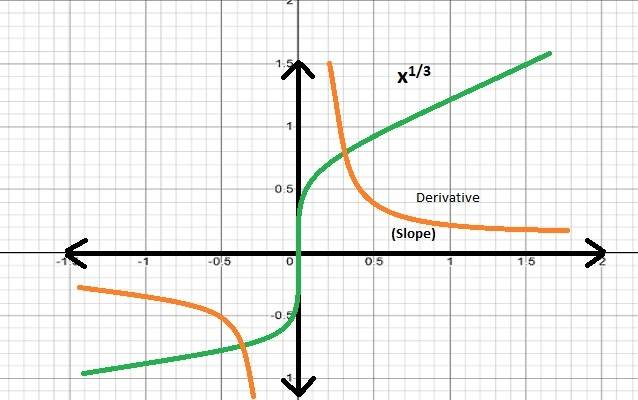
3. Analyse the differentiability of f (x) = x1/3 for x = 0.
Solution:
From the below figure, we can clearly observe that there is no break in the graph, so the given function is a continuous function.
Now, let us examine whether f’(0) exists or not.
Now, f’(0) = Limx→0 f(x) – f(0)/ x- 0 = Limx→0 x1/3- 0/ x
= Limx→0 x-2/3
= Limx→0 1/ x2/3 → ∞
FAQs on Continuity and differentiability
Q: Is it vice versa if differentiability into continuous function exists?
Q: Can differentiability be measured for open and close intervals?
Q: How will you know that a function is differentiable on the open interval?
Q: What does "no break in the curve" represent?
Q: What is a discontinuous function?
Maths Differentiation Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test