RPSC RAS main exam 2021 was conducted based on the new syllabus. RPSC Syllabus was revised on November 21, 2021. The candidates need to prepare as per the new syllabus because the exam will be conducted based on the new scheme and syllabus as defined by the Commission recently. The RAS syllabus incorporates all the important topics related to the History, Geography, Economy and the Art and Culture of Rajasthan. Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC) conducts the Rajasthan State and Subordinate Services Combined Competitive Examination to recruit the candidates for its highest state civil services- Rajasthan Administrative Services (RAS). Hence this exam is also called the RAS exam.
RAS exam is a three-phase exam and each phase is as important as the other one. The three phases of the RAS exam are as follows
- Prelims (Qualifying exam)
- Main exam (800 marks)
- Interview (100 marks)
The RPSC syllabus for all three phases is different and requires a different strategy to prepare for the exam. Before moving to the syllabus part, the candidates must see the RPSC RAS exam pattern.
- RPSC RAS Main Exam Paper Structure
- RPSC RAS Syllabus- Prelims Exam
- RPSC RAS Syllabus - Main Exam
RPSC RAS Main Exam Paper Structure
Before going into the details of the RPSC syllabus, the candidates must see the exam pattern in detail because the exam pattern is revised by the commission and the RAS main exam will be conducted based on the new exam pattern. The RPSC main exam pattern is defined as:
RAS Main Paper-I
The total marks of the RAS Paper-I is 200. The RAS main paper I will be conducted as per the structure given below:
| Part | No. of Questions | Marks Per Question (Total Marks) | Word Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 25 | 02 (25 x 2=50) | 15 |
| B | 16 | 05(16 x 5=80) | 50 |
| C | 07 | 10(07 x 10=70) | 100 |
| Total Questions = 48 | Total = 200 Marks |
The candidates need to stick to the word limit to complete the full paper.
RAS Main Paper-II
RAS main exam Paper-II will also be of 200 marks but the number of questions is different from paper-I. The candidates can see below the paper-II structure:
| Part | No. of Questions | Marks Per Question (Total Marks) | Word Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | 02 (15 x 2=30) | 15 |
| B | 14 | 05(14 x 5=70) | 50 |
| C | 10 | 10(10 x 10=100) | 100 |
| Total Questions = 39 | Total = 200 Marks |
RAS Main Paper-III
The paper-III has a similar structure as the paper-I. The candidates can see below the paper structure.
| Part | No. of Questions | Marks Per Question (Total Marks) | Word Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 25 | 02 (25 x 2=50) | 15 |
| B | 16 | 05(16 x 5=80) | 50 |
| C | 07 | 10(07 x 10=70) | 100 |
| Total Questions = 48 | Total = 200 Marks |
The total number of questions and their break-up is the same as paper-I.
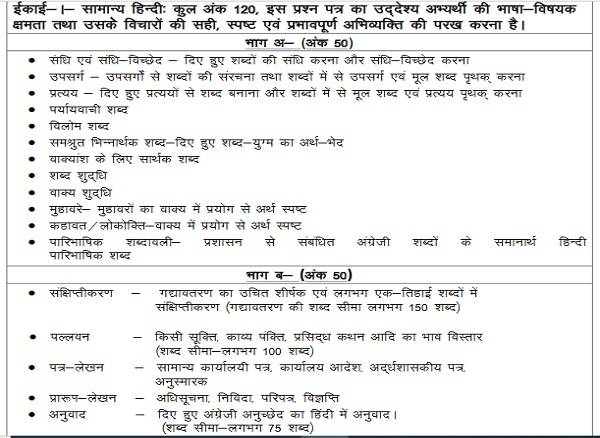
RAS Main Paper-IV
Paper-IV is different among all because there is no word limit for each of the questions. The commission did not specify the word limit for the questions. See below the RAS main paper-IV structure:
| Part | Total Marks |
|---|---|
| A | 70 |
| B | 80 |
| C | 50 |
| Total Marks | 200 |
The marks are the same but there is no count of questions, word limit or anything specified for this paper.
