NEET Biology syllabus is one of the most important aspects of preparing for this important exam. This section carries the highest weightage of NEET exam. To help NEET aspirants, here we bring the Biology syllabus for NEET along with the Biology chapter-wise weightage for the exam based on previous years’ analysis.
NEET Biology Syllabus: The Biology section of NEET consists of the highest weightage. As this subject is further segregated into Botany and Zoology, the number of questions from the Biology section is maximum. With the NEET 2025 approaching in May, it is high time aspirants complete the NEET Biology syllabus to ace the exam. Candidates must pay extra focus on this subject.
Explore colleges based on NEET
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has finalised and released the NEET 2025 syllabus. The syllabus has remained the same as last year, when it underwent major changes. While some topics were removed, some were added to the revised NEET syllabus. This article brings the complete NEET 2025 Biology syllabus.
Q: What are the important chapters of the NEET syllabus?
Q: Has there been any change in the syllabus of NEET 2025?
No, there has not been any change in the NEET 2025 syllabus. Last year, the NEET syllabus underwent major changes as per the recommendation by the National Medical Commission (NMC). A number of chapters and topics were removed from Physics, Chemistry and Biology subjects. On the other hand, certain topics and chapters were added and some of the topics were modified. Since such major changes were brought in to last year's NEET syllabus, the NEET 2025 syllabus is unchanged.
NEET syllabus 2025 has been released officially by NMC in December 2024. Hence, students preparing for NEET 2025 should start preparing, or continue their preparation based on last year's NEET syllabus. Even if some changes are introduced to the NEET 2025 syllabus, those would not be something major.
Q: What is the syllabus of NEET UG?
NEET UG Syllabus is divided among 4 sections- Physics Chemistry Zoology Botany All these 4 sections hold same marks for the examination and all the sections have 45 questions to be attempted in 45 minds itself. From the link NEET Exam Syllabus you can check the complete syllabus and important topics for 11th and 12th for Physics, Chemistry, and Zoology & Botany. The NEET syllabus underwent major changes last year and this year it has remained the same. The NEET syllabus is the same as the Board exam syllabus. Hence, it is mandatory for students to study and prepare Class 11 and Class 12 syllabus thoroughly to complete NEET syllabus. Unlike previous years, the NEET subject-wise syllabus is not segragated into Class 11 and Class 12 topics, and experimental subjects have been added to Physics subject.
This article of Shiksha brings the complete NEET Biology syllabus PDF along with the NEET Biology syllabus weightage or the NEET important chapters for Biology. Candidates can refer to this article to learn how to prepare for Biology section of NEET exam.
Also Read:
- NEET UG 2025 Syllabus Released @nmc.org.in; Download PDF Here
- NEET Biology Questions and Answers PDF Download
NEET 2024 Biology Syllabus
Although there is no segregation of syllabus for Class 11 and Class 12, for the convenience of students, the following table brings the NEET Biology syllabus for both Class 11 and Class 12. The chapters are mixed between Botany and Zoology. Some of the topics are common for both areas.
| NEET Biology Syllabus for Class 11 |
NEET Biology Syllabus for Class 12 |
|---|---|
| Diversity in Living World |
Reproduction |
| Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants |
Genetics and Evolution |
| Cell Structure and Function |
Biology and Human Welfare |
| Plant Physiology |
Biotechnology and Its Applications |
| Ecology and Environment |
NEET 2024 Biology Syllabus
In this section, we bring to you the topics under each unit of the chapter under the Biology syllabus for NEET.
Unit I: Diversity in Living World
-
What is living?; Biodiversity; Need for classification; Taxonomy & Systematics; Concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature.
-
Five kingdom classifications; salient features and classification of Monera; Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens; Viruses and Viroids.
-
Salient features and classification of plants into major groups - Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category);.
-
Salient features and classification of animals-nonchordate up to phyla level and chordate up to classes level (three to five salient features and at least two examples)
Unit II: Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
-
Morphology and modifications; Tissues; Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence- cymose and recemose, flower, fruit and seed (To be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical Syllabus). Family (malvaceae, Cruciferae, leguminoceae, compositae, graminae).
