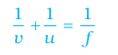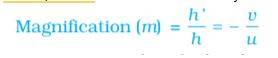Introduction
When a mirror reflects light, it forms an image. A plane mirror has a flat spherical surface whereas mirrors whose reflecting surfaces are spherical are called spherical mirrors. The best example for the spherical mirror is a spoon. A spoon has two curved surfaces, one is concave and other is convex.
- Spherical Mirror
- Terminologies of Spherical mirrors
- Spherical Mirrors for Class 10
- Illustrative Examples
- FAQs
Spherical Mirror
A spherical mirror is a curved mirror. It is formed with the help of a part of a hollow glass sphere having a reflecting surface. The reflecting surface may be curved inwards or outwards.
They are two types of spherical mirrors.
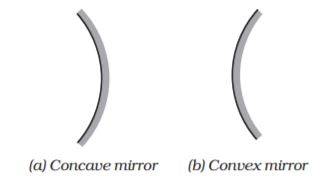
- Concave mirror
A spherical mirror, with a reflecting surface curved inwards, facing towards the centre of the sphere, is called a concave mirror.
- Convex mirror
A spherical mirror with a reflecting surface curved outwards is called a convex mirror.
Terminologies of Spherical mirrors
Pole
The centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is the pole, P.
Centre of curvature
The reflecting surface of the mirror forms part of a sphere. The centre point of the sphere is called the centre of curvature, C. For convex, lies outside the reflecting surface. For a concave mirror, it lies in front of it.
Radius of curvature
- The distance from the vertex to the centre of the curvature is called the radius of curvature of the mirror.
- The relation between radius and focal length is R= 2f.
- The diameter of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is called its aperture.
Principal Axis
The principal axis is the line joining the centre of curvature to the middle of the mirror.
Focus
A focus point, F is the point at which the rays falling on the mirror and the reflected rays from the mirror intersect.
Spherical Mirrors for Class 10
The topic is all about types of spherical mirrors and its uses. The terminologies that describe the spherical mirrors and about the image formation by spherical mirrors. The weightage of this topic is 10 marks from this chapter. Both short and long answer type questions on spherical mirrors, mirror formula and magnification, image formation by mirrors or lenses.
Illustrative Examples
- An object is placed 30cm in front of a concave mirror. A real image of the object is formed 50cm from the mirror. Calculate the focal length?
1/f = 1/50+1/30 =70/120
f= 1.71 cm
- A convex rear view mirror of a car has a radius of curvature of 3.00 m. Find the position of the image if a truck is standing at 5.00 m from it?
R= 2f
f =R/2 = 3/2=1.5m
U = -5m
1/v =1/f-1/u =1/1.5-1/-5
V =1.15m
The image is 1.15 m at the back of the mirror.
- A concave mirror produces three times bigger real images of an object located at 10 cm in front of it. Where do you think the image is located?
M =-v/u
V =-mu =-30cm in front of the mirror.
FAQs
Q: A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm.Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
A: Height of the needle, ℎ1 = 4.5 cm
Object distance, u = - 12 cm
Focal length of the convex mirror, f = 15 cm
Image distance = v
The value of v can be obtained using the mirror formula
1/u + 1/v = 1/ff or 1/v = 1/ff - 1/u = 1/15 - 1/-12 = 1/15 + 1/12 = 9/60
v = 60/9 = 6.7 cm
Hence, the image of the needle is 6.7 cm away from the mirror. Also it is on the other side of the mirror.
The image size (ℎ2) is given as
m = h2/h1= − ?/u = − 6.7/12 = 6.7/12
= 6.7/12 X 4.5 = 2.5 cm
Hence m = 2.5/4.5= 0.56
The height of the image is 2.5 cm. The positive sign indicates that the image is erect, virtual and diminished. If the needle is moved farther from the mirror, the image will also move away from the mirror and the size of the image will reduce gradually.
Q: What is Mirror Formula?
A: The distance between the object and the pole is the object distance (u). The distance between the image and the mirror's pole is called the image distance (v). The distance between the pole and the principal focus is called focal length, f.
Q: What is Magnification?
A: It is expressed as the ratio of the object distance to the image distance.
Q: What are the uses of concave mirrors?
A: Concave mirrors are commonly used in torches, satellite dishes, search-lights, shaving mirrors and vehicle headlights to get powerful parallel beams of light.
Q: What are the uses of convex mirrors?
A: They are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles. These mirrors are preferred because they give an erect, though diminished, image.
Q: What are examples of real and virtual images?
A: The virtual image reflects the mirror, and the real image is the image we see on the cinema screen.
Physics Optics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test