RPSC RAS Syllabus- Prelims Exam
RPSC syllabus for the prelims exam is a mixture of all the important topics from the general studies syllabus in general. The candidates need to focus on the topics related to Rajasthan as there are several questions related to the state-level issues.
See here: RPSC RAS question papers
RPSC Syllabus is unique in the sense that there is only one paper in the RAS prelims exam and the candidates need to focus on one paper only. The RPSC syllabus for the RAS prelims exam is divided into various sections. The details are as follows
History, Art, Culture, Literature, Tradition & Heritage of Rajasthan
- Pre-historical sites of Rajasthan- from Palaeolithic to Chalcolithic and Bronze Age.
- Historical Rajasthan: Important historical centres of Early Christian Era. Society, Religion and Culture in Ancient Rajasthan.
- Political and Cultural achievements of prominent rulers of major dynasties - Guhila, Pratihar, Chauhan, Parmar, Rathore, Sisodiya and Kachchawa. Administrative and Revenue
System in Medieval Rajasthan. - Emergence of Modern Rajasthan: Agents of Social Awakening in Rajasthan. Political Awakening: role of newspapers and political institutions. Tribal
and Peasant movements, Praja Mandal movements in various princely states. Integration of Rajasthan. - Architectural Tradition of Rajasthan- temples, forts, palaces and man-made water bodies; Various schools of paintings and handicrafts.
- Performing Art: Classical Music and Classical Dance; Folk Music & Instruments; Folk Dances & Drama.
- Language & Literature: Dialects of Rajasthani Language. Literature of Rajasthani language and Folk literature.
- Religious Life: Religious Communities, Saints and Sects in Rajasthan. Folk Deities of Rajasthan.
- Social Life in Rajasthan: Fairs and festivals; Social customs and traditions; attires and ornaments.
- Leading Personalities of Rajasthan
Indian History
Ancient & Medieval Period:
- Cultural Foundations of India - Indus and Vedic Age; Renunciatory tradition and new religious ideas of Sixth Century BC- Ajivakas, Buddhism and Jainism.
- Achievements of prominent rulers of major dynasties: Maurya, Kushan, Satavahan, Gupta, Chalukya, Pallava and Chola.
- Art and Architecture in Ancient India.
- Development of Language and Literature in Ancient India: Sanskrit, Prakrit and Tamil.
- Sultanate Period: Achievements of prominent Sultanate Rulers. Cultural achievements of Vijaynagar.
- Mughal Period: Political challenges and reconciliation- Afghan, Rajput, Deccan States & Maratha.
- Development of Art & Architecture, Paintings and Music during the medieval period.
- Religious & Literary contribution of Bhakti & Sufi movement.
Modern Period (from early 19th century to 1964):
- Evolution of Modern India & Emergence of Nationalism: Intellectual awakening; Press; Western education. Socio-religious reforms: various leaders and
institutions. - The Freedom Struggle & Indian National Movement- its various stages, streams and important contributors, contributions from different parts of the country.
- Post-independence Nation Building: The linguistic reorganisation of the states, Institutional building during Nehruvian age, Development of science and technology.
Geography of World and India
World Geography:
- Major Landforms-Mountains, Plateaus, Plains & Deserts
- Major Rivers & Lakes
- Types of Agriculture
- Major Industrial Regions.
- Environmental Issues- Desertification, Deforestation, Climate Change & Global Warming,
- Ozone Layer Depletion
Geography of India:
- Major Landforms- Mountains, Plateaus, Plains
- Mechanism of Monsoon & Rainfall distribution
- Major Rivers & Lakes
- Major Crops- Wheat, Rice, Cotton, Sugarcane, Tea & Coffee
- Major Minerals- Iron ore, Manganese, Bauxite, Mica
- Power Resources- Conventional & Non-Conventional
- Major Industrial Regions.
- National Highways & Major Transport Corridors
Geography of Rajasthan
- Major physiographic regions and their characteristics
- Climatic characteristics
- Major Rivers & Lakes
- Natural Vegetation & Soil
- Major Crops- Wheat, Maize, Barley, Cotton, Sugarcane & Bajra
- Major Industries.
