Abhishek DhawanAssistant Manager – Editorial Content
What is Elastic Potential Energy?
Potential energy is the energy that an object holds in the starting relative to other objects, its electric charge, and other significant factors. The name of potential energy was first discovered by physicist William Rankine in the 19th century. There are several types of potential energies associated with the relative objects and their factors including the elastic potential energy. One needs to elasticate the object to potential energy to work.
Types of Potential Energy
Potential energy is categorised into two types, which are as follows:
- Gravitational Potential Energy - When an object is raised to a certain height above the ground, the energy possessed can be defined as gravitational potential energy.
- Elastic potential energy - The second type of energy is elastic potential energy. The elastic potential energy can be stretched or compressed in either way. The object needs to be elasticated for elastic potential energy to work.
Elastic Potential Energy
As discussed above, Potential energy that can be compressed and stretch from one form into another is called Elastic Potential energy. The object needs to be elasticated, pulled from one endpoint to the other to reach an elastic potential so the energy within can work. Some examples of elastic potential energy are as below:
- Rubber band
- Stretch bow of an archer
- Spring of a clock
- Diver board, etc.
Formula for Elastic Potential Energy
The force applied to stretch the spring of elastic is directly proportional to the displacement in the elastic. This theory is also known as Hooke's Law.
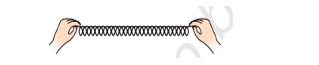
It can be seen below:
Stretched Spring
According to Hooke’s Law, the formula is:
F = kx
- F is the force
- K is the spring constant
- X is the displacement of the spring.
The formula of Elastic Potential energy can be written as:
- E. = ½ kx2
Note: P. E. denotes the elastic potential energy. The SI unit of potential energy is Joule.
Elastic Potential Energy for Class 11
The chapter Energy holds a weightage of 6 marks in total as per the guideline of CBSE. It contains one very short question (2 marks), one objective type question (1 mark), and one short question (2 marks).
Elastic Potential Energy: Illustrated Examples
Example 1) Write the SI unit of Elastic potential energy.
Answer – The SI unit of Elastic potential energy is Joules.
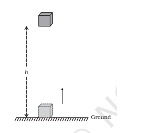
Example 2) Illustrate an example of Gravitational Potential energy.
Answer – The illustration of Gravitational potential energy is shown below:
Example 3) Calculate displacement if P. E. is 20 J and spring constant is 200 N / m.
Answer – Potential energy = 20 J,
K = 200 N / m
FAQs on Elastic Potential Energy
Q: List a few examples which can be used to understand/study the concept of elastic potential energy.
- Rubberband
- Stretch bow of an archer
- Spring of a clock
Q: What is Gravitational Potential energy?
Q: What are the forms of Potential Energy?
- Gravitational Potential energy
- Magnetic Potential energy
- Electrical Potential energy
- Chemical Potential energy
- Elastic Potential energy
Q: What are the two examples of Gravitational Potential energy in everyday life?
Q: What is the mathematical formula of Potential Energy?
News & Updates
Work, Energy and Power Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test