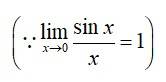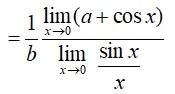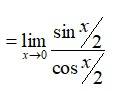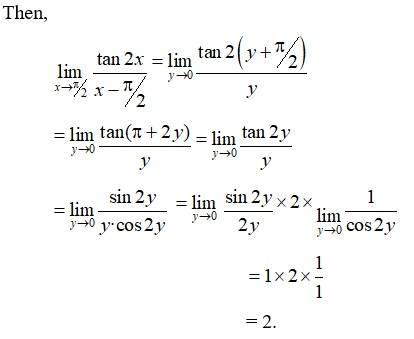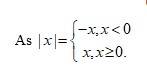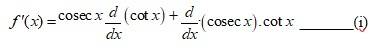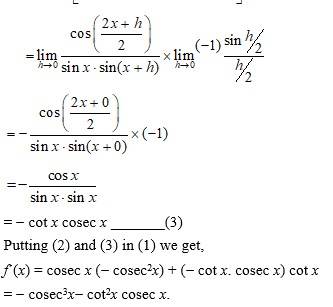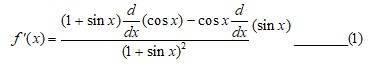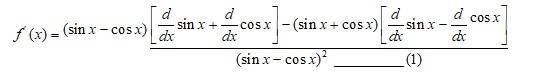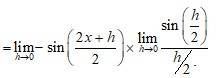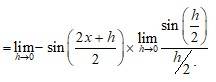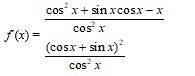Ex 13.1
Q1.
x+ 3
A.1.
x + 3 = 3 + 3 = 6.
Q2.
A.2.
Q3.
A.3.
Q4.
A4.
Q5.
A.5.
Q6.
A.6.
(0)4 + 5(0)3 + 10(0)2 + 10(0) + 5
= 5.
Q7.
A.7.
Q8.
Q.10
A.10.
We know that,
So,
Q11.
A.11.
Q12.
A.12.
Q13.
A.13.
Q14.
A.14.
Q15.
A15.
Q16.
A.16.
Q17.
= 4
Q18.
A18.
Q19.
A.19.
= 0.
Q20.
A.20.
= 1.
Q21.
A.21.
Q.22.
A.22.
Put y = x
. So that as y 0 cos
Q23. Find
and
, where f (x)
A.23. Given f (x)
for
left hand limit, L.H.S =
=
= 2 0 + 3 = 3.
Right hand limit, R.H.L =
= (0 + 1) = 3 1 = 3.
Thus,
For
L.H.L =
R.H.L =
Thus,
Q26.Find
wheref (x)
A.26.Given, f (x)
L.H.S =
R.H.L
Thus,
i e,
does not exist.
Q27.Find
f (x)
A27.
= | 5 |
5
= 5
5
= 0
Q28. Supposef (x) =
and if
= f (1) what are possible values of a and b?
A.28. Given, f (x) =
Since we need
we need,
LHL =
= a + b × 1 = a + b
and RHL =
= b - a × 1 = b - a
Given,
we have the following equations
a + b = 4 ____ (1)
b - a = 4 ____ (2)
Adding (1) and (2) we get,
2b = 8
b = 4
Putting b = 4 in (1) we get
a + 4 = 4
a = 0
Thus,
So,
does not exist at a = 0.
Q31. If the function f(x) satisfies
, evaluate
A.31. Given,
Ex 13.2.
Q1.Find the derivative
A.1. Given, f(x)=x2- 2 .,
We have,
=
=
=20
Q2.Find the derivative of x at x = 1.
A.2. Given, f(x)=x, f (1)=?
We have,
=1
Q3.Find the derivative of 99x at x = l00
A.3. Given, f(x)= 99x, f (100)= ?
So, f(100)=
=99
Q4.Find the derivative of the following functions from first principle.
(i)
(ii) (x -1)(x-2)
(iii)
(iv)
A.4.(i) Given,
So,
=0+3 x(x+ 0)
=3x2
(ii) Given, f(x) =(x-1)(x-2)
=x2- 3x+2
So,
=
=
= 2x – 3.
(iii) Given, f(x)=
So,
(iv) Given, f(x)=
Q5.For the function
Prove that
A.5. Given
At x=0,
f(X) =1.
and at x=1,
=100
1
=100
Hence,
Q6.Find the derivative of
for some fixed real number a.