- Major Irrigation Projects & Water Conservation Techniques
- Population-Growth, Density, Literacy, Sex-ratio & Major Tribes
- Minerals- Metallic & Non-Metallic
- Power Resources- Conventional & Non-Conventional
- Biodiversity & its Conservation
- Tourist Centres & Circuits
Indian Constitution, Political System & Governance
- Indian Constitution: Philosophical Postulates:
- Constituent Assembly, Salient features of Indian Constitution, Constitutional Amendments.
- Preamble, Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy, Fundamental Duties.
Indian Political System:
- President, Prime Minister and Council of Ministers, Parliament, Supreme Court & Judicial Review.
- Election Commission of India, Comptroller and Auditor General, NITI Aayog, Central Vigilance Commission, Lokpal, Central Information Commission, National Human Rights
Commission. - Federalism, Democratic Politics in India, Coalition Governments, National Integration.
Political and Administrative System of Rajasthan
State Political System:
- Governor, Chief Minister and Council of Ministers, Legislative Assembly, High Court.
Administrative System:
- District Administration, Local Self Government, Panchayati Raj Institutions.
Institutions:
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission, State Human Rights Commission, Lokayukt, State
- Election Commission, State Information Commission.
Public Policy & Rights:
- Public Policy, Legal Rights and Citizen’s Charter.
Economic Concepts and Indian Economy
- Basic Concepts of Economics
- Basic Knowledge of Budgeting, Banking, Public Finance, Goods and Service Tax, National
- Income, Growth and Development
- Accounting- Concept, Tools and Uses in Administration
- Stock Exchange and Share Market
- Fiscal and Monetary Policies
- Subsidies, Public Distribution System
- e-Commerce
- Inflation- Concept, Impact and Control Mechanism
Economic Development & Planning
- Major Sectors of Economy: - Current Status, Issues & Initiatives of Agriculture, Industry, Service and Trade sectors
- Major Economic Problems and Government Initiatives. Economic Reforms and Liberalization
Human Resource and Economic Development
- Human Development Index
- Happiness Index
- Poverty and Unemployment: - Concept, Types, Causes, Remedies and Current Flagship
Schemes.
Social Justice and Empowerment
- Provisions for Weaker Sections.
Economy of Rajasthan
- Macro overview of Economy.
- Major Agricultural, Industrial and Service Sector Issues.
- Growth, Development and Planning.
- Infrastructure & Resources.
- Major Development Projects.
- Major Welfare Schemes of State Government for SC/ST/Backward Classes/ Minorities/Disabled Persons, Destitute, Women, Children, Old Age People, Farmers & Labourers.
Science & Technology
- Basics of Everyday Science.
- Computers, Information and Communication Technology.
- Defence Technology, Space Technology and Satellites.
- Nanotechnology, Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering.
- Food and Nutrition, Blood Groups and Rh Factor.
- Health care; Infectious, Non-Infectious and Zoonotic diseases.
- Environmental and Ecological Changes and their Impact.
- Biodiversity, Conservation of Natural Resources and Sustainable Development.
- Agriculture, Horticulture, Forestry and Animal Husbandry with special reference to Rajasthan.
- Development of Science and Technology with special reference to Rajasthan.
Reasoning & Mental Ability
Logical Reasoning (Deductive, Inductive, Abductive):
- Statement and Assumptions
- Statement and Argument
- Statements and Conclusion
- Statement and Courses of Action
- Analytical Reasoning
Mental Ability:
- Number /Letter sequences
- Coding/Decoding
- Problems related to Relations
- Direction sense test
- Logical Venn diagram
- Mirror / Water images
- Shapes and their sub sections
Basic Numeracy:
- Ratio, Proportion and Partnership
- Percentage
- Simple and Compound Interest
- Perimeter and Area of Plane figures
- Data Analysis (Tables, Bar diagram, Line graph, Pie-chart)
- Mean(Arithmetic, Geometric and Harmonic), Median and Mode
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability (Simple Problems)
Current Affairs
- Major Current Events and Issues of Rajasthan, India and International Importance.
