Rachit Kumar SaxenaManager-Editorial
Statistics PDF
The Probability Density Function(PDF) is the likelihood work spoken to for the thickness of a consistent irregular variable lying between a specific scope of qualities. It is additionally called a likelihood circulation work or simply a likelihood work. In numerous sources, this capacity is expressed as the capacity over an overall arrangement of qualities. At times, it is alluded to as aggregate appropriation work or, in some cases, as likelihood mass function(PMF). However, the real truth is PDF is characterized for constant arbitrary factors, while PMF is characterized for discrete irregular factors.
The likelihood thickness work is characterized as a fundamental of the thickness of the variable thickness over a given reach. It is meant by f (x). This capacity is positive or non-negative at any time of the chart, and the vitality of PDF over the whole space is consistently equivalent to one.
Probability Density Function Formula:
In the event of a consistent irregular variable, the likelihood taken by X on some given worth x is consistently 0. For this situation, it does not work on the off chance that we discover P(X = x). Rather than this, we need to figure the likelihood of X lying in a stretch (a, b). Presently, we need to ascertain it for P(a
P(a
Properties:
Leave x alone the persistent arbitrary variable with thickness work f(x); the likelihood circulation capacity ought to fulfill the accompanying conditions:
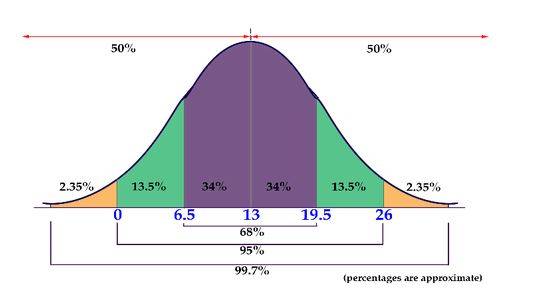
For a persistent arbitrary variable that takes some an incentive between specific cutoff points, state an and b, and is determined by finding the zone under its bend and the X-hub, inside as far as possible (a) and maximum cutoff (b), at that point the pdf is given by P(x)=∫baf(x)dx
The likelihood thickness work is non-negative for all the potential qualities, for example, f(x)≥ 0, for all x
The zone between the thickness bend and level X-pivot is equivalent to 1, for example ∫∞−∞f(x)dx=1
Because of the property of constant irregular variables, the thickness work bend is nonstop for everywhere on the given reach, which characterizes itself over a scope of persistent qualities or the variable's area.
Weightage of Statistics Pdf in Class 11
Statistics has been explained to analyze the data and its management in accordance. The probability theorem has also been explained with its usage, formula, and derivations.
The chapter has a weightage of 30 Marks.
Illustrative Example of Statistics Pdf
1.What is the probability of guessing an MCQ?
Solution.
Since all the appropriate responses are autonomous (the response to one inquiry makes little difference to the responses to the others), at that point, this is the situation with each question, so the odds of speculating all answers effectively is 1/3 × 1/3 × 1/3 = 1/27
2. What can be the conditional expressions be calculated?
Solution.
The restrictive assumption, E(X |Y = y), is contingent upon y. If Y affects the estimation of X, at that point, Y will impact the normal estimation of X. Thus, for instance, we would anticipate E(X |Y = 2) to be unique about E(X |Y = 3).
3. What will be the expected value of x as a continuous variable?
Solution.
∫ X P(X)
FAQs on Statistics PDF
Q: What is the area under the conditional cumulative density function?
Q: What do mutually exclusive contents do?
Q: When a variable assumes the given value within two points, what is it called?
Q: Which formula gives the expected discrete value of x?
E(z – x) = E(z) – E(x)
= 4 – 2 = 2.
News & Updates
Statistics Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams: BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams: UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams: CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams: LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test