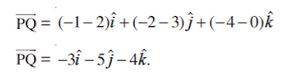- What is Vector Calculus?
- Weightage of Vector Calculus
- Illustrative Examples on Vector Calculus
- FAQs on Vector Calculus
What is Vector Calculus?
A quantity that has magnitude, as well as direction, is called a vector. Point A from where the vector starts is called its initial point, and the point B where it ends is called its terminal point. The distance between the initial and terminal points of a vector is called the magnitude (or length) of the vector. The arrow indicates the direction of the vector.
Addition of Vectors
Let a and b be any two vectors. From the terminal point of a vector, b is drawn. The vector from the initial point O of A to a terminal point B of b is called the sum of vectors a and b. This sum is denoted by a + b. This is called the triangle law of the addition of vectors.
Parallelogram Law
Let a and b be any two vectors. From the initial point of a vector b is drawn and a parallelogram
OACB is completed with OA and OB as adjacent sides. The vector OC is defined as the sum of
a and b. This is called the parallelogram law of the addition of vectors. The sum of two vectors is also called their resultant and the process of addiction as composition.
Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar
Let a be a given vector and λ be a scalar. Then, the product of the vector a by the scalar λ is λ.a. This is called the multiplication of vectors by the scalar.
The Position Vector of a Point
The position vector of a point P concerning a fixed point, say O, is the vector OP. The fixed point is called the origin. Let PQ be any vector, then,
PQ = PO + OQ = — OP + OQ = OQ — OP = Position vector of Q — Position vector of P.
Vector or Cross Product of two Vectors
The vector product of the vectors a and b is denoted by a * b and it is defined as a * b = (|a| |b| sin θ) n = ab sin θ n …..(i). Here, a = |a|, b= |b|, θ is the angle between the vectors a and b. Also, n is a unit vector perpendicular to both a and b, such that a, b and n form a right-handed triad of vectors.
Weightage of Vector Calculus
This section has the highest weightage in Class 12th Mathematics. The Calculus unit carries 35 marks, and the Vectors and 3-D Geometry carries 14 marks.
Illustrative Examples on Vector Calculus
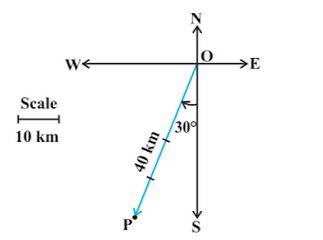
1. Represent graphically a displacement of 40 km, 30° west of south.
Solution.
The vector OP is the required placement.
2. Classify the following measures as scalars and vectors:
(i) 5 seconds (ii) 1000 cm3 (iii) 10 Newton (iv) 30 km/hr (v) 10 g/cm3 (vi) 20 m/s towards north
Solution. (i) Time-scalar (ii) Volume-scalar (iii) Force-vector (iv) Speed-scalar (v) Density-scalar (vi) Velocity-vector
3 Find the vector joining the points P(2, 3, 0) and Q(– 1, – 2, – 4) directed from P to Q.
Solution. Since the vector is to be directed from P to Q, clearly P is the initial point and Q is the terminal point. So, the required vector joining P and Q is the vector PQ, given by
Image source: NCERT
FAQs on Vector Calculus
Q: What is the distributive law for three vectors?
Q: What is a scalar triple product?
Q: What is the reciprocal system of vectors?
Q: Define a linear combination of vectors.
called a linear combination of vectors a, b, c,...
Q: What is the resolution of the components of a vector in a plane?
Maths Vector Algebra Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test