- Persons, Places and Institutions in News.
- Games and Sports related activities
RPSC RAS Syllabus - Main Exam
RPSC RAS Main exam has four papers, each of 200 marks. The Commission has given syllabus of all the papers separately.
RAS Main Paper-I (General Knowledge and General Studies)
The RAS main paper-I has three units. The unit-wise syllabus of paper-I is given below:
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-I Part-A (History, Art, Culture, Literature, Tradition and Heritage of Rajasthan)
- Major landmarks in the History of Rajasthan from Pre-historic time to close of 18th century, Important dynasties, their administrative and revenue system.
- Peasant & Tribal Movements. Political Awakening, Freedom Movement and Integration.
- Heritage of Rajasthan: Performing & fine Art, Handicraft, Architecture and major sites of World Heritage and Tourism in Rajasthan, Fairs, Festivals, Folk Music and Folk Dance.
- Important works of Rajasthani Literature and Dialects of Rajasthan.
- Saints, Lok Devtas and eminent personalities of Rajasthan.
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-I Part-B (Indian History & Culture)
- Indian heritage: Fine Art, Performing Art, Architecture & Literature from Indus Civilization to British Era.
- Religious Movements and religious philosophy in Ancient and Medieval India.
- History of Modern India from beginning of 19th Century to 1965 A.D: Significant events, personalities and issues.
- Indian National Movement- its various stages & streams, important contributors and contribution from different parts of the country.
- Socio-religious reform movements in 19th and 20th century.
- Post Independence consolidation and reorganisation – Accession of princely states & Linguistic reorganisation of the states.
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-I Part-C (History of Modern World up to 1950A.D)
- Renaissance and Reformation.
- American War of Independence, French Revolution (1789 A.D.) and Industrial Revolution.
- Imperialism and colonialism in Asia and Africa.
- Impact of World Wars.
RAS Paper-I Unit II Economy
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-II Part-A (Indian Economy)
- Agriculture – growth and productivity trends in Indian agriculture. Food processing sector and food management. Agricultural reforms and challenges.
- Trends in Industrial Sector- Industrial Policy and Industrial Finance. Liberalization, Globalization, Privatization and economic reforms.Infrastructure and economic growth. Inflation, Prices and demand/supply management.
- Centre-State financial relations and Latest Finance Commission. Fiscal Responsibility & Budget Management Act and fiscal reforms in India.
- Budgetary trends and fiscal policy. Tax reforms in India. Subsidies- cash transfer and other related issues. Trends in revenue and expenditure.
- Role of Government in economic activities. Private, Public and Merit Goods.
- Social Sector- poverty, unemployment and inequality. Healthcare and Education Policy. Problem of regulatory effectiveness. Redefining the role of state in economic development and an employment-oriented growth strategy.
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-II Part-B (World Economy)
- Global Economic issues and trends: Role of World Bank, IMF & WTO.
- Sustainable Development and Climate Change.
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-II Part-C (Economy of Rajasthan)
- Agriculture Scenario- production and productivity. Water resources and Irrigation. Agricultural marketing. Dairy and animal husbandry.
- Rural development and rural infrastructure. Panchayati Raj and State Finance Commission.
Institutional framework for industrial development. Industrial growth and recent trends. Khadi and village industries. - Infrastructure development- power and transportation. Private Investment in
- Infrastructure and Public-Private Partnership projects- outlook and prospects.
- Major development projects of Rajasthan. State budget and Fiscal management issues and challenges.
- Economic welfare schemes of Rajasthan. Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Basic Social Services- education and health. Poverty, unemployment and Sustainable Development goals.
RAS Paper-I Unit III- Sociology, Management, Accounting & Auditing
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-III Part A- Sociology
Development of Sociological Thought in India-
- Caste and Class in Indian Society: Nature, Origin, Functions and Challenges.
