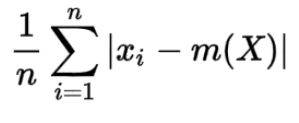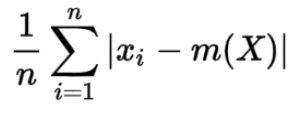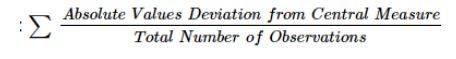- What is Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD)?
- Weightage of Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) in Class 11
- Illustrative Example on Mean Absolute Deviation
- FAQs on Mean Absolute Deviation
What is Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD)?
The definition of MAD is the process of finding it, which makes it super simple to remember.
Mean = Average of the observation
Deviation = Departure/variation from preset standard
Collectively, it is the distance between the calculated mean and each data point.
Simple Steps to Find MAD
STEP 1- Find the mean of the data.
Mean = Sum of the elements of the data set
------------------------------------------------
number of elements in the data set
STEP 2- Calculate how far each element is from the mean. Here, the absolute value used as the distance needs to always be a positive number.
MAD = Total the difference
-------------------------
Number of elements in the data set
What Does MAD Tell You?
In simple words, it indicates how far your data is spread. A large MAD indicates that the data set is more spread out relative to the mean.
Weightage of Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) in Class 11
MAD is an integral part of the maths syllabus of Class 11 and is relevant not just for Class 11 exams, but also for various engineering exams such as JEE. You may well have explored the idea of chance in earlier classes as a measurement of the uncertainty of different phenomena. Here, focused on the class 11 maths syllabus, a summary of MAD is given, which will help to quickly learn the relevant terms and also to achieve good marks in exams.
Illustrative Example on Mean Absolute Deviation
1: Students of a class scored the following marks in an exam. Find the M.A.D of the Score.
55, 65, 70, 70, 72, 85, 90, 90, 93, 100
Solution:
The Mean of the given data
Mean = Sum of the elements of the data set
------------------------------------------------
number of elements in the data set
= 55 + 65 + 70 + 70 + 72 + 85 + 90 + 90 + 93 + 100 = 790
------------------------------------------------------------------- --------
10 10
Mean = 79
Calculate the deviation for the mean-
| Marks |
Deviation |
| 55 |
55 - 79 = - 24 |
| 65 |
65 - 79 = - 14 |
| 70 |
70 - 79 = - 9 |
| 70 |
70 - 79 = - 9 |
| 72 |
72 - 79 = - 7 |
| 85 |
85 - 79 = 6 |
| 90 |
90 - 79 = 11 |
| 90 |
90 - 79 = 11 |
| 93 |
93 - 79 = 14 |
| 100 |
100 - 79 = 21 |
Mean Deviation = Sum of all the deviations from mean
----------------------------------------------
Total Number of Observations
Note: All the results that we get in negative need to be converted to positive numbers. This is done to reach conclusive results. For better understanding, if we use all the numbers exactly the way they were found, then it will give the following result:
[- 24 - 14 - 9 - 9 - 7 + 6 + 11 + 11 + 14 + 21 = 0]
The result is not giving any measurable value. These values in some cases may turn out to be [-number]. So, irrespective of the output being a negative value, it will be converted into a positive number and the Mean deviation will be found.
Mean Deviation= 24 + 14 + 9 + 9 + 7 + 6 + 11 + 11 + 14 + 21 = 126 = 12.6
----------------------------------------------------------- ------
10 10
This gives us a clear picture of the deviation of the observation from the centre. Thus, we can say that each score in the data set averages a distance of 12.6 from the mean of 79.
Generally, to calculate M.A.D (Mean Absolute Deviation) mean and median are used but any other measure of Central Tendency can also be used to calculate M.A.D.
FAQs on Mean Absolute Deviation
Q: What is the formula of Mean Deviation?
Q: What is the formula of Mean Absolute Deviation?
Q: What are the easy steps to calculate Mean Absolute Deviation?
Step 1: Calculate the mean from the given observations.
Step 2: Find the difference between each observation and the calculated mean.
Step 3: Apply the formal to find the difference calculated from Step 2.
Q: How are you going to get the absolute mean deviation?
Q: Will there ever be a negative value to the mean absolute deviation?
Maths Statistics Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Bivariate Analysis
- Relative Frequency
- Difference between Average and Mean
- Difference between Mean and Median
- Difference between Parametric and Non Parametric T
- Grouping data
- Statistics pdf
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Population and Sample
- Data Collection Methods
- Standard Deviation
- Correlation
- Bar Graph
- Chi Square Test
- Measures of Central Tendency
Other Class 11th Maths Chapters
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test