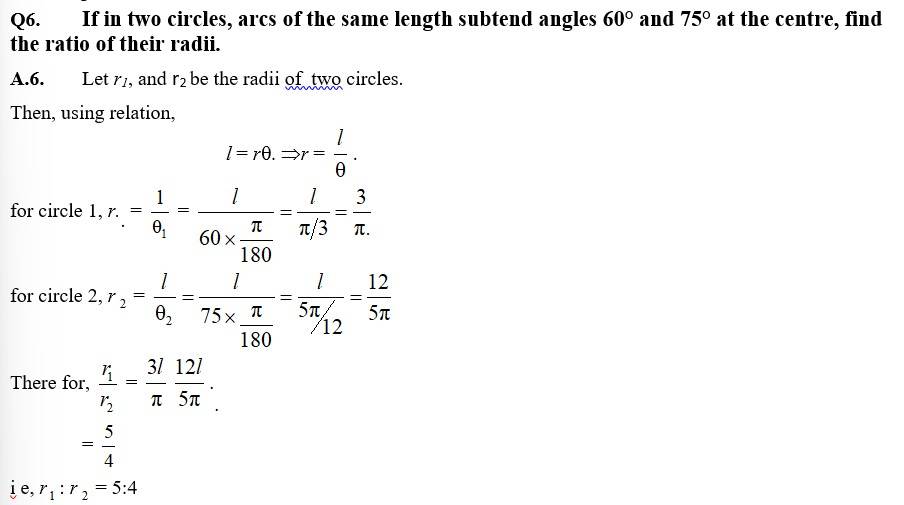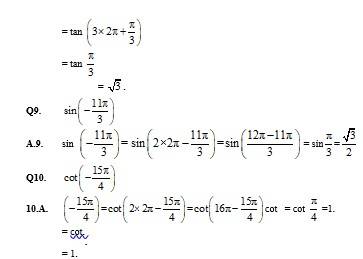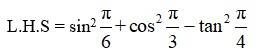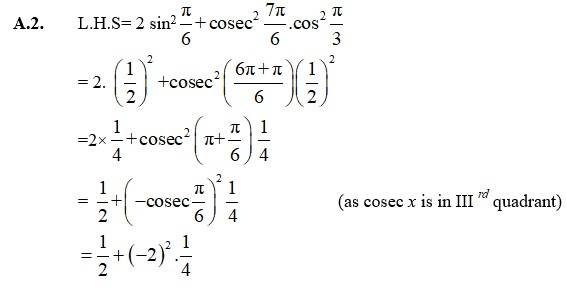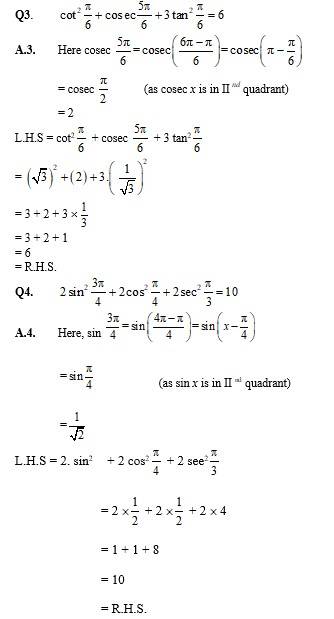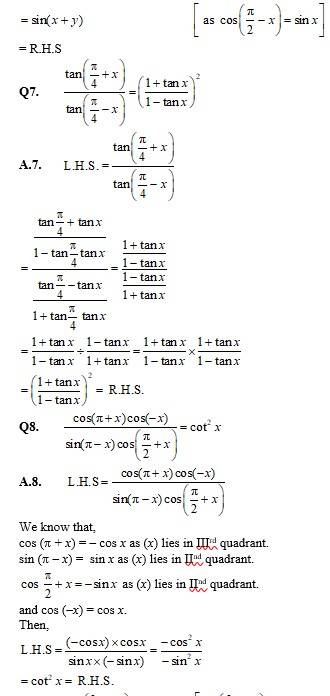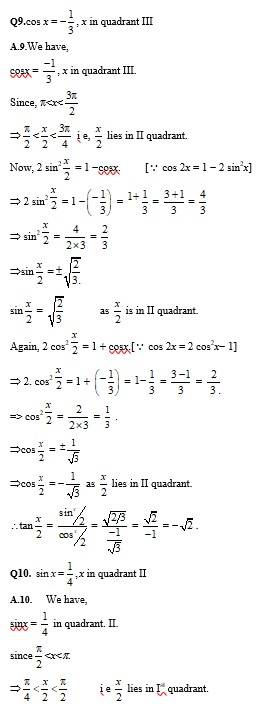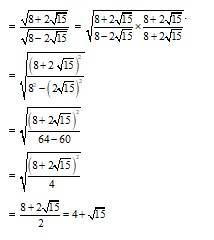NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions: We have provided NCERT Solutions Maths Class 11th Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions on this page. The NCERT Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions solutions are prepared by our expert teachers. Students can access the NCERT Solutions Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions for free. This chapter has many equations which students have to learn thoroughly. In Trigonometry Class 11 NCERT solutions, students will learn the concept of trigonometric ratios to trigonometric functions and their properties. Class 11th Trigonometry is important for JEE and NEET.
