Rachit Kumar SaxenaManager-Editorial
What is Union of Sets?
The union of two sets, say set A & B is equal to the elements present in both the sets, and union of sets is the operation that focuses on collecting together the elements of both into a singular, third set. It should not be confused with a universal set, which is a set in itself. It is represented as -
A ∪ B = {x:x ∈ A or a ∈ B}
A part of set theory, the union of two given sets, is defined as the smallest set containing all values of both sets. It is among the top 3 basic operations that can be performed on a set, alongside intersection and difference sets.
Similar to Mathematics, where people tend to perform the basic operations such as multiplication, division, subtraction, and addition, as part of the set theory, some basic operations are performed on two sets of values to give a common set of elements depending upon the operation performed. It is important to note that all elements are included in the set when it comes to the union.
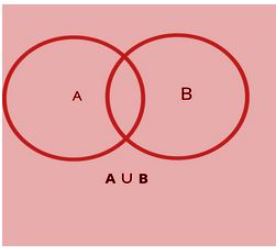
Venn Diagram: Representing Union of Sets
In order to represent the union of sets, you can use a Venn diagram. Let us consider that for a universal set X. We have two sets, A and B, which are subsets of the universal set X, whose union would be a combination of all the elements in the set A and B altogether, represented by the symbol ∪.
Illustrated Examples of Union of Sets
1. A = {4,3,5} & B = {6,8,7}; represent union of sets using a venn diagram.
Solution. A∪B = {3,4,5, 6,7,8}
2. When P = {3, 5, 8} & Q = {4, 9, 2}, find P∪Q.
Solution. P∪Q = {3,5,8,4,9,2}
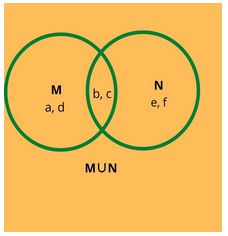
3. When M = {a, d, e} & N = {b, c,f}, represent M ∪ N, using a venn diagram.
Solution. M∪ N = {a,d,e, b,c,f}
FAQs on Union of Sets
Q: What are sets?
Q: What is the cardinal number of a set?
Q: What is a Venn diagram?
Q: What is the complement of a set?
Q: What is the intersection of sets?
News & Updates
Maths Sets Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test