- Processes of Change: Sanskritization, Westernization, Secularization and Globalization.
- Challenges before Indian Society: Issues of Dowry, Divorce and Child Marriage, Corruption, Communalism, Poverty, Unemployment, Drug Addiction, Vulnerable sections especially Dalit, Elderly and Disabled.
- Tribal community of Rajasthan: Bhil, Mina (Meena) and Garasia- Problems and Welfare.
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-III Part B- Management
- Modern concept of Marketing, Marketing Mix - Product, Price, Place and Promotion; Supply Chain Management, Logistics Mix; E-Commerce and E-Marketing; Business and Corporate Ethics.
- Wealth Maximization, Sources of Finance- Short and Long Term, Capital Structure, Cost of Capital, Distribution of Profit; Banking and Non-Banking
- Financial Institutions (NBFIs), Stock Market, Multi-National Companies (MNCs), Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), Foreign Institutional Investment (FII).
- Leadership Theories and Styles, Group Behaviour, Individual Behaviour, Attitude, Values, Team Building; Motivation Theories, Conflict Management, Time Management, Stress Management, Training, Development and Appraisal Systems.
- Entrepreneurship: Incubation, Startups, Unicorns, Venture Capital, Angel Investors.
- Management of Essential Services: Education Management, Healthcare and Wellness Management; Tourism and Hospitality Management.
RAS Main Paper-I Unit-III Part C- Accounting & Auditing
- Basic knowledge of Double Entry System of Accounting, Techniques of analysis of Financial Statements, Responsibility and Social Accounting.
- Meaning & Objectives of Auditing, Social, Performance and Efficiency Audit, Elementary knowledge of Government Audit.
- Basic knowledge of Performance Budgeting, Zero-Base Budgeting
RAS Main Paper-II
RAS main paper-II is concerned with administrative and governance issues.
RAS Main Paper-II Unit I- Administrative Ethics
- Ethics and Human Values: Lessons from lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators. Role of family, society and educational institutions in inculcating values.
- Ethical concepts- Rit and Rin, concept of Duty, concept of Good and Virtue.
- Ethics in private and public relationships- Behaviour, Moral and Political attitudes of administrators, Philosophical basis of Integrity.
- Ethics of Bhagavad Geeta and its role in administration.
- Gandhian Ethics.
- Contribution of Moral Thinkers and Philosophers from India & World.
- Ethical concerns, dilemmas and challenges in administration.
- Ethical decision-making and contributing factors; social justice, humanitarian concerns, accountability in governance and code of ethics.
- Case Studies on above mentioned topics.
RAS Main Paper-II Unit II- General Science & Technology
- Chemistry in everyday life; States of Matter; Atomic Structure; Metal, Non-Metal and Metalloids, Metallurgical Principles and methods, Important ores and alloys; Acid, Base and Salts, concept of pH and Buffers; Important Drugs (Synthetic and Natural), Antioxidants, Preservatives, Insecticides, Pesticides, Fungicides, Herbicides, Fertilizers, Binders and Sweeteners; Carbon, its compounds and their domestic and industrial applications; Radioactivity-concepts and applications.
- Physics in everyday life; Gravitation; Human eye and Defects; Heat; Static and Current Electricity; Magnetism, Electro-Magnetism, Sound and Electro-Magnetic Waves, Magnetic Resonance imaging and Nuclear magnetic resonance; Nuclear fission and Fusion.
- The Cell; Control and Coordination, Reproductive, Excretory, Respiratory, Circulatory and Digestive systems in Human being; Blood groups, Composition and Functions of blood; Hormones; Genetics and Lifestyle Diseases; Human diseases- Communicable and Non-communicable, Endemic, Epidemic, Pandemic their Diagnosis and Control, Immunization and Vaccination; Drugs and Alcohol abuse. Plant parts and their functions, Plant nutrition, Plant growth regulators, Sexual and asexual reproduction in plants, Important medicinal plants with special reference to Rajasthan; Organic farming; Biotechnology and its applications.
