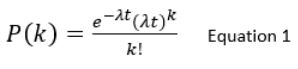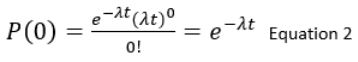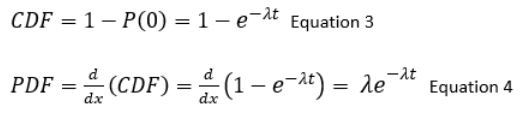Rachit Kumar SaxenaManager-Editorial
What is Exponential Distribution?
Probability distribution is the list of all possible outcomes of a random variable along with their corresponding probability value. Exponential distribution is used to model the probability distribution of the time periods between the process in which events occur continuously at the fixed rate.
Recognize the Exponential Distribution
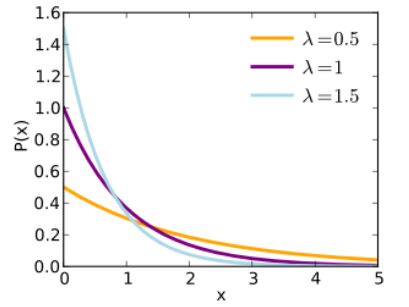
In Exponential distribution, the corresponding probability value of the random variable occurs in such a way that the probability of occurrence will be larger for fewer samples and it will be smaller for larger samples.
For example, If the amount of money customers spend in one trip to the supermarket follows an exponential distribution then there will be more people who spend small amounts of money and fewer people who spend large amounts of money.
Derivation of PDF of Exponential Distribution
The Poisson process is a model for a series of events where the average time between events is known, but the exact timing of events is random. (You will learn more about the Poisson process in higher studies)
Illustrated Examples of Exponential Distribution
A: Exponential distribution deals with the amount of time for which a product lasts and is often used to model the longevity of an electrical or mechanical device. The measurement of radioactive decay can be modelled through exponential distribution.
A: The exponential distribution is skewed to the right, with no negative values and it will contain many observations relatively close to 0 and a few observations to the right from 0.
A: In exponential distribution. Every instant is like the beginning of a new random period, which has the same distribution regardless of how much time has already elapsed. The exponential is the only memoryless continuous random variable.
A: P(T>13|T>10)=P(T>3)
A: The sum of two Exponentially distributed random variables with same rate parameter results into a Gamma distribution.
FAQs on Exponential Distribution
Q: When would you use an exponential distribution?
Q: How do you know if data is exponentially distributed?
Q: Why is exponential distribution memoryless?
Q: How do you find the CDF of an exponential distribution?
Q: What is the sum of two exponential random variables?
News & Updates
Probability Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test