Trigonometric functions are the functions of an angle of a triangle. Sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant are the basic trigonometric functions. The NCERT Solutions Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is a best tool for the Class 11 students to perform well in the board exams. They can expect questions from Applications of trigonometry for entrance exams. Students can access out NCERT Solutions for free.
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions - Topics Covered
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions FAQs
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions - Topics Covered
- Angles
- Trigonometric functions
- Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles
- Trigonometric Equations
Check the NCERT Solutions Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions below.
Q 3.1 Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures:
(i) 25°
(ii) – 47°30'
(iii) 240°
(iv) 520°
A 3.1
(i) 25°
Solution:We know that 180° = π radian.
Hence, 25° = π/180 X 25 radian= 5π/36 radians.
(ii).-47°30'
Solution: We know that 180°=π radian,
Hence, -47°30' = -47 × 1/2 degree= -47/2× π/180 radians.
= -19π/72 radians
(iii) 240°
Solution:We know that, 180°=π radian.
Hence, 240°= 240× π/180 radian.
= 4π/3 radian.
(iv) 520°
Solution: We know that, 180°= π radian.
Hence, 520°= 520°× π/180 radian.
= 26π/9 radian.
Q 3.3 A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second?
A 3.3 Given that a wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute
Then, number of revolutions in one second = 360/60 =6.
In 1 complete revolution the wheel turns 360°= 2 π radian.
So, In 6 revolution, the wheel will turns 6×2π radian = 12π radian.
Hence, in one second the wheel will turn an angle of 12π radian.
Q Find the values of the trigonometric functions in sin 765°
A 3.2.6
sin 765°
We know that value of sun x repeats after an interval of 2π or 360°.
Sin (765°) = sin (2×360°+45°)
= sin 45°
= 1/√2
Download Here NCERT Class 11th Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions FAQs
Exercise 3.1
Q1. Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures:
(i) 25° (ii) – 47°30′ (iii) 240° (iv) 520°
A.1. (i)25°
Solution:We know that 180° = π radian.
Hence, 25° = 25 radian= radians.
(ii).47°30′
Solution: We know that 180° = π radian,
Hence, -47°30′= -47 × degree= × radians.
= radians
(iii) 240°
Solution:We know that, 180°= radian.
Hence, 240°= 240× radian.
= radian.
(iv) 520°
Solution: We know that, 180= radian.
Hence, 520°= 520°× radian.
= radian.
Q2. Find the degree measures corresponding to the following radian measures
(i) (ii)-4 (iii) (iv)
A.2. (i)
We know that radian= 180°,
Hence, radian= × = × = × ×180
=
=39 0
= 39 + minute (as 1 =60′)
=39°+22′+
=39°+22′+ (as 1′=60”)
=39°+22′+30”.
=39° 22′ 30”.
(ii) -4
We know that radian = 180°.
Hence: -4 radian = -4× = 4× = 4×180°× .
= -
=229 0
=229+
=229+5′+ .
=229°+5′+27″
=229° 5′27″
(iii) .
Solution: We know that, π radian= 180°.
Here radian = × =300°
(iv)
Solution: We know that radian =180° .
Here, radian = × =210°
Q3. A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second?
A.3. Given that a wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute
Then, number of revolutions in one second = =6.
In 1 complete revolution the wheel turns 360°= 2π radian.
So, In 6 revolution, the wheel will turns 6×2π radian = 12π radian.
Hence, in one second the wheel will turn an angle of 12π radian.
Q4. Find the degree measure of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 cm by an arc of length 22 cm
A.4. Here l = 22cm.
r =100cm.
Ø = ?