-
Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect (frog). (Brief account only)
Unit III: Cell Structure and Function
-
Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell; Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles-structure and function; Endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, micro bodies; Cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultra structure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus.
-
Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbodydrates, lipids, nucleic acids; Enzymes-types, properties, enzyme action, classification and nomenclature of enzymes.
-
B Cell division: Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance.
Unit IV: Plant Physiology
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; Site of photosynthesis take place; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea); Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Cyclic and non cyclic and photophosphorylation; Chemiosmotic hypothesis; Photorespiration C3 and C4 pathways; Factors affecting photosynthesis.
-
Respiration: Exchange gases; Cellular respiration-glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); Energy relations- Number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratory quotient.
-
Plant growth and development: Seed germination; Phases of Plant growth and plant growth rate; Conditions of growth; Differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; Sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators-auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA.
Unit V: Human physiology
-
Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory organs in animals (recall only); Respiratory system in humans; Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-Exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration Respiratory volumes; Disorders related to respiration-Asthma, Emphysema, Occupational respiratory disorders.
-
Body fluids and circulation: Composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; Composition of lymph and its function; Human circulatory system-Structure of human heart and blood vessels; Cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG, Double circulation; Regulation of cardiac activity; Disorders of circulatory system-Hypertension, Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure.
-
Excretory products and their elimination: Modes of excretion- Ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; Human excretory system-structure and fuction; Urine formation, Osmoregulation; Regulation of kidney function-Renin-angiotensin, Atrial Natriuretic Factor, ADH and Diabetes insipidus; Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders; Uraemia, Renal failure, Renal calculi, Nephritis; Dialysis and artificial kidney.
-
Locomotion and Movement: Types of movement- ciliary, fiagellar, muscular; Skeletal musclecontractile proteins and muscle contraction; Skeletal system and its functions (To be dealt with the relevant practical of Practical syllabus); Joints; Disorders of muscular and skeletal systemMyasthenia gravis, Tetany, Muscular dystrophy, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout.
-
Neural control and coordination: Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humanscentral nervous system, peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse; Reflex action; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear.
-
Chemical coordination and regulation: Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine systemHypothalamus, Pituitary, Pineal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads; Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary Idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders (Common disorders e.g. Dwarfism, Acromegaly, Cretinism, goiter, exopthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addison’s disease). (Imp: Diseases and disorders mentioned above to be dealt in brief.)
Unit VI: Reproduction
-
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure; Development of male and female gametophytes; Pollination-types, agencies and examples; Outbreeding devices; Pollen-Pistil interaction; Double fertilization; Post fertilization events- Development of endosperm and embryo, Development of seed and formation of fruit; Special modes-apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation.
-
Human Reproduction: Male and female reproductive systems; Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; Gametogenesis-spermatogenesis & oogenesis; Menstrual cycle; Fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; Pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea); Parturition (Elementary idea); Lactation (Elementary idea).
-
Reproductive health: Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD); Birth control-Need and Methods, Contraception and Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP); Amniocentesis; Infertility and assisted reproductive technologies – IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness)
Unit VII: Genetics and Evolution
-
Heredity and variation: Mendelian Inheritance; Deviations from Mendelism- Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, Multiple alleles and Inheritance of blood groups, Pleiotropy; Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; Chromosome theory of inheritance; Chromosomes and genes; Sex determination-In humans, birds, honey bee; Linkage and crossing over; Sex linked inheritance-Haemophilia, Colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans-Thalassemia; Chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes.
-
Molecular basis of Inheritance: Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central dogma; Transcription, genetic code, translation; Gene expression and regulation- Lac Operon; Genome and human genome project; DNA finger printing, protein biosynthesis.
-
Evolution: Origin of life; Biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution from Paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence); Darwin’s contribution, Modern Synthetic theory of Evolution; Mechanism of evolution-Variation (Mutation and Recombination) and Natural Selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy-Weinberg’s principle; Adaptive Radiation; Human evolution.
Unit VIII: Biology and Human Welfare
-
Health and Disease; Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. Typhoid, Pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm); Basic concepts of immunologyvaccines; Cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse, Tobacco abuse.
-
Improvement in food production; Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification; Apiculture and Animal husbandry.
