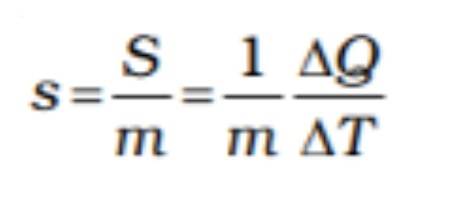Before understanding the concept of specific heat, its applications, and its uses, let's talk a bit about the chapter’s core concept mentioned here: “Thermodynamics".
As the name suggests, thermodynamics refers to the heat involved in transit. Heat can also be referred to as energy in the concepts of thermodynamics. Before the concept of modern thermodynamics, it was believed that there was an invisible fluid present in the substances which held the heat levels of the material, which defined the heat capacity of the material. After the laws of thermodynamics were made clear and understood in the modern era, the measures changed.
What is Specific heat capacity?
As per the understanding of modern thermodynamics, the total measure of the internal heat present inside a material can be defined as Specific heat capacity. This explains the part wherein the word itself breaks down to clarify the definition of the process.
Specific Heat Capacity Formula
This can be defined as the temperature or the amount of heat required at a certain part to tweak up the temperature of the unit mass by just 1 degree of the material. In all essence, it can be defined as the amount of heat it takes for the material to reach an increase in its temperature per unit mass. The formula for this is defined as below :
The above formula states the indication it requires the material to start resisting the change in its temperature. One of the other easier ways of stating this is by defining it as thermal inertia.
This formula can be used to understand the concept of heat transfer, which changes the material’s heat. This proves that either heat can be supplied to the material to alter the substance’s temperature, or there could be some work done on the material to achieve the same result, if not something close to it.
Specific heat capacity for Class 11
The chapter on thermodynamics covers the concept of Specific Heat Capacity as a topic. The chapter, as per the latest CBSE marking pattern covers a total of 8 marks. The breakdown of the marks contains 1 short one-mark objective question, 2 short type questions containing 2 marks each, and one 5 marks long question.
Illustrated Examples
Example 1) - Define the formula for Heat Capacity.
Answer – The formula of heat capacity is:
Example 2) – Explain heat capacity unit mathematically.
Answer – Mathematically, the heat capacity unit is Q=msΔT.
Example 3) – State the SI unit for heat capacity.
Answer – The SI unit for heat capacity is Joule per Kelvin (J/K).
FAQs on Specific Heat Capacity
Q: Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following : (a) What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B ? (b) What is the change in internal energy of the gas ? (c) What is the change in the temperature of the gas ? (d) Do the intermediate states of the system (before settling to the final equilibrium state) lie on its P-V-T surface ?
A: (a) When the stopcock is opened, the volume became double between cylinders A and B. Since volume is inversely proportional to pressure, the pressure will become half. So the initial pressure of 1 atm in cylinder A will become ½ atm in cylinder A and B. (b) The internal energy will change when there is work done by the gas. In absence of any work done, there will be no change in internal energy. (c) In absence of any work done, there will be no change in the temperature. (d) The given process is a case of free expansion. It is rapid and cannot be controlled. The intermediate states do not satisfy the gas equation and since they are non-equilibrium states, they do not lie on the P-V-T surface of the system.
Q. What is one other name of specific heat capacity?
A. Thermal inertia is one other name that can be used for this process
Q. How is specific heat transfer related to the energy of the material?
A. The increase in the specific heat capacity would also increase the energy of the material. They are practically the same thing.
Q. How does the external temperature apply to a material affect its specific heat capacity?
A. An increase in the material’s external temperature by 1 degree can change the material’s unit mass temperature by 1 degree.
Q. What else could be done to a material apart from applying external temperature to make a shift in the material’s internal energy?
A. If there is no heat applied from an external front on the material, some work could be done on the material to shift in the specific heat capacity. It will increase the temperature that will cause a shift in its unit mass by a degree.
Q. What’s the SI unit of heat capacity?
A. Joule per Kelvin (J/K)
News & Updates
Thermodynamics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test