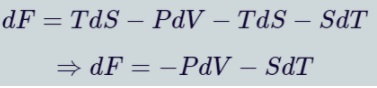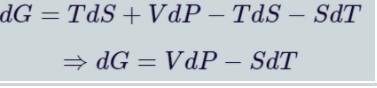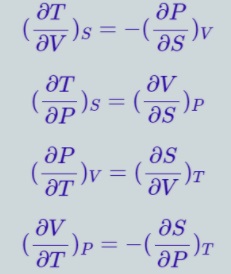- Introduction
- Thermodynamic Potentials
- Internal Energy
- Enthalpy
- Helmholtz Free Energy
- Gibbs Free Energy
- Maxwell Relations
- Derivation of Maxwell’s Relations
- Maxwell Relations For Class 12
- FAQ’s on Maxwell Relations
- Q: What are the Natural variables?
Introduction
In thermodynamics, we will have about 8 thermodynamic variables which could all be related to each by some function. Till now you have been familiar about the laws of thermodynamics, Enthalpy, Entropy, Gibbs free energy and Helmholtz Free Energy. Now, let’s move on to learn Maxwell’s relations of thermodynamic potentials.
Thermodynamic Potentials
A thermodynamic potential is a quantity used to represent the state of a system. We will consider four thermodynamic potentials for generating Maxwell relations
Internal Energy
The internal energy (U) of a system is the energy contained in it due to motion and interaction of particles that exclude the energy outside of the system(due to external forces).
For the Hydrostatic system, the combined first and second law of thermodynamics gives a differential equation. Here, the entropy S and Volume V are the Natural variables.
Enthalpy
Enthalpy(H) is a thermodynamic potential which is equal to the internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and volume. Here, the entropy S and pressure P are the Natural variables. The differential form of enthalpy is given by:
Helmholtz Free Energy
Helmholtz free energy(H) of a system is equal to the internal energy of the system minus the product of its entropy and temperature. Volume V and temperature T are the Natural variables. The differential form of Helmholtz free energy is:
Gibbs Free Energy
Gibbs free energy(G) used to calculate the amount of work a system performs at constant temperature and pressure. The Natural variables are pressure P and temperature T. The differential form of Gibbs free energy is
Maxwell Relations
Maxwell relations connect two derivatives of thermodynamic variables and emerge due to equivalence of potential second derivatives under a change of operation order.
F is thermodynamic potential, and X and Y are two of its natural independent variables. Maxwell Relations named after James Maxwell
Derivation of Maxwell’s Relations
- Here we discuss the mathematical properties of these functions and consequences of the relationship between thermodynamic potentials. It will allow us to connect quantities that are difficult for measurements like the entropy and chemical potential.
- All thermodynamic potentials have multiple independent variables. The derivatives of potentials involve other thermodynamic potentials. So here we get four Maxwell relations after differential functions of thermodynamic potentials of Internal energy, Gibbs Free energy, Helmholtz Free Energy and Enthalpy.
Summary Table
Maxwell Relations For Class 12
FAQ’s on Maxwell Relations
Q: What are the Natural variables?
Physics Thermodynamics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test