-
Microbes in human welfare: In household food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
Unit IX: Biotechnology and Its Applications
-
Principles and process of Biotechnology: Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology).
-
Application of Biotechnology in Health and Agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy; Genetically modified organisms-Bt crops; Transgenic Animals; Biosafety issuesBiopiracy and patents.
Unit X: Ecology and Environment
- Organisms and environment: Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; Population attributes-growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
-
Ecosystem: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; Energy flow; Pyramids of number, biomass, energy.
-
Biodiversity and its conservation: Concept of Biodiversity; Patterns of Biodiversity; Importance of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity; Biodiversity conservation; Hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, biosphere reserves, National parks and sanctuaries, Sacred Groves.
-
Environmental issues: Air pollution and its control; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals and their effects; Solid waste management; Radioactive waste management; Greenhouse effect and global warning; Ozone depletion; Deforestation; Any three case studies as success stories addressing environmental issues.
List of Chapters Removed from NEET Biology Syllabus
The following chapters were removed from the NEET Biology syllabus last year.
| Unit | Chapters |
|---|---|
| Diversity in Living World | Three domains of life, Tools for study of Taxonomy – Museums, Zoos, Herbaria, Botanical gardens |
| Plant Physiology |
|
| Human Physiology | Digestion and absorption; Alimentary canal and digestive glands; Role of digestive enzymes and Neural Control and Coordination: Reflex action; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear. |
| Reproduction | Reproduction in organisms: Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; Modes of reproduction – Asexual and sexual; Asexual reproduction; Modes-Binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants. |
| Biology and Human Welfare | Improvement in food production; Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification; Apiculture and Animal husbandry. |
| Ecology and Environment | Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche; Population and ecological adaptations Nutrient cycling (carbon and phosphorous); Ecological succession; Ecological Services-Carbon fixation, pollination, oxygen release Environmental issues: Air pollution and its control; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals |
Click here to download the NEET 2025 Biology Syllabus PDF
NEET Biology Syllabus Chapter Wise Weightage
The following table brings the topics from the NEET Biology syllabus in NEET along with their weightage.
| Biology Chapters and Topics |
Average No. of Questions from the Chapter |
Weightage of the Chapter and Topic |
|---|---|---|
| Botany |
50 |
100% |
| Cell Biology
|
4
|
8%
|
| Ecology-Biodiversity and Conservation
|
5
|
10%
|
|
1
|
2%
|
| Genetics - I
|
4
|
8%
|
| Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
|
3
|
6%
|
| Ecology-Ecosystem
|
1
|
2%
|
| Anatomy of Flowering Plants
|
3
|
6%
|
| Biotechnology
|
4
|
8%
|
| Morphology of Flowering Plants
|
4
|
8%
|
| Plant Physiology - Plant Growth and Growth Hormones
|
4
|
8%
|
| Plant Physiology-II-Photosynthesis In Higher Plants
|
3
|
6%
|
| Genetics-II
|
4
|
8%
|
| Biomolecule-I
|
2
|
4%
|
| Ecology-Organisms and Population
|
1
|
2%
|
| Plant Physiology-II-Respiration in plants
|
2
|
4%
|
| Biomolecule-II
|
2
|
4%
|
Biology In Human Welfare
|
1
|
2%
|
| Biological Classification
|
2
|
4%
|
| Zoology |
50 |
100% |
| Cell Biology
|
4
|
8%
|
| Genetics-I
|
2
|
4%
|
| Biotechnology
|
4
|
8%
|
| Genetics - II
|
2
|
4%
|
Ecology-Organisms and Population
|
1
|
2%
|
| Biomolecule - II
|
2
|
4%
|
| Body fluids and circulation
|
2
|
4%
|
| Animal Kingdom - I
|
3
|
6%
|
| Human Reproduction and Reproductive Health
|
7
|
14%
|
| Excretory Products and Their Elimination
|
2
|
4%
|
| Neural Control and Coordination
|
2
|
4%
|
| Locomotion and Movement
|
2
|
4%
|
| Biology In Human Welfare-Human Health and Disease
|
5
|
10%
|
| Breathing and Exchange of Gases
|
2
|
4%
|
| Origin and Evolution
|
4
|
8%
|
| Chemical Coordination and Integration
|
2
|
4%
|
| Structural Organisation in Animal
|
1
|
2%
|
| Animal Kingdom - II
|
3
|
6%
|
Q: Is the NEET syllabus tough?
