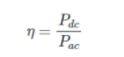- Introduction
- Half-Wave Rectifier
- Working Procedure
- Capacitor Filter
- The Efficiency of a Half-Wave Rectifier
- Half-Wave Rectifier Diagram for Class 12
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs
Introduction
A diode is an electric component that allows the current to pass in a single direction. When the alternating voltage is applied across the diode, the current flows only in that part of the cycle when the diode is forward-biased. This property helps in rectifying alternating voltages. The circuit used for this purpose is called a rectifier.
- The different applications of the diode include rectifiers, inverters, clampers and parameter amplifiers.
- In simple terms, rectification is the conversion of alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Half-Wave Rectifier
- A half-wave rectifier is a single PN junction diode connected in series to a load resistor. The diode is placed between the transformer and the load resistor.
- In a half-wave rectifier, the rectification process occurs only during half-periods. Another half cycle is not in use.
Working Procedure
- The diode is connected in series with the secondary of the transformer and the load resistor. The primary of the transformer connects to the AC mains.
- The alternating current provided as input. And it reaches the transformer to supply the desired voltage across terminals A and B.
- When the voltage at A is positive, the diode is forward biased whereby it conducts current.
- When the voltage at A is negative, the diode is negative biased and does not conduct current.
- The reverse saturation of the current is negligible and considered as zero.
- The output voltage developed across the load resistor is not steady dc.
Capacitor Filter
The waveform appears as a pulsating DC waveform because of using a rectifier without a filter. Filters like capacitor filters change the pulsating input into a constant dc output.
The Efficiency of a Half-Wave Rectifier
The ratio of dc power output to the applied input a.c power is known as rectifier efficiency, denoted by η. The maximum efficiency is 40.6%.
Half-Wave Rectifier Diagram for Class 12
The half-wave rectifier is the subtopic of the ‘Applications of Junction Diodes as a Rectifier.’ One must be aware of all the formulas because the numerical based questions are more from this topic.
Illustrated Examples
- In half-wave rectification, what is the output frequency if the input frequency is 50 Hz?
For Half-wave rectification, the output frequency is equal to the input frequency. So it is 50 Hz.
- What is the transformer utilisation factor of a half-wave rectifier?
Transformer utilisation factor is the ratio of DC output power to the AC of the secondary winding. The value is 0.287
- What is the peak inverse voltage (PIV) of a half-wave rectifier, if the peak voltage of the circuit is 5V and the diode cut-in voltage is 0.7?
PIV is the maximum voltage that the diodes resist. Therefore, the PIV is 5V.
FAQs
Q: What are the advantages of a half-wave rectifier?
Q: What is the ripple factor of the half-wave rectifier?
Q: What are the applications of the half-wave rectifier?
Q: What is the peak inverse voltage of the half-wave rectifier?
Q: How to protect the diode from a reverse breakdown?
Physics Current Electricity Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test