Rachit Kumar SaxenaManager-Editorial
What is Paired T-Test?
In statistics, if the null hypothesis is defined, a t-test may be interpreted as a statistical hypothesis test where the test statistic supports the t distribution. In the Combined T-Test, two sets of observations equate the means. Both of the two classes must be allocated randomly to the findings such that the difference in reaction observed is due to the treatment and not because of any other variables. If two samples are given, then it is possible to pair the observation of one sample with the observation of the other. This procedure can be used before and after an incident to make conclusions on the same sample.
Description of Paired T-Test
For a group of random samples whose deviations are almost normally distributed, the paired t-test offers a hypothesis analysis of the distinction between population means. In a before-after example or with subjects as close as possible, subjects are also tested. The paired t-test is a test demonstrating that there are zero discrepancies between the two observations.
The Formula of Paired T-Test
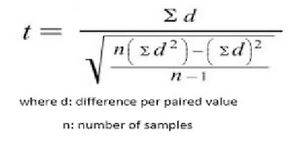
The Paired T-test is a test based on the variations between the values of a single pair, one of which is subtracted from the other. This differentiation is marked as d in the formula for a paired t-test. The paired t-test formula is defined as the sum of the differences divided by the square root of each pair of n times the sum of the differences squared minus the sum of the differences squared, n-1 overall.
The paired t-test formula is given by
Paired T-Test Table
The paired T-test table requires the t-value to be transformed from a t-test to a statement of importance. The table is given below:
Weightage of Paired T-Test in Class 11
This concept is taught under the chapter Statistics. You will learn about the formula and its application in solving questions. The weightage of this chapter is 8 marks.
Illustrated Examples on Paired T-Test
1. What is a paired t-test sample used for?
Solution.
Two populations mean that you have two experiments in which findings in one sample can be combined with observations in the other sample and correlated with a paired t-test.
2. How do you know if data is paired or unpaired data?
Solution.
A paired t-test is designed to measure the means in two different cases with the same category or entity. The definitions of two separate or incompatible classes are contrasted by an unpaired t-test. The difference between groups is presumed to be equal in an unpaired t-test. The variation is not considered to be equal in a paired t-test.
FAQs on Paired T-Test
Q: What is a paired t-test sample, and why is it used?
Q: What is the differentiation between the paired t-test and the t-test?
Q: What's calculated by a paired t-test?
Q: What are the T-test assumptions?
Q: What is the null hypothesis of a paired t-test?
News & Updates
Statistics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test