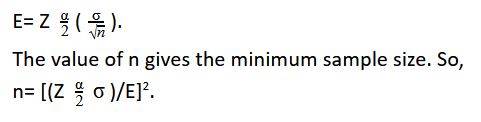- What is Sample Size?
- Weightage of Sample Size in class 11
- Illustrative Example on Sample Size
- FAQs on Sample Size
What is Sample Size?
For research, survey, or experiment a set of data is taken into account. The branch of mathematics that deals with a set of data and their operations is known as statistics.
The sample size is generally used for selecting the number of observations to analyse the given statistical data. Selecting a sample size is a critical part of any study to make inferences about the given elements from a given sample.
The statistical data is majorly classified into population data and sample data. Population data includes the entire area of study. The sample data is a part of the population data that represents the entire set.
The sample size is interpreted as the number of measurements used to determine the evaluation of a population. The dimension of the sample is extracted directly from the population set.
Sampling is the method of election of a subset of quantifiers from the entire population, to evaluate the features of the aggregate population. A fraction of entities in a subset of a population is chosen for analysis.
The formula to determine the sample size of a population is-
Ss= {Z2P(1- P)}/C2.
In this formula, Ss denotes the sample size, Z denotes the Z-factor, P represents the percentage of a population, and C denotes the interval confidence.
The mean of a population gives a value of the average quantity in the entire population interval. The mean of a sample of this population gives the average value for that particular sample set. The mean value of the sample may vary from the population mean. This difference is known as a deviation or error.
The error E in a sample mean is calculated using the formula-
Weightage of Sample Size in class 11
The topic- the sample size is a part of the section- statistics in the syllabus of class 10 and 11. The chapter- collection of data includes this topic in class 11 economics. It carries a weightage of around 5-6 marks in the examination.
Illustrative Example on Sample Size
1. P is to create a one-sample z interval to estimate what proportion of her neighbourhood favour the construction of a park. The confidence level should reach above 95% and the error allowed is 2%. Determine the smallest sample size.
Solution:
So the smallest sample size to consider to get an error of less than 2% with a confidence level above 95% is 2401.
FAQs on Sample Size
Q: What is statistics?
Q: What is the sample size?
Q: What is a small sample size?
Q: What is a large sample size?
Q: What influences the sample size?
Maths Statistics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test