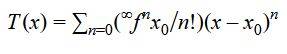Rachit Kumar SaxenaManager-Editorial
What is the Analytical Function?
Analytical functions are described as the converging sequence, which orbits around the variable x for which the series has been generalised. Almost all the functions we have learned from the simple algebraic and arithmetic operations and the elementary transcendental functions are analytical in any part of their field.
Analytic Function is described as an infinitely differentiable function over a variable named x such that the extended Taylor sequence can be represented as seen below.
This describes the extended Taylor overvalue Xo; this function is an analytic function for the value x in its domain. Another value in the domain converges the sequence to one point.
Analytical Function Types
Analytical functions may be divided into two distinct groups, which are identical in certain respects but have different characteristics. The two forms of analytic functions are as follows:
- Real Analytic Function
- Complex analytic function
Real Analytic Function
If a series agrees with the Taylor series and has a different order derivative on its any domain point, then that series is a real analytic function.
Complex analytic function
The function is said to be analytic in the region T of the complex plane x if, at each point, f(x) has a derivative of x and f(x) has unique values that are one to one function.
Analytic Function Properties
- The fundamental properties of analytic functions are as follows:
- The limit of a universally convergent sequence of analytical functions is indeed an analytical function.
- If f(z) and g(z) are analytical functions on U, their sum f(z) + g(z) and the result f(z).g(z) are both analytical functions.
- If f(z) and g(z) are the two analytical functions, and f(z) is the domain of g for all z, so their composite g(f(z)) is also an analytical function.
- Function f(z) ≠ 1/z (z) is an empirical function.
- All bound functions are constant functions.
- Any non-constant polynomial p(z) has its origin. That is, there is a z0 such that p(z0) = 0.
Weightage of Analytic Function in Class 11
This concept is taught under the chapter Relations and Function. You will learn about the types of functions, their formulas, and their application while solving questions. Analytic functions are a small part of the weightage of 23 marks in the exam.
Illustrated Examples on Analytic Function
1. Is log Z analytic?
Solution.
Log(z) is analytic except when z is a negative real number or 0.
2.What is the argument of the complex number 1+i/1−i?
Solution.
π/2
3.The product of 1 + i and 2 - 5i is:
Solution.
7 - 3i
FAQs on Analytic Function
Q: What is the analytical function in the complex analysis?
Q: How do you know if the function is analytical?
Q: Why are analytical functions important?
Q: Which is the analytical function everywhere?
Q: What is the real analytic function?
News & Updates
Relations and Functions Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test