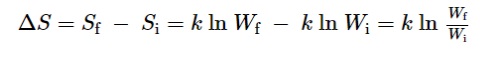Introduction
Entropy is a thermodynamic state function like pressure, temperature and volume. Entropy is a measure of the degree of randomness or disorder in the system. To calculate the degree of disorderliness or chaotic distribution of energy among molecules, we use statistical methods. The other method is to relate this process to the heat involved in a process. The greater the disorder, the higher is the entropy of the system.
Entropy
- Rudolf Clausius introduced this new property which relates to heat flow. Whenever heat is added to the system, it increases molecular motions causing increased randomness in the system.
- So a system at higher temperature has greater randomness than at lower temperatures. Both heat and temperature influence the system.
- It suggests that entropy change is inversely proportional to the temperature. ∆S is related to q and T for a reversible reaction as:
Reference: NCERT
- The total entropy change of the system acts as the criteria for the spontaneous process.
ΔStotal = ΔSsurrounding + ΔSsystem
- Another thermodynamic property, Gibbs free energy is key in determining the spontaneity of the chemical reaction.
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Gibbs energy change = Enthalpy change-temperature(entropy change).
- Ludwig Boltzmann developed a model that relates the system’s entropy to the number of microstates possible for the system. A microstate is an arrangement of the energy of each molecule in a whole system.
- Where K is the boltzmann constant, and its value is 1.38 × 10−23 J/K.
- Change of entropy of a process is a difference in the final and initial values
- For example, if energy shared between molecules of a system comprised of N molecules distributed among n boxes, the number of microstates possible for the system is nᶰ. If the number of microstates increases for the system, then the entropy increases.
What is Entropy for Class 11
In this chapter thermodynamics, the second law of thermodynamics states the changes in entropy. Entropy is also explained with the spontaneity process and when energy is involved. The weightage of this topic is below 10 marks. Problems on the relation of entropy with internal energy, enthalpy, gibbs free energy.
Illustrative Examples
1. For an isolated system∆U = 0; what will be ∆S?
Provided the change in the internal energy of an isolated system is zero, it does not exchange energy with the surroundings. For spontaneous reactions, entropy increases. So ∆S>0 or positive.
2. Calculate the entropy change in surroundings when 1.00 mol of H2O(l) formed under standard conditions. ∆?H⁻ = –286 kJ mol–1.
q (rev) = ∆?H⁻ = –286 kJ mol–1 = 286000 J/mol
∆S(surroundings) = q(rev)/T = 286000/298 = 959 J k-1 mol-1
3. If the change in entropy of a system where heat added is 12 J/K, and the temperature of the system is 250 K, what is the amount of heat added to the system?
q =∆S*T= 12*250 = 3000J
FAQs on Entropy
Q: A reaction, A + B—>C + D + q is found to have a positive entropy change. The reaction will be (i) possible at high temperature (ii) possible only at low temperature (iii) not possible at any temperature (iv) possible at any temperature
A: (iv) possible at any temperature
Q: For the reaction; 2Cl (g) → Cl2 (g); what will be the signs of ∆H and ∆S?
A : ∆H: negative (-ve) because energy is released in bond formation
∆S: negative (-ve) because entropy decreases when atoms combine to form molecules.
Q : Calculate the entropy change in surroundings when 1.00 mol of H2O (l) is formed under standard conditions. ΔfH⸰ = – 286 kJ mol^–1.
A:
- qrev = (-ΔfH⸰) = - (- 286kJ mol-1) = 286 x 103 Jmol-1 = 286000 J mol-1
- ΔS (surroundings) = qrev/ T = 286000 J mol-1 / 298 K
- = 959.73 J mol-1 K-1
Q: What is Negentropy?
A: Negentropy is reverse entropy. It is the reduction in entropy and the corresponding increase in order.
Q: Which molecules have large entropy?
A: Complex molecules have no entropy because there are no bonds and can rotate freely. Gas molecules have more microstates when compared to liquid molecules, so gas molecules have the highest entropy.
Q: What does the standard entropy mean?
A: It is the entropy content of one mole of a pure substance under a standard state(not standard temperature and pressure). The symbol of standard entropy is S° and has units of (J⋅mol−1⋅K−1)
Q: What is the effect of solution formation on entropy?
A: The formation of the solution will increase the microstates of the system, thereby entropy increases.
Q: Why can entropy not decrease?
A: In closed systems, the entropy of the system either increases or remains constant. In an open system, the entropy may decrease.
News & Updates
Thermodynamics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test