Hence by r =
= Ø = = radian
= ×
= × 180° ×
=
=12 = 12°
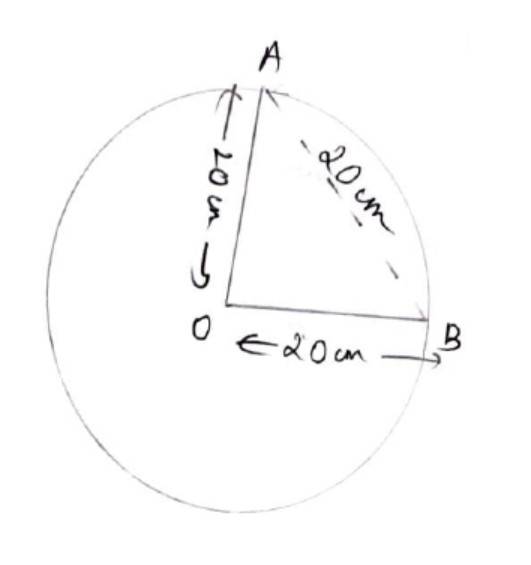
Q5. In a circle of diameter 40 cm, the length of a chord is 20 cm. Find the length of minor arc of the chord.
So, radius, r = cm = 20 cm
Length of chord (AB) = 20cm
In OAB
OA = OB=AB=20 cm
Hence, AOAB is equilateral triangle and end of the angle is 60°
:. Ø =60° = 60 × radian = radian
Hence, length of minor are of the chord, l=rØ.
l = 20 × cm
l = cm.
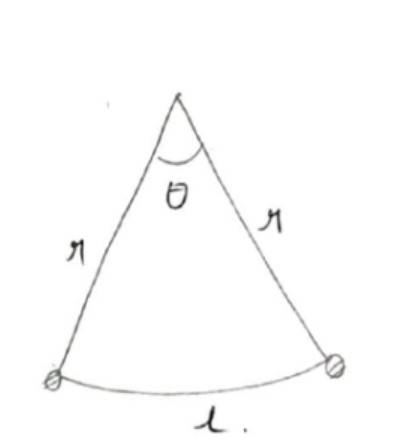
Q7. Find the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if its length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(i) 10 cm (ii) 15 cm (iii) 21 cm
A.7. Here,
r= length of pendulum.
r= 75 cm.
(i)Are of length, l = 10 cm
Ø= = radian.
(ii) are of length, l = 15 cm.
So, Ø= = radian.
(iii) are for length, l= 21 cm.
So, Ø= radian.
Exercise 3.2
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions in Exercises 1 to 5.
Exercise 13.3
Q1.
A.1.
=R.H.S
Q2.
= R.H.S.
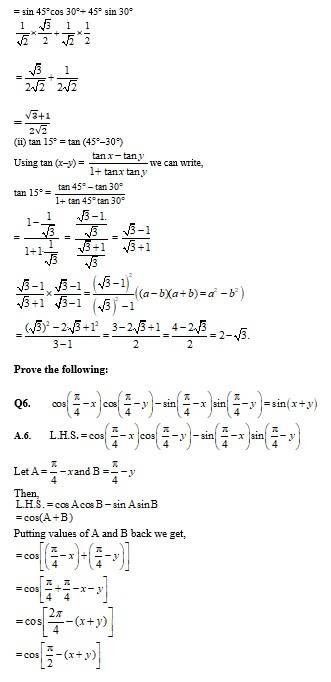
Q5. Find the value of:
(i) sin 75° (ii) tan 15°
A.5. (i) sin 75°= sin (45°+30°)
Using sin (x + y)= sin x cos y + cos x sin y we can write
sin 75°
Q9.
A.9.
Here,
So.
= 1
= R.H.S.
Q10. sin (n + 1)xsin (n + 2)x + cos (n + 1)x cos (n + 2)x = cos x
A.10.
Let A
So, L.H.S=
Putting values of A and B we get,
Q11.
A.11. L.H.S
Using cos (A + B) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B
and cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
Q12. sin26x – sin24x = sin 2x sin 10x
A.12.
Using
and
So,
As we can write.
Q13. cos22x – cos26x = sin 4x sin 8x
A.13.
Using
As sin 2Ø = 2 sin ØcosØ.
L.H.S. = sin (2× 4x) sin(2× 2x)
= sin 8x sin 4x
= R.H.S.
Q14. sin2 x + 2 sin 4x + sin 6x = 4 cos2x sin 4x
A.14. L.H.S. = sin 2x + 2 sin 4x + sin 6x
Using sin A + sin B = 2 sin cos we have,
L.H.S. = (sin 2x + sin 6x) + 2 sin 4x
We know that,
Hence,
= R.H.S.