A.6. Given,
We know that,
So,
Q7. For some constants aand b, find the derivative of
(i)(x- a) + (x - b)(ii)
(iii)
A.7. (c) Given, f(x)=(x-a)(x-b)
where a and b are constants.
So,
=(x-a)+(x-b)
= 2x– a- b.
(ii) Given f(x)=
where ab are constant
So,
=
=
(iii) Given, f(x)=
where a and bare constants
So,
Q8. Find the derivative of
for some constant a.
A.8. Given, f(x)=
So,
Q9. Find the derivative of
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
A.9. (i)
=2.
(ii) Given, f(x)=
So,
=
(iii) Given, f(x) =
So,
(iv) Given, f(x)=
=
(v) Given, f(x)=
So,
(vi) Given, f(x)=
So,
Q10. Find the derivative of cos x from first principle.
A.10. Given, f(x) = cos x
By first principle,
Q11.Find the derivative of the following functions:
(i)sin x cos x
(ii)
(iii)5 sec x + 4 cosx
(iv)
(v)3cot x + 5 cosec x
(vi)
(vii)
A.11. (i) f(x)=sin x cos x
So,
So,
(iii) Given f(x)=5 sec x+4 cosx.
So,
(v) Given,f(x)=3 cot x+5cosecx.
So,
(vi) Given,
(vii) Given
Miscellaneous Exercise.
Q2.
A.2. Given, f(x) = x + a.
So, f(x) =
= 1
Q3.
A.3. Given, f(x) =
Q4. (ax + b) (cx + d)2
A.4. Given, f (x) = (ax + b) (cx + d)2
So, f´(x) = (ax +b)
Q5.
A.5. Given, f (x) =
So, f (x) =
Q6.
A.6. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
=
Q7.
A.7. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
Q8.
A.8. Given, f (x) =
So, f(x) =
Q9.
A.9. Given, f (x) =
Q10.
A.10. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
Q12. (ax + b)n
A.12. Given, f (x) = (ax + b)n
Chain rule,
where
u(x) is a function of x.
So, f´(x) =
Q13. (ax + b)n (cx + d)m
A.13. Given, f´ (x) = (ax + b)n (cx + d)m
So, f’(x) =
Q14. sin(x + a)
A.14. Given, f (x) = sin(x + a)
So, f (x) =
= cos (x + a)
Q15. cosec x. cot x
A.15. Given f (x) = cosec x. cot x.
By Leibnitz product rule,
So, g´(x) =
= -cosec2x.______(2)
And h´(x) =
Q16.
A.16. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
Putting (2) and (3) in (1) we get,
Q17.
A.17. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
Let g(x) = cos x and p(x) = sin x.
{from so g’(x) A ) (upto equation 3)
Let g(x) = cos2 and p(x) = sin x.
So, g´(x) =
= -sin x ______ (2)
And p´(x) =
= cos x _____ (3)
Putting (2) and (3) in (1) we get,
Q18.
A.18. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
Let g(x) = cos x.
So, g´(x)
= -sin x.
So, f´(x)
Q19. sinnx
A.19. Given, f(x) =sinnx
By chain rule,
f´(x) = n(sin x)n-1
sin x
Let (gx) = sinx
So, g´(x)
=
= cos x.
So, f´(x) = n(sin x)n-1 cos x.
Q20.
A.20. Given, f (x) =
f´(x) =
{Copy (A)}
So, g´(x) =
= sin x ______ (2)
And p´(x) =
= cos x _____ (3)
So, put (2) and (3) in (1) we get,
Q22. x4 (5 sin x 3 cos x)
A.22. Given, f (x) = x4. (5 sin x 3 cos x)
As
and
Thus,
Q23. (x2 + 1) cos x
A.23. Given, f (x) = (x2 + 1) cos x
f´(x) = (x2 + 1)
= x2 sin x sin x + 2x cos x.
Q24. (ax2 + sin x) (p +q cos x)
A.24. Given, f (x) = (ax2 + sin x) (p +q cos x).
So, f´(x) = (ax2 + sin x)
= q sin x(ax2 + sin x) + (p + q cos x) (2ax + cos x)
Q26.
A.26. Given, f (x) =
So,
Q27.
A.27. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
Q28.
A.28. Given, f (x) =
Dividing numerator and denominator by cos2x we get,
Q29. (x + sec x) (x tan x)
A.29. Given, f (x) = (x + sec x) (x tan x)
So, f´(x) = (x + see x)
Let g(x) = tan x.
Q30.
A.30. Given, f (x) =
So, f´(x) =
=