The NEET syllabus is same as that of Class 11 and Class 12 CBSE Board exam syllabi. Hence, it is not that difficult or students need not study anything additional apart from their school or Board exam studies. However, the difficulty level of the exam depends on the question types, which is generally tricky in nature, which makes the difference in the difficulty level.
The best way to tackle the NEET syllabus is through revision and taking as many mock tests as possible. According to experts and previous years' NEET analysis, Physics section is the toughest followed by Chemistry and Biology. Moreover, toughness is subjective and it depends on the preparation level and aptitude of students.
Q: What is the Biology syllabus for NEET?
The Biology syllabus for NEET has undergone changes based on the recommendations by the National Medical Commission (NMC). Although earlier the NEET syllabus for Biology was categorised into Class 11 and Class 12 syllabus, it has now been merged. The units of the NEET 2024 Biology syllabus is given below.
Unit I: Diversity in Living World
Unit II: Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
Unit III: Cell Structure and Function
Unit IV: Plant Physiology
Unit V: Human Physiology
Unit VI: Reproduction
Unit VII: Genetics and Evolution
Unit VIII: Biology and Human Welfare
Unit IX: Biotechnology and Its Applications
Unit X: Ecology and Environment
Q: Why was the NEET 2024 syllabus changed?
The National Testing Agency (NTA), had clarified the reason behind changing the NEET 2024 syllabus. NTA stated, "Due to the COVID-19 scenario, various School Boards deleted portions of each subject's syllabus. The deleted portion is still not being taken back by these Boards. The deletions were not uniform across various boards. Hence, a number of requests were received by the NTA for the revision of the syllabus." Last year, before the NEET exam, several students and parents asked NTA to release the rationalised NEET syllabus. Since the syllabus of NEET was already released before the rationalisation took place,
Q: Which chapters carry a high weightage in NEET Physics syllabus?
The chapters carrying high weightage in the NEET Physics syllabus are as follows:
- Thermodynamcs
- Current Electricity
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
The following table brings the chapter-wise weightage of NEET Physics syllabus based on previous year's analysis.
Name of the chapter | Number of questions asked (Approx.) | Weightage in percent |
|---|---|---|
Alternating current | 1 | 4 |
0-1 | 1.5 | |
Current electricity | 2 | 8 |
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 2 | 6 |
Electric Charges and Fields | 1 | 4.5 |
Electromagnetic induction | 1 | 4 |
Electromagnetic waves | 1 | 5 |
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | 1 | 4.5 |
0-1 | 2 | |
Kinetic theory | 1 | 3 |
1 | 3 | |
Magnetism and Matter | 1 | 2.5 |
Mechanical Properties of Fluids | 0-1 | 2 |
Mechanical Properties of Solids | 0-1 | 2 |
Motion in a Plane | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Motion in a Straight Line | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Moving Charges and Magnetism | 1 | 2.5 |
Nuclei | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Oscillations | 0-1 | 1.5 |
Physical World, Units and Measurements | 0-1 | 2 |
Ray optics and optical instruments | 1 | 5 |
Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits | 2 | 6 |
System of Particles and Rotational Motion | 1 | 5 |
Thermal Properties of Matter | 0-1 | 2 |
2 | 9 | |
Wave optics | 1 | 5 |
0-1 | 1.5 | |
Work, Energy and Power | 1 | 4 |
Total | 45 | 100 |
Also Read: NEET Physics Syllabus with Chapter-wise Weightage
Q: What is the distribution of questions in the Biology section of the NEET 2025 syllabus?