- Basic computer science; Networking and types; Analogue and digital telecommunication; Frequency spectrum; Mobile telephony, Recent developments in information and communication technology- Artificial intelligence; Big data, Cloud computing, Internet of things, Crypto currency, OTT platforms and Social media and their impacts; IT industry in India, Digital India initiatives.
- Contribution of Indian Scientists in Science and Technology, Scientific and technological advancements- Robotics, Machine learning, Augmented reality, Nanotechnology, RFID, Quantum computing etc, Development of science and technology in Rajasthan, Government policies related to Science and Technology.
- Space technology- Indian space programme, Satellites and their orbits, various launch vehicles; Remote sensing.
- Defence technology- Missiles, Indian missile programme, Chemical and Biological weapons.
RAS Main Paper-II Unit III- Earth Science (Geography & Geology)
Part A - World
- Structure of the Earth and Geological Time Scale.
- Broad Physical Features: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains, Deserts.
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Types, distribution and their impact.
- Major Geopolitical Issues.
- Major Environmental Issues.
Part B - India
- Broad Physical Features: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains, Deserts.
- Major Physiographic Divisions of India.
- Major Rivers.
- Climate- Origin of Monsoon, Climatic characteristics, Distribution of rainfall and Climatic regions.
- Natural Resources: Types and uses of (a) Water, Forest, Soil (b) Rocks & Minerals.
- Population: Growth, Distribution and Density, Sex-ratio, Literacy, Urban and Rural Population.
Part C - Rajasthan
- Broad Physical Features: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains, Deserts.
- Major Rivers and Lakes.
- Climatic: Characteristics and their classification.
- Major Vegetation types.
- Agriculture- Major Crops: Production and Distribution.
- Metallic Minerals and Non- Metallic Minerals- Types, distribution and industrial uses.
- Conventional and Non-conventional Energy Resources.
- Demographic characteristics and Major Tribes.
- Wildlife and Biodiversity: Threats and Conversation.
- Concept of UNESCO Geo-parks and Geo-heritage sites: Potential in Rajasthan.
- Major Environmental Issues.
RAS Main Paper-III
RPSC RAS main paper-III is related to the Political System that governs the formation and working of the government.
RAS Main Paper-III Unit I- Indian Political System, World Politics and Current Affairs
- Constitution of India: Framing, Features, Amendments, Basic Structure.
- Ideological Contents: Preamble, Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy, Fundamental Duties.
- Institutional Framework- I: Parliamentary System, President, Prime Minister and Council of Ministers, Parliament.
- Institutional Framework- II: Federalism, Centre-State relations, Supreme Court, High Courts, Judicial Review, Judicial Activism.
- Institutional Framework- III: Election Commission of India, Comptroller and Auditor General, Union Public Service Commission, NITI Aayog, Central Vigilance Commission, Central Information Commission, National Human Rights Commission.
- Political Dynamics: Role of Caste, Religion, Class, Ethnicity, Language and Gender in Indian Politics, Political Parties and Electoral Behaviour, Civil Society and Political Movement, Issues related to National Integrity and Security, Potential areas of Socio-Political conflicts.
- State Politics of Rajasthan: Party System, Political Demography, Different phases of Political competition in Rajasthan, Panchayati Raj and Urban self Government Institutions.
- Emerging World Order in the post-Cold War era, USA’s hegemony and its resistance, UN and Regional Organizations, Dynamics of International Economy, International Terrorism and Environmental issues.
- Foreign Policy of India: Evolution, Determinants, India’s relations with USA, China, Russia, European Union and Neighbouring Countries, India’s role in UN, NAM, BRICS, G- 20, G- 77 and SAARC.
- Geo-political and Strategic issues in South Asia, South East Asia, West Asia and Far- East and their impact on India.
- Current Affairs: Current events, persons and places of Rajasthan, National and international importance, recent activities related to games and sports.
Get prep tips, practice papers, exam details and important updates
RPSC RAS Exam

 Exam On - 2 Feb '25
Exam On - 2 Feb '25