Rachit Kumar SaxenaManager-Editorial
Three lines combine to form a triangle. Triangle is a closed 2-D shape with three sides, angles, and vertices. It’s a polygon with three sides. Different types of triangles are classified either based on the lengths of the side and the interior angles.
Types of Triangle
Six Different Types of Triangles:
The triangles vary based on the following parameters:
- Based on the sides
- Based on the angles
Source: NCERT
Based on the Length of the Sides:
According to sides, the triangles can be classified into three categories:
Equilateral triangle:
- All sides are equal.
- The interior angles are equal to each other and are equal to 60 degrees.
- It is also known as an equiangular triangle.
- The value of interior angles, i.e. 60 degrees, is irrespective of the length of the sides.
- The length of all medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisector is equal.
Isosceles triangle:
- It has only two equal sides.
- The angle opposite to the equal sides is also equal.
Scalene triangle:
- It has no equal sides.
- None of the angles is equal
Based on the Interior Angle
Based on the interior angle, triangles can be classified into three categories:
Acute triangle:
- It has all its three interior angles less than 90 degrees.
Obtuse triangle:
- It has one of its interior angles greater than 90 degrees.
- The remaining two angles are acute, i.e., they are less than 90 degrees.
- The side opposite of the obtuse angle is the largest.
Right triangle:
- It has one of the interior angles equal to 90 degrees.
- The side opposite to the right angle is the longest side and is known as the hypotenuse.
- The remaining two angles are acute, i.e., less than 90 degrees.
- The sum of the other two angles is equal to 90 degrees.
- The side opposite of the right angle is the largest.
- When the other two angles are equal, i.e., 45 degrees, the triangle is known as isosceles right-angled triangles.
Weightage of Types of Triangle
The different types of triangles are a part of the chapter ‘Triangles’. It carries a weightage of 14 marks.
Illustrative Examples on types of Triangle
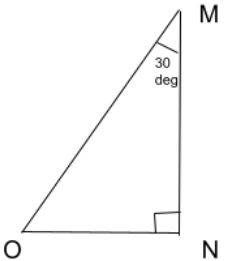
1: In the given triangle, identify the vertex opposite to side MN.
Solution:
The vertex opposite to side MN is O.
2: Calculate the measure of angle ACB.
Solution:
We are given That angle CAB is 30 degrees. Angle ABC is 90 degrees.
By angle sum property, we know that the sum of the three angles is 180 degrees.
We have,
30+90+ACB = 180
ACB+120 =180
ACB =180-120
ACB =60
Hence, angle MON is 60 degrees.
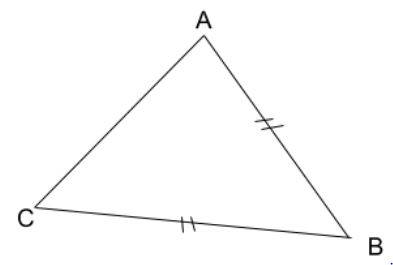
3: Identify the type of triangle, as shown in the figure below.
Solution:
As the triangle has no right angle or obtuse angle, it is identified as an acute-angled triangle. AB and BC are equal. Thus, the triangle is isosceles.
FAQs on Types of Traingle
Q: What is the sum of interior angles of a triangle?
Q: Can an obtuse-angled triangle have an acute angle?
Q: What is the longest side of a right-angled triangle?
Q: How is a vertex of a triangle denoted?
Q: Define isosceles right-angled triangle.
News & Updates
Triangle Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test