The Biology section of NEET is divided into two sub-sections: Zoology and Botany. Each of these sections will have 50 questions, out of which candidates will have to attempt 45 questions. The total number of questions on Biology in the NEET question paper will be 90. The topics and chapters from Zoology and Botany subjects will be equally distributed. Among the three subjects, Biology has the highest weightage in NEET syllabus. Based on the last year's NEET analysis, the important topics of Botany and Zoology along with their weightages are given in the below table.
| Botany | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Cell Biology - Introduction, Prokaryotic Cell | 5 |
| Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Sexual Reproduction Introduction | 4 |
| Application Biology (Biotechnology) - Principles of Biotechnology | 4 |
| Plant Physiology-II-Photosynthesis In Higher Plants - Introduction (Early experiments), site of photosynthesis and photosynthetic pigments | 4 |
| Genetics II - Nucleic Acids (The Generic Material, DNA, RNA) | 4 |
| Zoology | Number of Questions |
| Cell Biology - Introduction, Prokaryotic Cell | 4 |
| Animal Kingdom-1 - Porifera | 4 |
| Human Reproduction and Reproductive Health - Male Reproductive System | 6 |
Note: The above table carries topic-wise weightages based on last year's NEET exam. Candidates may use it for reference by omitting the removed topics.
Best Books to Prepare for NEET Biology Syllabus
The best books to prepare for the NEET Biology syllabus are given below:
- NCERT Biology Books for Class 11 and Class 12
- Biology by Trueman (Volume 1 and 2)
- Objective Botany by Ansari
- Pradeep Guide on Biology
- G R Bathla publications for Biology
- Moderns ABC of Biology for XI and XII by B B Arora, A K Sabharwal (Modern Publishers)
- Exploring Biology (Vol 1 and 2) by Sanjay Sharma and Sudhakar Banerjee (Arihant Publications)
- Objective Biology (Vol 1, 2 and 3) by K N Bhatia/ K Bhatia (Dinesh Publications)
- Medical Entrances Biology (Vol 1, 2 and 3) Mamta R Solanki and Lalita Ghotik (Target Publications)
- Together with Biology by S Venugopal
NEET 2024 Analysis of Biology Section
As per the NEET 2024 analysis, Biology questions in NEET 2024 were mostly NCERT-based. Questions were mostly from topics such as Human Physiology, Genetics, and Plant Physiology. Unlike previous years, this year's question papers featured six figure-based and three direction-based questions, along with 30 'match the following' and 17 statement-based questions. As 30 per cent of the questions were of the 'match the following' type, some students found the paper a bit lengthy.
The following infographic brings the weightage of NEET Biology questions for Class 11 and Class 12.
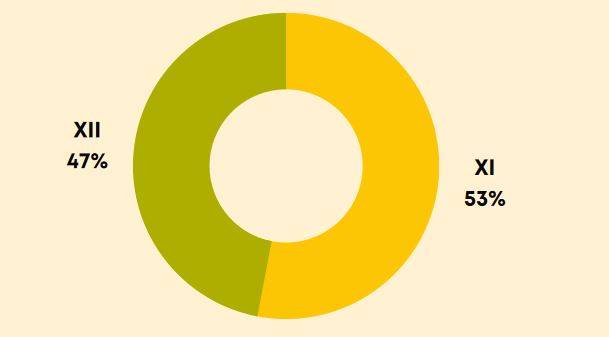
NEET 2025 will be conducted tentatively in the first week of May 2025. The NEET exam pattern and syllabus are likely to remain the same as last year. The exam will be conducted for a duration of 200 minutes and the NEET question paper will carry 200 questions, out of which 180 questions have to be attempted. Each subject will be divided into two sections. The first section will have 35 questions all of which are compulsory to attempt. The second section will have 15 questions, out of which 10 questions need to be attempted.
Read More:

Sreetama has over a decade of editorial experience in the higher education beat. A wanderlust by passion, she is also an avid reader and a music lover. Among friends, she is popular for her sense of humour.
News & Updates
Explore Other Exams
Jun '20 | AIIMS MBBS 2020 Results |
May '20 | AIIMS MBBS 2020 Exam |
Jun '20 | JIPMER 2020 exam (tentative) |
Jan '25 | FMGE 2024 December Session Sco... |
19 Jan '25 | FMGE 2024 December Session Res... |
20 Mar '25 | OJEE 2025 Last Date of Registr... |
25 Apr '25 | OJEE 2025: Admit Card Release |
Jul '22 | DAVV CET 2022 Registration |
Mar '25 | PU CET (UG) 2025 Application F... |
Mar '25 | PU CET (UG) 2025 Registration ... |
Student Forum
Answered 17 hours ago
In India, the BHMS is typically regulated by the National Testing Agency (NTA), which conducts the NEET UG for admission to Medical courses including BHMS. However, some colleges offer BHMS programs without requiring NEET scores.
