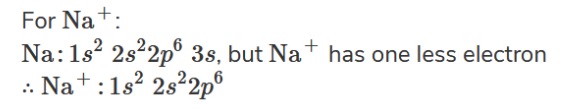Matter is made of particles and how these particles react depends on their properties, so understanding the difference between atoms and ions is important to understand how reactions occur. In Class X and XI, this topic can have a weightage of 10 marks.
- What are Atoms and Ions?
- Differences between Atoms and Ions
- For Class 10 Ions form ionic compounds when elements react through their tendency to form complete valence shells.
- For Class 11
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs on Difference between Atom and Ion
What are Atoms and Ions?
An atom is defined as the smallest unit of matter which forms an element. Earlier thought to be indivisible, later experiments proved that atoms can in fact be broken down further into subatomic particles - the proton, neutron, and electrons.
All atoms have the same number of electrons and protons and are therefore electrically neutral.
When an atom loses or gains electrons, they become charged. Such charged particles are called ions. They can be positively charged if electrons are lost and these are called cations, or negatively charged if electrons are gained, called anions.
Differences between Atoms and Ions
| Atom |
Ion |
|---|---|
| Basic unit of an element. |
An atom or molecule with a charge. |
| Have equal number of protons and electrons |
Have an unequal number of protons and electrons. |
| Have a neutral charge |
Can be positively or negatively charged |
| They are unstable due to incomplete valence shells and are highly reactive when independent. Exception: noble gases |
They have a complete valence shell and can exist independently with high stability. |
| Can form covalent or ionic bonds |
Can only form ionic bonds |
| Atoms form molecules |
Ions can be polyatomic or monoatomic. They can also form lattice networks |
| Not attracted to electrical field |
Can be attracted to an electrical field depending on the charge of the ion |
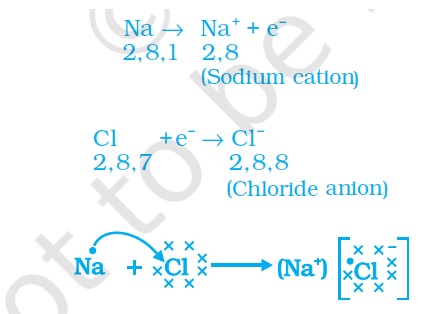
For Class 10 Ions form ionic compounds when elements react through their tendency to form complete valence shells.
For eg.
Here the electron in the outer valence shell of sodium is lost to give a positively charged Sodium cation.
Chlorine gains an electron to form chloride anion.
The two ions form an ionic bond to give a stable Sodium Chloride molecule.
Such ionic compounds are aggregates of ions. They are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
For Class 11
The first atomic theory was provided by John Dalton and proposed that the atom was indivisible. Later experiments proved that atoms were in fact made up of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Many models of the atom were proposed, until settled upon by the quantum mechanical model of the atom. According to this, the electrons in the atom are said to be arranged in shells which are further divided into subshells and orbitals. The electrons in the completely filled shells are known as core electrons, and the electrons that are added to the electronic shell with the highest principal quantum number are called valence electrons.
Here is how the configuration of the sodium ion will look like when it loses its outer electron.
Illustrated Examples
1. Show the formation of magnesium chloride with the help of electron dot structures. What are the ions present in it?
Answer:
FAQs on Difference between Atom and Ion
Q: Can all atoms be ions?
Q: What determines the charge of a monoatomic ion?
Q: Is an ion different than their parent atom?
Q: Is there a difference between covalent compounds and ionic compounds?
Q: Can a polyatomic ion have different kinds of bonds?
Chemistry Structure of Atom Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test