- Whats are Population and Sample?
- Weightage of Population and Sample in Class 11
- Illustrated examples on Population and Sample
- FAQs on Population and Sample
Whats are Population and Sample?
Statistics, in the simplest form, can be defined as a way to study data. It starts with a collection of data that is analysed, interpreted, organised, and then presented in a specific form. Population and sample are amongst the most important elements of statistics that have been simplified for a better understanding and application.
Population
It is a collection of all the data that is directly related to the area of study. The data set is inclusive of some measurable characteristics that are called parameters. Parameters are mean and variance deviation. The simplest example: all people living within a region will be considered its population. The population is further classified into the following:
Finite population: An easily countable group of individuals is a finite population.
Infinite population: A larger group of individuals that can’t be counted or is uncountable is referred to as an infinite population.
Existent population: Concrete individuals or objects are collectively called an existent population; for example, books, coins, students, etc.
Hypothetical population: As the term suggests, it is a larger group that is nearly impossible to count.
Sample
It is a set of smaller groups that are selected from the larger set for analysis. In statistics, there can be one or more sample groups to analyse. The process of observing and withdrawing measurable results from the sample is referred to as statistics. A sample involves:
Probability sampling
Here the researcher chooses the sample group out of the larger group to study. The selection process is based on the below-mentioned techniques:
- Simple random sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Disproportionate sampling
- Proportionate sampling
- Optimum allocation stratified sampling
- Multi-stage sampling
Non-probability sampling
Here all the members of the population do not have an equal chance to be in a sample. The selection techniques used are:
- Quota sampling
- Judgment sampling
- Purposive sampling
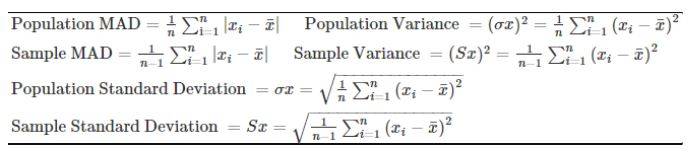
Population and Sample Formulas
Weightage of Population and Sample in Class 11
It is an integral part of the maths syllabus of Class 11 and for various engineering exams such as JEE. You may have explored the idea of chance in earlier classes to measure the uncertainty of different phenomena. It has a weightage of almost 15% of the final exams’ marks.
Illustrated examples on Population and Sample
1 What does 0.05 mean in statistics?
Solution.
P > 0.05 is the probability that the null hypothesis is true. 1 minus the P-value is the probability that the alternative hypothesis is true. A statistically significant test result (P ≤ 0.05) means that the test hypothesis is false or should be rejected.
2.What does the P-value of 1 mean?
Solution.
When the data is perfectly described by the restricted model, the probability to get data that is less well described is 1. For instance, if the sample means in two groups are identical, the p-values of a t-test are 1.
3. What is the p-value for a 95 confidence interval?
Solution.
A quick way to remember the relationship between the 95% confidence interval and p-value of 0.05 is to consider the confidence interval as arms that ‘embrace’ values that are consistent with the data.
FAQs on Population and Sample
Q: What are the examples of population and sample?
Sample: Specific groups of people such as short males in China, the non-vegetarian population in Delhi, etc.
Q: What are the factors contributing to sample size collection?
Size of the population
Standard deviation
Q: What factors influence the sample size?
The total size of the population
Margin of error
Confidentiality level
Standard deviation
Q: Why is it easier to use a sample than to use a population?
Q: Define the sampling population.
Maths Statistics Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Relative Frequency
- Difference between Average and Mean
- Difference between Mean and Median
- Difference between Parametric and Non Parametric T
- Grouping data
- Statistics pdf
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Population and Sample
- Data Collection Methods
- Standard Deviation
- Correlation
- Bar Graph
- Chi Square Test
- Measures of Central Tendency
- Variance
Other Class 11th Maths Chapters
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test