Q15. cot 4x (sin 5x + sin 3x) = cot x (sin 5x – sin 3x)
A.15.
Hence, L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Q16.
A.16. L.H.S
= R.H.S
Q17.
A.17. L.H.S
Q18.
A.18. L.H.S
Q19.
A.19.
Q20.
A.20. L.H.S
= 2 sin x
= R.H.S.
Q21.
A.21. L.H.S
Q22. cot x cot 2x – cot 2x cot 3x – cot 3x cot x = 1
A.22. L.H.S. = cot x cot 2x – cot 2x cot 3x – cot 3x cot x.
= cot x cot 2x – cot 3x (cot 2x + cot x)
= cot x cot 2x – (cot 2x + cot x)[cot (2x + x)]
We know that,
we can write
= cot x cot 2x – cot 2x cot x + 1
= 1
= R.H.S.
Q23.
A.23. L.H.S. = tan 4x
We know that,
, we can write
= R.H.S.
Q24. cos 4x = 1 – 8sin2x cos2x
A.24. L.H.S. = cos 4x.
= cos 2(2x)
= 1 – 2 Sin2(2x) [ cos 2x = 1 – 2 Sin2x]
= 1 – 2 [2 sin xcosx]2[ sin 2x = 2 sin xcos x]
= 1 – 2 [4 sin2xcos2x]
= 1 – 8 sin2xcos2x
= R.H.S.
Q25. cos 6x = 32 cos6x – 48cos4x + 18 cos2x – 1
A.25. L.H.S. = cos 6x
= cos 3(2x)
= 4 cos32x – 3 cos 2x [Q cos 3A = 4 cos3A – 3cos A]
= 4[(2 cos2x – 1)3] – 3[(2 cos2x – 1)] [Q cos 2x = 2 cos2x – 1]
= 4[(2 cos2x)3 + 3[(2 cos2x)2(–1) + 3(2 cos2x)(–1)2 + (–1)3] – 3(2 cos2x) + 3
{Q (a + b)3= a3 + b3 + 3a2b + 3ab2}
= 4[8 cos6x – 12 cos4x + 6cos2x – 1] – 6 cos2x + 3.
= 32 cos6x – 48 cos4x + 24 cos2x – 4 – 6cos2x + 3
= 32 cos6x – 48 cos4x + 18 cos2x – 1
= R.H.S.
Exercise 3.4
Find the principal and general solutions of the following equations:
sin sin = 0
sin 3x sin x = 0.
sin 3x = 0 or sin x = 0
3x = nπ or x = nπ, n € z,
x = or x = nπ, n € z,
Q6. cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
A.6. We have,
cos 3x + cosx-cos 2x = 0.
(cos 3x + cosx) cos 2x = 0
Using cos A + cos B = 2 cos cos
2 cos cos - cos 2x = 0.
2 cos cos - cos 2x = 0
2 cos 2xcosx - cos 2x = 0
cos 2x. (2 cosx - 1) = 0.
cos 2x = 0 or 2 cosx -1 = 0.
2x = (2n + 1) , n∈z or cosx = = cos
x = (2n + 1) , n∈z or x = 2nx± , n∈z.
Q7. sin 2x + cos x = 0
A.7. We have,
sin 2x + cosx = 0.
2 sin cosx + cosx = 0( sin 2x = 2 sin xcosx)
cosx (2 sin x + 1) = 0.
cosx = 0 or 2 sinx + 1 = 0.
x = (2n + 1) , n∈z or sin x = = -sin = sin π + = sin
x = (2n + 1) , x∈z or x= nπ + (-1)n n∈z.
Q8. sec22x = 1– tan 2x
A.8. We have,
sec2 2x = 1 tan 2x
1 + tan2 2x = 1 tan 2x[ sec2x = 1 + tan2x]
tan2 2x + tan 2x = 0.
tan 2x (tan 2x + 1) = 0.
tan 2x = 0 or tan 2x + 1 = 0.
2x = nπ, x∈z or tan 2x = -1 = -tan = tan π- = tan
x= , n∈z or 2x = nπ + , n∈z.
x = n∈z
Q9. sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
A.9. We have,
sinx + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0.
(sinx + sin 5x) + sin 3x = 0.
Using sin A + sin B = 2 sin cos .
2 sin cos + sin 3x = 0.
2 sin cos + sin 3x = 0.
2 sin 3xcos (-2x) + sin 3x = 0.
sin 3x [2 cos 2x + 1] = 0[ cos (-x) = cosx].
sin 3x = 0 or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0.
