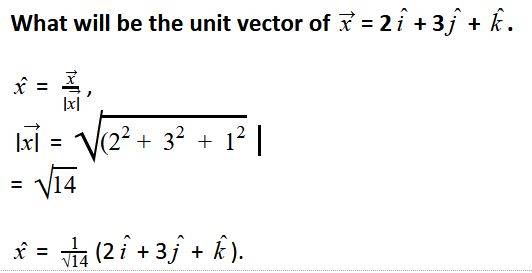- What are the types of Vector?
- Weightage of Topic
- Illustrative Examples on Types of Vectors
- FAQs on Types of Vector
What are the types of Vector?
In mathematics, a quantity that has both direction and magnitude is a vector. Vector has its importance in each field like in determining position, the direction of an object, etc.
There are in total, ten types of vectors present. They are defined below:
1. Unit Vector: A vector is a unit vector if its magnitude is 1. It is written with the ‘^’ "hat" symbol.
2. Like and Unlike Vectors: When the vectors' directions are opposite with respect to each other, they are known as Unlike Vectors. When their directions are the same, they are known as Like Vectors.
3.Equal Vector: An equal vector has the same direction and magnitudes.
4. Negative Vector: When the magnitude of the two vectors are equal, but their directions are opposite, then they are negative vectors of each other.
5. Zero Vector: A vector whose magnitude and components are zero is a Zero Vector. It is represented by 0 or with (→) on 0.
6. Position Vector: Position vector denotes a point's position or location in the three-dimensional Cartesian system with respect to a reference origin. It is represented by ( rˆ ).
7. Co-initial Vector: Suppose we have two vectors and both have the same starting point then they will be termed as Co-initial Vectors.
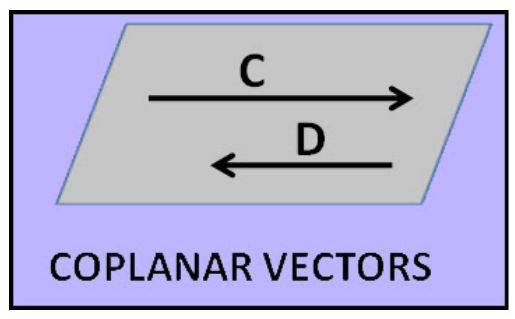
8. Co-planar Vector: When three vectors or more than that lie in the same plane or parallel to the same plane, they are termed co-planar vectors.
9. Collinear Vector: When the vectors lie on parallel lines or the same line, they are called collinear vectors.
10. Displacement Vector: A displacement vector represents the shortest distance when a point is shifted from one place to another.
Weightage of Topic
Types of Vectors is present in class XII mathematics chapter Vector Algebra. The chapter's applications also have its importance in other subjects like physics. In class XII mathematics exams the weightage of vector algebra along with three-dimensional geometry ranges from 12 to 14 marks.
The chapter of Vector Algebra also includes topics such as:
- Operations of Vectors(Addition, Subtraction)
- A Scalar multiplication with a Vector
- 2 Vectors' Product
Illustrative Examples on Types of Vectors
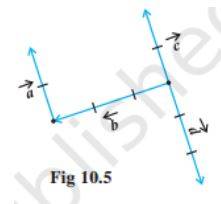
1. From the given figure, identify which vectors are Collinear, Coinitial, and Equal Vectors.
Solution.
2. If the given vectors are equal vectors then evaluate the values of a, b, and c.
Solution.
If the 2 given vectors are equal then
a = 2,
b = 2,
and c = 1.
3.
FAQs on Types of Vector
Q: If a vector's magnitude is zero, then what will be its direction?
Q: What is the other name of Collinear Vectors?
Q: Which among the two is a scalar quantity and which one is a vector quantity?
Distance
Speed
Density
Velocity
Q: What is the formula to find the unit vector of x?
Q: Mention one real-life use of Vectors?
Maths Vector Algebra Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test