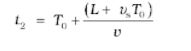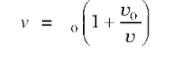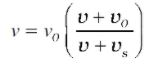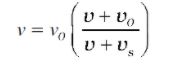- What is Doppler Effect?
- Case 1: Source Moving-Observer Stationary
- Case 2: Observer Moving- Source Stationary
- Case 3: Both Source and Observer Are Moving
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs on Doppler Effect
What is Doppler Effect?
As a general rule, the frequency of a wave goes up when the source is approaching us and goes down when the source travels away from us. This motion-related frequency change is called the Doppler Effect. Doppler effect or Doppler shift describes the changes in the frequency of any sound or electromagnetic wave produced by a moving source concerning an observer. It is a wave phenomenon first proposed by Johann Christian Doppler in 1842.
The changes in frequency are analysed under three conditions.
Case 1: Source Moving-Observer Stationary
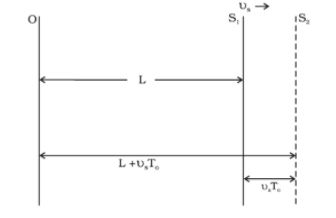
Let us consider a source S moving with a velocity vₛ and an observer O who is stationary and medium at rest. Let the speed of wave of angular frequency ω and period T₀, both measured by an observer at rest for medium v.
Let’s assume the observer has a detector that counts a wave crest when it reaches it.
At the time, t=0, the source at point S₁ located at a distance L from the observer emits a crest. This reaches the observer at time t₁= L/v.
At time t= T₀, the source has moved a distance vₛT₀ at point S₂. Distance from the observer is L+ vₛT₀ and reaches the observer at time t₂.
After an observer detects ‘n’ crests, the period of the wave is given by
The observer measures high frequency when the source approaches him, and it measures lower frequency when the source moves away from him.
Case 2: Observer Moving- Source Stationary
Doppler shift when the observer is moving with velocity and source at rest. The frequency observed is,
If v₀/v is small, the Doppler shift is the same whether the source or observer is moving.
Case 3: Both Source and Observer Are Moving
This is the general expression of the Doppler shift when both the source and observer is moving. The frequency v observed by the observer is given by
Doppler Effect for Class 11
The topic falls under the category of minimum weightage (less than 5 marks). Short answers and problem-based questions are more from this topic.
Illustrated Examples
1. A train moving at 40 m/s on a day when the speed of sound is 350m/z has a horn 170Hz. What is the frequency observed by a stationary person as the train approaches and passes by?
2. What is the frequency when source and observer are moving at an angle?
3. If the observer speed is 60 m/s and source speed is 40 m/s. What is the frequency observed if the observer is moving towards a stationary source if the speed of the sound is 340 m/s and frequency of sound is 1000Hz?
FAQs on Doppler Effect
Q.15.8 A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y(x, t) = 3.0 sin (36 t + 0.018 x + π/4) where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right. (a) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave? If it is travelling, what are the speed and direction of its propagation? (b) What are its amplitude and frequency? (c) What is the initial phase at the origin? (d) What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
A.15.8

Q: What are the applications of the Doppler Effect?
A: It has applications in diverse fields like medical science and astrophysics (measure velocity of stars). It is used in airports to guide aircraft. Sonography is a technique which forms the basis of Doppler shift. It is used to check the over speeding of the vehicles.
Q: What is the Inverse Doppler Effect?
A: It refers to the frequency shifts that are in the opposite direction when compared to conventional Doppler shifts.
Q: What are the Doppler Effects of redshift and blueshift?
A: They describe how the light shifts toward shorter and longer wavelengths.
· RedShift -Longer wavelengths -Object moves away.
· Blueshift - Shorter wavelengths.
Q: How does the Doppler Effect be avoided?
A: To avoid Doppler spread that causes fading, we have to predict the effect and correct the signals accordingly.
Physics Waves Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test