3x = nπ, n∈z. or cos 2x = = -cos = cos π - = cos
x= , n∈z or 2x = 2nπ± .
x = nπ± , n∈z.
Miscellaneous Exercise
Q1.
A.1. L.H.S. = 2 cos cos + cos + cos =∂ .
= 2 cos cos + 2 cos cos
= 2 cos cos + 2. cos cos
= 2 cos cos + 2 cos cos [ cos (x) = cosx].
= 2 cos
= 2 cos
= 2 cos
= 2 cos × 2 ×cos × cos .
= 2 cos 2× 0×cos
= 0
= R.H.S.
Q2. (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x = 0
A.2. L.H.S = (sin 3x + sin x) + sin x + (cos 3x - cosx) cosx.
Using
Sin A + sin B = 2 sin cos
cos A - cos B = -2 sin sin .
L.H.S. = sin x + cosx
= 2 sin cos sin x -2 sin sin cosx.
= 2 sin 2xcosx sin x -2 sin 2x sin xcosx
= 0 = R.H.S.
Q3. (cos x + cos y)2 + (sin x – sin y)= 4 cos2
A.3. L.H.S. = (cos x + cos y)2 + (sin x- sin y)2
Using,
cos A + cos B = 2 cos cos
sin A - sin B = 2 cos sin
L.H.S. = .
= 4. cos2 cos2 .. + 4 cos2 sin2 .
= 4 cos2
= 4 cos2 [ cos2∅+ sin2q∅ = 1].
= R.H.S.
L.H.S =
Q4. (cos x – cos y)2+ (sin x – sin y)2 = 4 sin2
A.4. L.H.S = (cos x-cos y)2 + (sin x- sin y)2
=
= 4 sin2 sin2 + 4 cos2 sin2
= 4 sin2
= 4 ..[ sin2∅ + cos2∅= 1]
= R.H.S.
Q5. sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x
A.5. L.H.S = sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x.
= (sin x + sin 7x) + (sin 3x + sin 5x)
Using,
sin A + sin B = 2 sin cos
L.H.S. = 2. Sin cos + 2 sin cos
= 2 sin cos + 2 sin cos
= 2 sin 4x cos 3x + 2 sin 4x cosx.[ cos (-x) = cosx]
= 2 sin 4x[cos 3x + cosx]
Using cos A + cos B = 2 cos cos
So, L.H.S. = 2 sin 4x
= 2 sin 4x
= 4 sin 4x. cos 2x cosx = R.H.S.
Q6.
A.6. L.H.S. =
Using sin A + sin B = 2 sin cos
cos A + cos B = 2 cos cos
Q7. sin 3x + sin 2x – sin x = 4sin x
A.7. L.H.S = sin 3x + sin 2x - sin x
= sin 3x - sin x + sin 2x.
= 2 cos .. sin + sin 2x
= 2 cos sin + sin 2x.
= 2 cos 2x sin x + 2 sin xcosx [ sin 2x = 2sin xcosx]
= 2 sin x [cos 2x + cosx]
= 2 sin x
= 2 sin x
= 4 sin xcos . cos = R.H.S.
Find sin , cos and tan in each of the following :
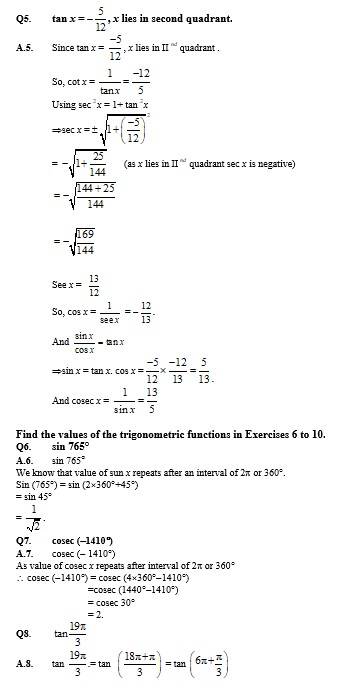
Q8. tan x = − , x in quadrant II
A.8. We have, tan x= , x in IInd quadrant.
Since,
sin , cos , tan are all positive.
Now, sec2x = 1 + tan2x = 1 + = 1 + = =
secx = ±
cosx = ± .
cosx = as x is in IInd quadrant.
Now, 2 sin2.. = 1 cosx. [cos 2x = 1 2 sin2x.]
2 sin2 = 1
2 sin2 = 1 + = = .
sin2 = =
Explore exams which ask questions on Maths Ncert Solutions class 11th
Select your preferred stream
Maths Ncert Solutions class 11th Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test