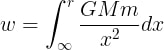Abhishek DhawanAssistant Manager – Editorial Content
What is Gravitational Potential Energy?
Gravitational potential energy is the energy acquired by an object due to the change in position in a gravitational field. When an object (m) is moved from infinity to a point inside the source mass (M) under the gravitational influence without accelerating it, the amount of work done in displacing it in the source field is called gravitational potential energy. Gravitational Potential Energy is denoted as Ug.
Formula for Gravitational Potential Energy
GPE or Gravitational Potential Energy is expressed using the following equation.
Gravitational Potential Energy Formula
| GPE = m × g × h |
|
|---|---|
| m |
Mass in kilograms |
| g |
Acceleration due to gravity (9.8 on Earth) |
| h |
Height in metres (above ground) |
Gravitational Potential Energy: Derivation
In gravitational potential energy derivation, let us consider an object of Mass (M) plotted at the x-axis and mass (m) at infinity. The work done for bringing it in without acceleration through minimal distance (dx) would be as follows:
dw = Fdx
Where,
- F = attractive force
- Dx = minimal distance
F and dx are in the same direction. Thus,
- dw = (GMm/x2) dx
Equating both the sides we get the following results -
As the work done is stored as potential energy U, the GPE at a point which is at a distance of ‘r’ from the source mass is represented as:
U = -GMm / r
Gravitational Potential Energy in Class 11
Gravitational Potential Energy is a part of Unit IV in class 11th Physics. Unit IV, Unit V, and Unit VI collectively have questions carrying 17 marking in the examination. Gravitational and Potential Energy has an approximate weightage of around 2% in the Class IX examinations.
Illustrated Examples on Gravitational Potential Energy
Example 1. Find the gravitational potential energy of body mass 10 kg, 25 m above the ground.
m (mass) = 10 kg
h (height) = 25 m
GPE = m x g x h
GPE = 10 x 9.8 x 24 = 2450 J
Example 2. A basketball of 2.3 kgs falls from a height of 50 m. Calculate the GPE of the ball when below:
m (mass) = 2.3 kg
h (height) = 50 m
GPE = m x g x h
GPE = 2.3 x 9.8 x 50
∴ GPE = 1127 J
Example 3. A 2 kg object falls from a height of 12 m. Calculate the work done by the force of gravity. (Consider the acceleration due to gravity as 10 m/s2.
m (mass) = 2 kg
h (height) = 12 m
g (acceleration due to gravity) = 10 m/s2
W = m x g x h
W = 2 x 10 x 12 = 240 N
FAQ on Gravitational Potential Energy
Q: State if each of the following statements is true or false. Give reasons for your answer. (a) In an elastic collision of two bodies, the momentum and energy of each body is conserved. (b) Total energy of a system is always conserved, no matter what internal and external forces on the body are present. (c) Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature. (d) In an inelastic collision, the final kinetic energy is always less than the initial kinetic energy of the system.
A:
- (a) False, The total momentum and energy is conserved, not the individual.
- (b) False, External forces can change the energy of a body.
- (c) False, Only work done by conservative force over a closed loop is zero.
- (d) True, In an inelastic collision, the final velocity reduces, resulting in loss of the initial kinetic energy.
Q: A body is initially at rest. It undergoes one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration. The power delivered to it at time t is proportional to (i) t^1/2 (ii) t (iii) t^3/2 (iv) t^2
A: Let us assume Body mass = m
- Acceleration = a
- According to Newton’s 2nd law F = ma (constant)
- We know a = dv/dt = constant. Hence dv = dt X constant
- On integrating, V = t + constant
- The relation of power is given by P = F X ν
- We have Hence, ν = u = at, Hence, P = F X (u+at)
- = ma (u+at)
- = mau + ma2t
- Therefore P ∝ t
Q: How much does a body weigh, at the centre of the Earth?
A: The weight of a body or an object at the centre of the Earth is zero (0), as the value of gravitation at the centre is zero.
Q: At which point is the gravitational field zero?
A: The point in the gravitational field where the gravitational potential energy is 0, the gravitational field is also zero.
Q: What is known as gravitational potential?
A: The work done in moving a test mass from infinity into the gravitational influence of source mass is called gravitational potential.
Q: The gravitational potential energy is related to which energy?
A: The gravitational potential energy is related to gravity or gravitational force.
Q: What is the unit of acceleration due to gravity on Earth?
A: The unit of acceleration due to gravity on Earth is around 9.8.
News & Updates
Work, Energy and Power Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test