Some colleges that may offer BHMS programs without NEET include:
BHMS Colleges | Entrance Accepted | BHMS Course Fees |
|---|---|---|
AYUSH | 6.75 L | |
AYUSH | 10.57 L | |
NEET, AYUSH | 14.04 K | |
KEAM, AYUSH | 11.97 K | |
KEAM, AYUSH | 11.97 K | |
KEAM, AYUSH | 25.5 K | |
Government Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan Rajasthan Ayurved University | AYUSH | 4.05 L |
AYUSH | 1.47 L | |
AYUSH | 85.5 K |
Note: T
J
Contributor-Level 7
Answered 17 hours ago
The NEET AYUSH Counselling for BHMS course BHMS degree (Bachelor of Homoeopathic Medicine and Surgery) is conducted by the AYUSH Admissions Central Counselling Committee (AACCC). Eligible candidates who have passed the NEET UG exam can participate in this centralized counselling process for admissio
M
Contributor-Level 7
Answered 19 hours ago
You normally need to have a very high NEET exam score to get an MBBS seat at CMC Vellore in the General category. Given that CMC Vellore is one of the most prominent medical schools in India with a small number of seats and fierce competition, recent trends indicate that a NEET score of 650+ is ofte
N
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 22 hours ago
Hi Riya,
Based on your 12th board results, you're almost certainly eligible to appear for NEET 2025, provided you meet the general eligibility criteria. Here's a quick overview:
Minimum Marks: You need at least 50% aggregate in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (40% for reserved categories). Your total
A
Contributor-Level 9
Answered 22 hours ago
Dear Mermaid,
To access the latest question papers for Kerala's 12th standard (Plus Two) examinations, you can refer to the following resources:
Official Directorate of General Education (DGE) Portal: The DGE Kerala provides a repository of question papers and model exams for various subjects. You ca
A
Contributor-Level 9
Answered Yesterday
Dear Rajan Balana Ji,
Aapne 11th class me PCM (Physics, Chemistry, Maths) liya tha aur 12th class me PCM ke saath additional subject ke roop me Biology padha hai, aur aapke total marks 53% hain.
NEET ke liye eligibility ke mutabik, General category ke candidates ko 12th me Physics, Chemistry aur Biol
A
Contributor-Level 9
Answered Yesterday
Dear Chacko,
In Karnataka, admission to the B.Sc. Nursing course is primarily conducted through the Karnataka Examinations Authority (KEA). Candidates are required to appear for the Common Entrance Test (CET) conducted by KEA, which assesses proficiency in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. This CET s
A
Contributor-Level 9
Answered 2 days ago
NEET, which stands for "National Eligibility cum Entrance Test," is a single-level national examination conducted in India for aspiring medical students seeking admission to undergraduate medical and dental courses like MBBS and BDS across various government and private colleges in the country; it i
A
Contributor-Level 10
Answered 2 days ago
Various online sources enable users to download NEET question papers in the Tamil language. KalviExpress provides Tamil medium NEET study materials along with question papers that include model questions and practice tests for NEET preparation ¹. The Tamil Nadu Directorate of School Education makes
K
Contributor-Level 7
Answered 3 days ago
Yes, the BUMS course in India generally requires NEET qualification for admission.
NEET is the common entrance exam conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for admission to undergraduate medical courses including BUMS, MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BHMS, etc.
P
Contributor-Level 10
 Registration - 7 Feb '25 - 7 Mar '25
Registration - 7 Feb '25 - 7 Mar '25



All the chapters are important for NEET 2025. However, the most number of questions are asked from the following chapters of the syllabus of NEET.
Physics:
Chemistry:
Botany
Zoology
Students must note that these are a handful of important topics for the NEET 2025 syllabus and they should not restrict their preparation to these topics only, and be prepared for all the other chapters and topics carrying a high weightage in the NEET question paper based on past years' exam analysis.