- What is Joint Probability?
- Weightage of Joint Probability
- Illustrated Examples on Joint Probability
- FAQs on Joint Probability
What is Joint Probability?
Probability is one of the most interesting topics taught in Mathematics. Not only is it a high-scoring topic but also consists of a lot of formulas and calculations. Probability is defined as the likelihood of an event occurring. A statistical measure of the chances of two random events occurring together and at the same point of time is known as joint probability.
A joint probability is expressed either as a joint cumulative distribution function or a joint probability density function or even a joint probability mass function at times.
Formula For Calculating Joint Probability
While the formula/notation to express a joint probability situation can take a few different forms, the following formula is used to represent the probability of an events intersection -
P (X⋂Y);
Where X = First event
Y = Second event
And; P(X and Y) and P(XY) = joint probability of both events occurring simultaneously.
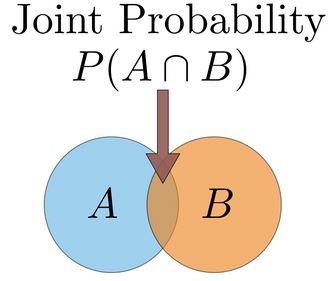
The symbol ‘⋂’ in a joint probability equation is known as an intersection. The probability of an event X and Y happening is the same thing as the point where both intersect, which proves that the joint probability is the intersection of two or more events.
The same phenomenon, for two events, A and B have been represented below using a Venn diagram.
What is a Joint Probability Distribution?
Let X, Y… be the random variables that have been defined in a probability space. The probability distribution which provides the probability that each of X and Y in a discrete series of numbers specified for a given variable is defined as the joint probability distribution of X and Y and in cases where it's expressed for only 2 variables, the phenomena is known as bivariate distribution, while if it is more than 2 variables, you can call it a multivariate distribution.
Joint Probability Table
A joint probability table is used to represent visually and segregate a joint probability distribution and to understand the probability of events A and B occurring together simultaneously.
Weightage of Joint Probability
The ‘Joint probability’ topic is a part of the Mathematics syllabus in class 10th, 11th & 12. In class 11th, the topic is a part of the ‘Probability’ chapter & contributes 10 marks to the question paper. It is imperative that the foundation of this topic is clear to the student so that they can score crucial marks in the paper.
Illustrated Examples on Joint Probability
1. Find the probability that the number “4” will occur twice when 2 dices are rolled simultaneously.
Solution. Number of possible outcomes when dice is rolled = 6
Let X be the event of number 4 occurring on the first die, whereas Y is the event of number 4 occurring on the second die.
X = 1/6
Y = 1/6
P(X,Y) = 1/6x 1/6 = 1/36
2. What is the joint probability of drawing two red cards with the number 9?
Solution. Event ‘C’ - Probability of drawing a 9 = 2/52 = 0.0384
Event ‘D’ - Probability of drawing a card that is red = 26/52 = 0.5
P(C,D) = 0.0384x0.5 = 0.0192 = 1.92
3. Express the probability that in a pack of cards, a card which is drawn is 4 and black.
Solution. Let ‘A’ be the probability that a card is 4
Let ‘B’ be the probability that a card is black.
P(A,B) = ?
A = 4/52 = 0.076
B = 2/52 = 0.038
P(A,B) = 2.9
FAQs on Joint Probability
Q: What is a probability distribution?
Q: What are the different types of probabilities?
- Marginal probability
- Joint probability
- Conditional probability
Q: What does P(AB) mean?
A: In the joint probability formula; P = Joint probability of 2 random variables, whereas A and B are the two random variables/events that are taking place cumulatively.
Q: What do you understand by a discrete random variable?
Q: What is an example of a joint probability distribution?
A: An example of the joint probability distribution is as follows -
Draws from an urn
Rolling of the dice
Maths Probability Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test