- What is a Simple Pendulum?
- The Time Period of a Simple Pendulum
- Derivation
- Weightage in Class 11
- FAQs
What is a Simple Pendulum?
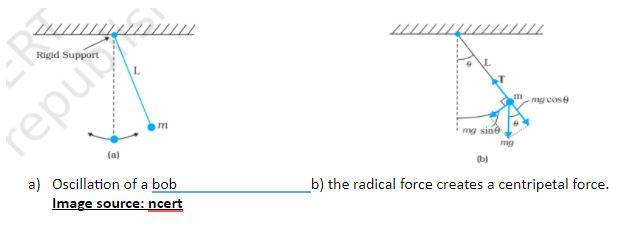
When a small mass in the shape of a round ball is attached at the end of a string and hung from the other end of that string to move freely in a to-and-fro motion, it is called a simple pendulum. Displacing the ball from one side and set free at the other end creates a to-and-fro movement. It takes around 2 seconds for it to go up and down and again from the start. It is said that Galileo found the oscillations of the chandelier and recorded the movements by his pulse beat.
It moves in a simple harmonic direction for small displacements from the rest position or the mean position. The mean position is the position when the bob doesn’t work and stays rigid at its rest place. The diagrammatic illustration of a simple pendulum is shown below:
The Time Period of a Simple Pendulum
On the top is rigid support to hold the structure of a pendulum. The mass suspended at the end can make the bob have a to-and-fro movement. For the procedure, there are certain assumptions used for the smooth and uninterrupted flow of the pendulum. These assumptions are as follows:
- Between the air and the simple pendulum system, it is assumed that there is no friction.
- The body, line, or arm of the bob is assumed to be straight; it is assumed that it does not bend or crack or compress.
- It is also assumed that the arm is massless.
- Gravity is assumed to be constant.
- The pendulum swings in a smooth manner, it is assumed that there is no restraint to the body.
Derivation
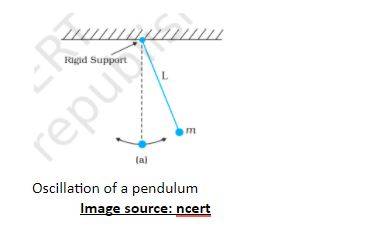
When the bob is its mean position, θ = 0.
When acceleration is provided, it forms:
T –mg cos θ (equation of motion)
Support of the torque provided by an intangible force:
τ = –L (mg sin θ).
Rotational motion of newton:
τ = I α,
where ‘I’ is the inertia and α is the angular acceleration. Thus,
I α = –m g sin θ L.
Weightage in Class 11
The chapter ‘Oscillations’ holds a weightage of 4-5 marks as per the new pattern. It contains 2 short questions, 2 marks each, and one objective type question of 1 mark.
Illustrated Examples
- Illustrate the oscillation of a pendulum or a bob.
Oscillation of a pendulum
Image source: ncert
- Explain the role of gravity throughout the oscillation.
Gravity is assumed to be constant.
- Explain the role of restraint during the oscillation.
The pendulum swings in a smooth manner, it is assumed that there is no restraint to the body.
FAQs
Q: Explain a simple pendulum.
Q: State one assumption about the simple pendulum experiment.
Q: Explain the motion of oscillation of the pendulum.
Q: What’s the value of θ in the mean position?
Q: What’s the equation for motion?
Physics Laws of Physics Concepts Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test