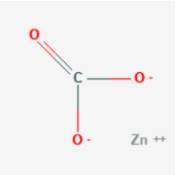
What is Zinc Carbonate?
Zinc Carbonate, also known as Zincspar, is a white crystalline powder that is insoluble in water. It poses a dangerous threat to our environment and should be used with utmost precautions. The chemical formula of Zinc Carbonate is ZnCO3. The ore ‘smithsonite’, commonly known as ‘Turkey Fat’ contains 52% of zinc in it and is otherwise known as Zinc Carbonate.
Physical properties of Zinc Carbonate
After understanding Zinc Carbonate’s chemical structure, let us now look at Zinc Carbonate’s physical properties.
- The molecular weight of Zinc Carbonate is 125.4 g/mol.
- It is a white, odourless, crystalline powder and is not soluble in water.
- The density of Zinc Carbonate is 3.5 g/cm3.
- The boiling point of Zinc Carbonate is 333.6 0C, and the melting point is 1970 0C.
- The topological surface area of Zinc Carbonate is 63.2 Ų.
- The refractive index Zinc Carbonate is 1.818, 1.618.
Chemical properties of Zinc Carbonate
Now let us look at some chemical properties of Zinc Carbonate.
- When Zinc Carbonate is chemically reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid, it produces Zinc Chloride and Carbon dioxide.
ZnCO3 + HCl → ZnCl2 + CO2
- When Zinc Carbonate decomposes at high temperature, it releases Carbon dioxide and Zinc Oxide, which is used in various industries.
ZnCO3 → CO2 + ZnO
Uses of Zinc Carbonate
Zinc Carbonate has many uses. Let us look at some of its uses.
- It is used in the manufacture of many medicines and dietary supplements.
- Zinc Carbonate is used as one of the major components in the food industry for preparing food colouring, food additives, and some spices.
- It is used alongside adhesives in various sectors.
- Zinc Carbonate is used in the manufacture of paper plates and disposable cutlery.
- It plays a vital role in manufacturing detergents, soaps for body care, and cleaning products.
- It is used to manufacture different metals, casting and production of metals, and surface treatment of metals.
- Zinc Carbonate finds its use in the manufacture of plastic and its various components.
- Zinc Carbonate is used in the manufacture of rubber.
- Zinc Carbonate in its powder form is used as a dusting agent on inflamed surfaces as an absorbent.
Zinc carbonate in Class X
Zinc Carbonate and the other Zinc compounds have been explained in the chapter ‘Acids, Bases, and Salts.’ You will also study about the different reactions between the acids and bases. There are many reactions which are provided in the chapter.
Illustrative Examples
1. Five solutions A, B, C, D, E when tested with an indicator showed pH as 4,1,11,7, and 9, respectively. Identify the solutions.
a. Neutral
b. Strong Alkaline
c. Strong Acid
d. Weak Alkaline
e. Weak Acid
Answer: (a) D (b) C (c) B (d) E (e) A
2. Why is plaster of Paris stored in moisture-proof containers?
Answer: When Plaster of Paris comes in contact with moisture, it turns into a hard substance and is rendered useless. So, it is stored in moisture-proof containers.
3. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer: It is a reaction in which an acid reacts with equal amounts of a base to produce salt and water.
Example: NaOH + HCl — NaCl + H2O
Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl — MgCl2 + 2H2O
FAQs on Zinc Carbonate
Q: What is the chemical formula of Zinc Carbonate?
Q: What is the molecular weight of Zinc Carbonate?
Q: What is the percentage of Zinc in Turkey fat?
Q: What is the density of Zinc Carbonate?
Q: What are some of the uses of Zinc Carbonate?
News & Updates
Acids, Bases and Salts Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test